Analyzing The Impact Of Reciprocal Tariffs On Indian Industries
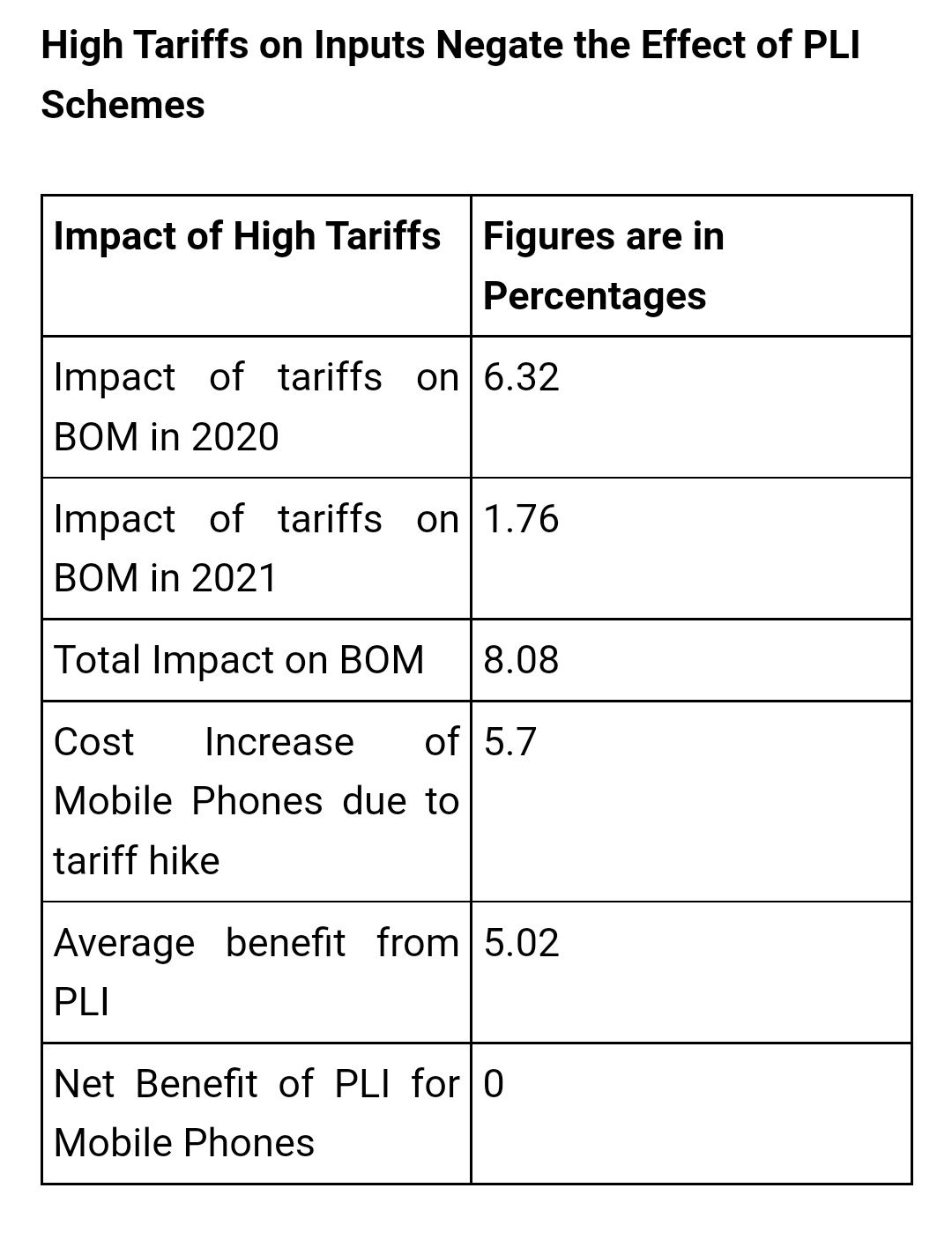
Table of Contents
Impact on Specific Sectors
Reciprocal tariffs directly affect India's export-oriented industries, leading to decreased competitiveness in global markets. Let's examine the impact on key sectors:
The Textile Industry
India's textile industry, a significant contributor to employment and exports, is particularly vulnerable to reciprocal tariffs. The impact of increased tariff barriers on Indian textile exports is multifaceted:
- Decreased export volumes: Higher tariffs make Indian textiles less competitive, reducing demand from importing countries.
- Increased production costs: Higher input costs due to tariffs on raw materials and machinery further erode profit margins.
- Job losses in specific regions: Reduced exports can lead to factory closures and job losses, particularly in labor-intensive regions.
- Potential for government subsidies or support packages: The government may intervene with subsidies or financial aid to mitigate the negative impact on the industry.
These factors significantly affect India's position in the global textile market, necessitating a strategic response to maintain export competitiveness and safeguard jobs within the Indian textile exports sector.
The Pharmaceutical Industry
India's pharmaceutical industry, renowned for its generic drug production, also faces significant challenges. Reciprocal tariffs can:
- Increase prices for exported medications: Higher tariffs increase the cost of generic drugs exported from India, potentially impacting affordability in global markets.
- Lead to a loss of market share to competing nations: Increased prices reduce competitiveness, allowing other nations to gain market share.
- Impact access to affordable medicines globally: Higher prices for generic drugs undermine access to affordable healthcare in developing countries.
- Trigger regulatory responses: Importing countries might implement stricter regulations in response to tariff barriers, further complicating the export process.
Navigating these challenges requires proactive strategies within the Indian pharmaceutical industry and a careful consideration of the global impact on healthcare access.
