Analysis Of NATO's Progress Towards The 2% Defense Spending Target
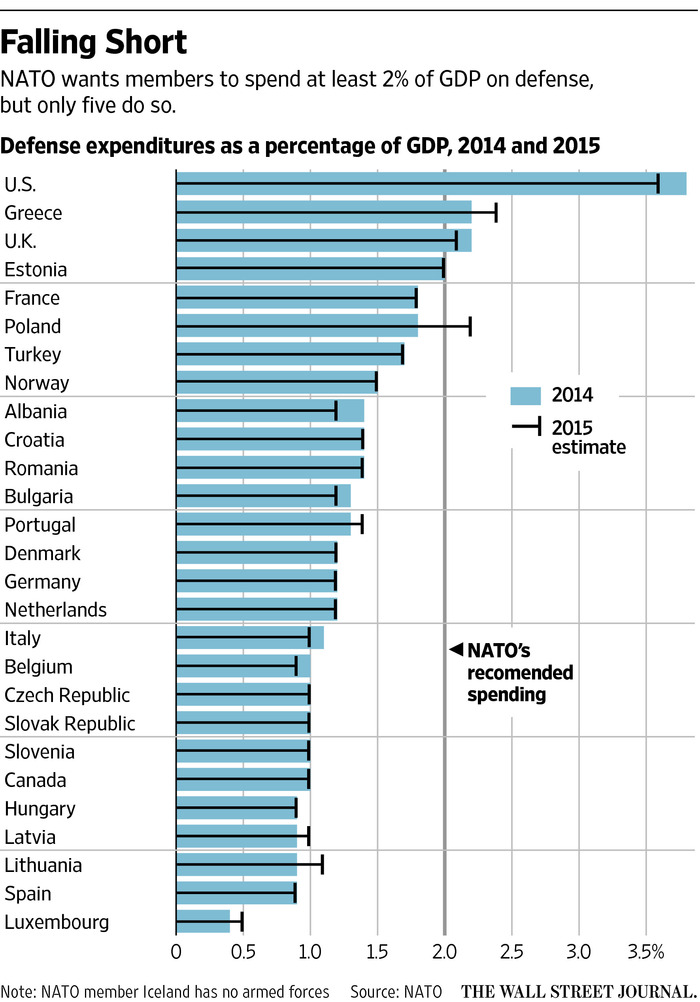
Table of Contents
Current Status of NATO Member Spending
Meeting the Target
Determining which nations have met the NATO 2% defense spending target and which are falling short requires careful examination of budgetary data. While some countries consistently surpass the target, others struggle to reach it due to various economic and political factors.
-
Countries Exceeding the Target: The United States, Greece, and several Baltic states consistently allocate more than 2% of their GDP to defense. Their commitment reflects a heightened perception of threat and strategic priorities. This significant investment enables them to maintain robust military capabilities and contribute substantially to NATO's collective defense efforts.
-
Countries Nearing the Target: Several European nations are making significant strides towards the 2% goal, increasing their defense budgets annually. This progress reflects a growing recognition of the importance of adequate defense spending in the face of evolving security challenges.
-
Countries Significantly Behind: A number of NATO members remain significantly below the 2% target. This shortfall poses challenges to the alliance's collective defense capabilities and necessitates further analysis to understand the underlying causes and potential solutions. These challenges often relate to domestic economic priorities and public opinion.
Challenges in Achieving the Target
Several interconnected factors impede some nations from reaching the 2% goal. These challenges are complex and require nuanced understanding.
-
Budgetary Constraints: Many countries face significant budgetary constraints, limiting their ability to allocate sufficient funds to defense. Competing priorities, such as healthcare and education, often take precedence, resulting in underinvestment in defense capabilities.
-
Competing Domestic Priorities: Public pressure for increased spending on social programs and infrastructure often clashes with the need for increased defense investment. This tension makes it politically challenging to raise defense budgets, even in the face of growing security concerns.
-
Public Opinion: Public support for increased defense spending is not always guaranteed, especially in countries with a history of pacifism or those experiencing economic hardship. Building public consensus on defense spending is therefore a crucial step toward achieving the 2% target.
-
Impact of Economic Downturns: Economic downturns significantly affect defense budgets, as governments are forced to cut spending across the board to address fiscal deficits. This can lead to a temporary or even long-term reduction in defense capabilities.
Impact of the Ukraine War on Defense Spending
Increased Spending Post-Invasion
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has dramatically altered the security landscape in Europe and had a profound impact on defense spending decisions across NATO member states.
-
Significant Budget Increases: Many countries, particularly those geographically closer to Ukraine, significantly increased their defense budgets following the invasion. This demonstrates a renewed commitment to collective defense and deterrence. This increase often involves upgrading existing weaponry and procurement of advanced technology.
