Analyzing The Success And Failures Of Trump's Tariffs On US Manufacturing.
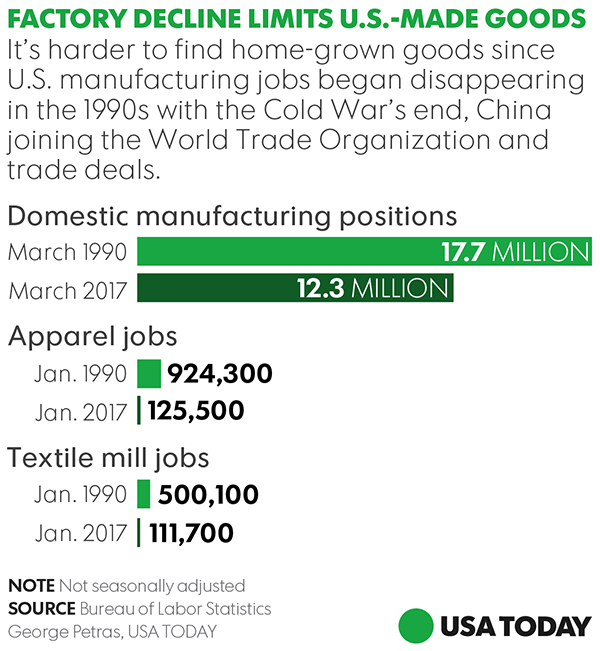
Table of Contents
The aim of these tariffs was primarily protectionist – shielding American manufacturers from foreign competition and reducing the trade deficit. This was implemented against a backdrop of rising global trade tensions and concerns about the competitiveness of US industries. However, the effectiveness and long-term implications of this protectionist strategy remain a subject of ongoing debate.
Intended Goals and Economic Theory Behind the Tariffs
The economic theory underpinning Trump's tariffs relied heavily on protectionism.
Protectionist Aims:
Protectionism aims to safeguard domestic industries by making imported goods more expensive, thus increasing the demand for domestically produced alternatives. The expected outcomes of Trump's tariffs included:
- Increased domestic production of steel and aluminum.
- Job creation in the targeted manufacturing sectors.
- A reduction in the US trade deficit.
The tariffs specifically targeted industries like steel and aluminum, deemed crucial for national security and vulnerable to foreign competition, particularly from China. The rationale was that protecting these "foundational" industries would bolster the entire manufacturing sector.
Retaliatory Measures and Trade Wars:
The imposition of tariffs rarely occurs in isolation. Predictably, other countries retaliated with their own tariffs on US goods, leading to a series of trade disputes and what many termed a "trade war."
- Significant impacts were felt by US agricultural exporters (soybeans, for example) facing retaliatory tariffs from China.
- The escalation of trade disputes disrupted global supply chains and negatively affected various US export industries.
The trade war with China, in particular, became a defining feature of Trump's trade policy. While the US aimed to reduce its trade deficit with China, the retaliatory tariffs imposed by China significantly impacted American businesses and consumers.
Actual Impact on US Manufacturing Employment and Output
Did the tariffs deliver on their promises? Let's examine the data.
Job Creation and Industry Growth:
While some job creation was reported in certain segments of the steel and aluminum industries, the overall impact on manufacturing employment was less dramatic than initially claimed.
- Employment growth in the targeted sectors was often modest and didn't always translate into a significant increase in overall manufacturing jobs.
- Some studies indicate a net loss of manufacturing jobs due to the negative ripple effects of the tariffs on other sectors.
- Regional variations were significant, with some areas experiencing job gains while others suffered losses.
The data does not uniformly support the assertion that the tariffs led to substantial job creation across the US manufacturing sector.
Impact on Prices for Consumers and Businesses:
The tariffs inevitably led to increased prices for consumers and businesses.
- Inflationary pressures increased as the cost of imported goods rose, impacting household budgets.
- Businesses faced higher input costs, affecting their profitability and potentially leading to price increases for their products.
- Changes in consumer spending patterns were observed as consumers adjusted to higher prices.
The ripple effect of these price increases was far-reaching, impacting various sectors of the economy beyond the directly targeted industries.
Unintended Consequences and Long-Term Effects
Beyond the direct impacts, the tariffs triggered several unintended consequences.
Shifting Supply Chains and Investment:
The tariffs significantly impacted global supply chains and investment decisions.
- Reshoring – the return of manufacturing to the US – occurred to a limited extent, but offshoring (moving production overseas) also continued.
- Businesses reevaluated their global supply chains, seeking alternative sourcing options to avoid tariffs.
- Foreign direct investment in the US may have been negatively affected by the uncertainty and instability created by the trade war.
The long-term implications for US manufacturing competitiveness are still being assessed, with concerns that the tariffs may have hampered innovation and long-term growth.
Economic Growth and the National Debt:
The overall impact of the tariffs on US economic growth and the national debt is complex and debated.
- Some economists argue that the tariffs negatively impacted GDP growth, while others contend the effect was minimal or even positive in specific sectors.
- The trade balance did not improve significantly, contrary to the initial expectations.
- The economic costs of the trade disputes and the resulting disruption to global trade may have increased the national debt.
Comparison to Alternative Policies
A crucial element in assessing the effectiveness of Trump's tariffs is to compare them with potential alternative policies.
Trade Agreements vs. Protectionism:
Strengthened trade agreements or other forms of industrial support, such as targeted subsidies or investments in research and development, could have potentially offered more effective and less disruptive ways to support US manufacturing.
- Trade agreements can promote mutual benefits through increased market access and reduced trade barriers.
- Targeted industrial policies could address specific challenges faced by particular industries more precisely than broad tariffs.
- Such alternative approaches might avoid the negative consequences of trade wars and protectionist measures.
Conclusion: Summarizing the Successes and Failures of Trump's Tariffs on US Manufacturing
In conclusion, while Trump's tariffs on US manufacturing aimed to protect domestic industries and reduce the trade deficit, the evidence suggests they fell short of their intended goals. While some industries saw limited job creation, the overall impact on manufacturing employment was modest at best. Furthermore, the tariffs led to significant price increases for consumers and businesses, negatively impacted global supply chains, and arguably hindered long-term economic growth. The trade wars instigated by these tariffs caused substantial economic disruption, raising questions about the effectiveness of protectionism compared to alternative policies such as fostering stronger international trade agreements. Understanding the complexities of trade policy is crucial; further research into the impact of tariffs on specific industries is encouraged to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the lasting effects of Trump’s tariffs on US manufacturing.

Featured Posts
-
 Patrick Schwarzeneggers Wedding Postponement The Real Reason
May 06, 2025
Patrick Schwarzeneggers Wedding Postponement The Real Reason
May 06, 2025 -
 Finding The Fortnite Sabrina Carpenter Skin Tips And Tricks
May 06, 2025
Finding The Fortnite Sabrina Carpenter Skin Tips And Tricks
May 06, 2025 -
 Martin Compstons Candid Thoughts On A Line Of Duty Comeback
May 06, 2025
Martin Compstons Candid Thoughts On A Line Of Duty Comeback
May 06, 2025 -
 Kilaueas Eruption A Unique Pattern Unseen In Four Decades
May 06, 2025
Kilaueas Eruption A Unique Pattern Unseen In Four Decades
May 06, 2025 -
 What Will The Next Pope Be Called Exploring Potential Papal Names
May 06, 2025
What Will The Next Pope Be Called Exploring Potential Papal Names
May 06, 2025