The Agricultural Sector
The agricultural sector, crucial for India's food security and rural livelihoods, is also vulnerable. Reciprocal tariffs can:
- Reduce demand for Indian agricultural products: Higher tariffs in importing countries lower the demand for Indian agricultural commodities like rice, wheat, and spices.
- Cause price fluctuations in domestic markets: Reduced export demand can lead to surplus production and lower prices for farmers in the domestic market.
- Negatively impact farmer incomes: Lower prices and reduced demand directly impact the income of farmers, potentially exacerbating rural poverty.
- Encourage diversification of exports: To mitigate risks, the government and farmers might explore diversifying exports towards markets less affected by tariffs.
Understanding the impact on Indian agriculture requires a nuanced understanding of commodity prices and market dynamics, as well as exploring diversification strategies for a more resilient agricultural sector.
Macroeconomic Consequences
The impact of reciprocal tariffs extends beyond individual sectors, affecting the overall macroeconomic landscape.
Inflationary Pressures
Reciprocal tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, leading to:
- Increased consumer prices: Higher import costs are passed on to consumers, leading to increased inflation.
- Impact on inflation rates: Increased inflation erodes purchasing power and impacts economic growth.
- Potential for monetary policy responses: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) may respond by adjusting interest rates to manage inflation.
- Effect on purchasing power: Higher prices reduce consumer purchasing power, affecting overall demand and economic activity.
Managing inflationary pressures resulting from reciprocal tariffs requires careful monitoring and strategic monetary policy responses.
GDP Growth Impact
Reciprocal tariffs can significantly impact India's GDP growth:
- Reduced economic activity: Decreased exports and higher import costs reduce overall economic activity.
- Potential for job losses across sectors: Reduced competitiveness and economic slowdown can lead to job losses in various sectors.
- Impact on foreign investment: Uncertainty and reduced economic growth can deter foreign investment.
- Government intervention strategies: The government may implement fiscal stimulus packages to counteract the negative impact on GDP growth.
Analyzing the impact on GDP growth requires a comprehensive assessment of various economic indicators and the effectiveness of government intervention strategies.
Balance of Trade Implications
Reciprocal tariffs directly affect India's balance of trade:
- Changes in import and export volumes: Tariffs lead to reduced exports and potentially increased imports, widening the trade deficit.
- Impact on the current account: A worsening trade deficit puts pressure on the current account of India's balance of payments.
- Potential for currency fluctuations: Changes in the balance of trade can affect the value of the Indian Rupee.
- Government trade policies: The government may adjust trade policies to mitigate the negative impact on the balance of trade.
Monitoring the balance of trade and implementing appropriate trade policies is crucial for maintaining macroeconomic stability.
Government Responses and Mitigation Strategies
The Indian government plays a critical role in mitigating the negative consequences of reciprocal tariffs.
Policy Interventions
The government can respond through various policy interventions:
- Trade negotiations: Engaging in bilateral and multilateral trade negotiations to reduce or eliminate tariff barriers.
- Financial aid packages for affected industries: Providing financial support to help industries overcome short-term challenges.
- Diversification strategies: Encouraging businesses to diversify their export markets to reduce dependence on countries imposing tariffs.
- Strengthening domestic demand: Implementing policies to support domestic consumption and reduce reliance on exports.
Effective policy interventions are crucial for navigating the complexities of international trade and protecting domestic industries.
Industry-Specific Support
Targeted support measures for specific sectors can mitigate the impact:
- Tax breaks: Offering tax incentives to encourage investment and production in affected industries.
- Export subsidies: Providing financial assistance to boost exports and offset the impact of tariffs.
- Technology upgrades: Supporting technology adoption to improve efficiency and competitiveness.
- Skill development programs: Investing in skill development to enhance the workforce's capabilities and adaptability.
These industry-specific support measures are crucial for ensuring the long-term competitiveness and sustainability of affected industries.
Conclusion
Reciprocal tariffs pose significant challenges to Indian industries, impacting various sectors and macroeconomic indicators. While some sectors may experience short-term disruptions, the long-term consequences depend heavily on effective government responses and the adaptability of Indian businesses. Understanding the multifaceted impact of reciprocal tariffs is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. To stay informed about the evolving landscape of reciprocal tariffs on Indian industries, continue researching updated data and policy announcements from relevant government bodies and economic research institutions. This ongoing analysis is crucial for navigating the complexities of international trade and ensuring the continued growth and stability of the Indian economy. Proactive monitoring and strategic responses are essential to minimize the negative impact of reciprocal tariffs on Indian industries and foster sustainable economic growth.

Featured Posts
-
 Dpr Mendukung Presiden Prabowo Proyek Giant Sea Wall Menuju Realisasi
May 15, 2025
Dpr Mendukung Presiden Prabowo Proyek Giant Sea Wall Menuju Realisasi
May 15, 2025 -
 L Eau Du Robinet Comment La Filtrer Pour Une Meilleure Qualite
May 15, 2025
L Eau Du Robinet Comment La Filtrer Pour Une Meilleure Qualite
May 15, 2025 -
 The Biden Warren Exchange A Look At The Presidents Mental Fitness
May 15, 2025
The Biden Warren Exchange A Look At The Presidents Mental Fitness
May 15, 2025 -
 Eastpointe Foot Locker Shooting 4 Shot 2 Killed
May 15, 2025
Eastpointe Foot Locker Shooting 4 Shot 2 Killed
May 15, 2025 -
 Playing Ps 1 Games Again Thanks To Steam Deck Verified
May 15, 2025
Playing Ps 1 Games Again Thanks To Steam Deck Verified
May 15, 2025