-
Impact on Specific Defense Sectors: Increased spending is not uniformly distributed. The conflict has driven investment in specific defense sectors, such as:
- Weaponry: Procurement of advanced weapons systems, including anti-tank and anti-aircraft missiles, has become a priority.
- Cybersecurity: Investment in cybersecurity capabilities has also increased significantly due to the rising threat of cyber warfare.
- Intelligence Gathering: Improvements to intelligence gathering and analysis are also prioritized to ensure better situational awareness and threat assessment.
Shifting Priorities in Defense Strategies
The war has also led to a reassessment of defense priorities within NATO, emphasizing deterrence and rapid response capabilities.
-
Changes in Military Doctrines and Strategies: NATO members are adapting their military doctrines and strategies to better address the challenges posed by the conflict in Ukraine. This includes increased focus on hybrid warfare and asymmetric threats.
-
Impact on Military Exercises and Joint Operations: NATO has intensified military exercises and joint operations to enhance interoperability and readiness. These exercises focus on deterring potential aggression and ensuring a swift, coordinated response to any threat.
Future Projections and Implications
Forecasting Future Defense Spending
Predicting future defense spending trends within NATO requires considering current data and geopolitical trends.
-
Projections for Achieving the 2% Target: While some countries are on track to meet the 2% target in the coming years, others face significant challenges. Meeting the target will require sustained political will, economic growth, and public support.
-
Potential Scenarios and Their Impact: Different scenarios, including escalating tensions with Russia and the rise of new threats, will impact future defense spending. Sustained high spending is likely in a scenario of heightened geopolitical instability.
The Role of Modernization and Technological Advancement
Modernization and technological advancements play a crucial role in optimizing defense spending.
-
Investments in Emerging Technologies: Investing in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), cyber warfare capabilities, and advanced weaponry offers potential cost-effectiveness and efficiency gains in the long run.
-
Impact on Future Defense Budgets and Strategies: The adoption of these technologies will significantly shape future defense budgets and strategies, leading to more efficient and effective defense systems.
Conclusion
This analysis of NATO's progress toward the 2% defense spending target highlights both successes and significant challenges. While several countries have exceeded the target and others are making progress, many remain below the benchmark. The Ukraine war has significantly impacted spending decisions, driving increased investment and shifting priorities towards deterrence and rapid response capabilities. Modernization and technological advancements are crucial for optimizing future defense spending and ensuring NATO's continued effectiveness. Continued monitoring of NATO's progress towards the 2% defense spending target is crucial for understanding the alliance's overall security posture and its ability to meet future challenges. Further research and analysis are needed to fully understand the long-term implications of current spending trends and the effectiveness of various strategies employed by member states to achieve the NATO 2% defense spending target. Stay informed about this crucial topic by following reputable sources for updates on NATO defense spending and security policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Broadhead Hero Ipswich Earns Crucial Victory Against Bournemouth
May 28, 2025
Broadhead Hero Ipswich Earns Crucial Victory Against Bournemouth
May 28, 2025 -
 U Turn On Short Term Rental Ban Contracts Could Be Back Soon
May 28, 2025
U Turn On Short Term Rental Ban Contracts Could Be Back Soon
May 28, 2025 -
 Euro Millions Results Ireland Jackpot Winners Announced Locations Of Winning Tickets Revealed
May 28, 2025
Euro Millions Results Ireland Jackpot Winners Announced Locations Of Winning Tickets Revealed
May 28, 2025 -
 Persemian Gerakan Bali Bersih Sampah Strategi Menuju Pulau Bersih
May 28, 2025
Persemian Gerakan Bali Bersih Sampah Strategi Menuju Pulau Bersih
May 28, 2025 -
 Game 1 Pacers Vs Knicks Tyrese Haliburton Betting Preview And Picks
May 28, 2025
Game 1 Pacers Vs Knicks Tyrese Haliburton Betting Preview And Picks
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Talk To Me Follow Up A More Terrifying Horror Experience
May 29, 2025
Talk To Me Follow Up A More Terrifying Horror Experience
May 29, 2025 -
 New Talk To Me Horror Film Trailers Increasingly Disturbing
May 29, 2025
New Talk To Me Horror Film Trailers Increasingly Disturbing
May 29, 2025 -
 A24 Delivers Another Hit Horror Thrillers Rotten Tomatoes Rating
May 29, 2025
A24 Delivers Another Hit Horror Thrillers Rotten Tomatoes Rating
May 29, 2025 -
 Bring Her Back Positive Rotten Tomatoes Reviews For New Horror Movie
May 29, 2025
Bring Her Back Positive Rotten Tomatoes Reviews For New Horror Movie
May 29, 2025 -
 Aanhouding In Onderzoek Schietincident Venlo Met Pasen
May 29, 2025
Aanhouding In Onderzoek Schietincident Venlo Met Pasen
May 29, 2025
