Are School Suspensions Doing More Harm Than Good? A Comprehensive Analysis
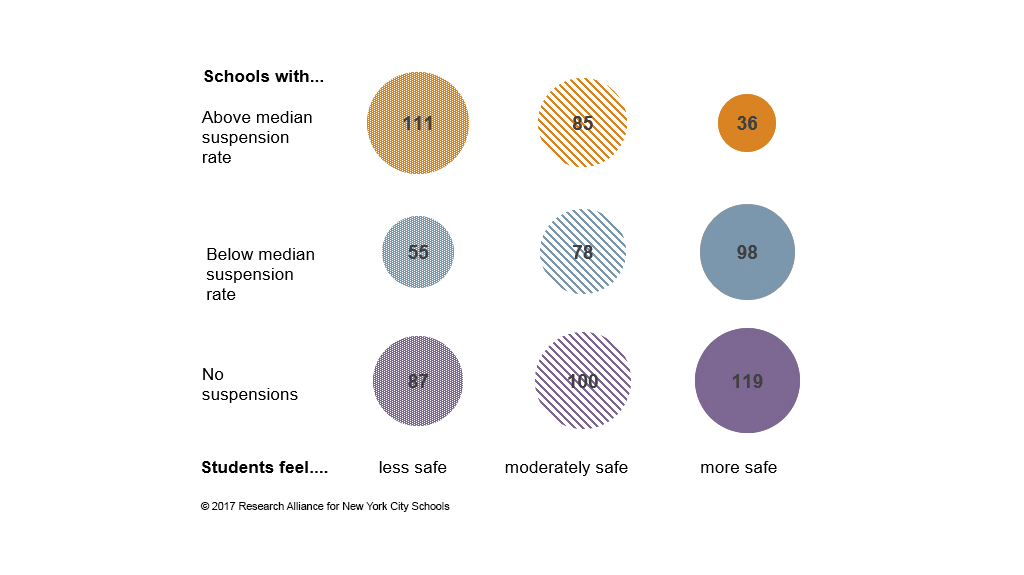
Table of Contents
The Negative Impact of School Suspensions on Student Achievement
School suspensions, while intended to address disruptive behavior, often have unintended and detrimental effects on a student's academic progress and overall well-being. The negative correlation between suspensions and academic success is well documented.
Increased Absenteeism and Dropout Rates
- Increased Absenteeism: Suspensions directly contribute to increased absenteeism. Missing even a few days of school can significantly impact a student's ability to keep up with coursework, leading to a decline in grades and overall academic performance.
- Lower Standardized Test Scores: Studies consistently show a negative correlation between suspension rates and standardized test scores. Students facing frequent suspensions often fall behind their peers, resulting in lower scores on crucial assessments.
- Higher Dropout Rates: Perhaps the most alarming consequence is the link between suspensions and increased dropout rates. Students who are repeatedly suspended are significantly more likely to disengage from school entirely, ultimately abandoning their education. This has profound implications for their future opportunities and life trajectories.
- Reduced Graduation Rates: The cumulative effect of absenteeism, falling grades, and disengagement often leads to a lower likelihood of graduating high school, limiting future educational and career opportunities.
Mental Health and Social-Emotional Well-being
The impact of school suspensions extends far beyond academic performance, significantly affecting students’ mental health and social-emotional well-being.
- Increased Feelings of Isolation and Rejection: Suspension often leaves students feeling isolated, rejected, and stigmatized. This can severely damage their self-esteem and sense of belonging within the school community.
- Elevated Anxiety and Depression: The experience of suspension can trigger or exacerbate feelings of anxiety and depression, particularly among vulnerable students.
- Increased Risk of Substance Abuse and Delinquency: Disconnected from school and support systems, suspended students are at a higher risk of engaging in risky behaviors, including substance abuse and delinquency.
- Involvement in the Juvenile Justice System: In some cases, suspension can serve as a gateway to the juvenile justice system, creating a cycle of negative consequences.
Alternative Disciplinary Approaches: Restorative Justice and Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (PBIS)
Fortunately, there are effective alternatives to school suspensions that address student misbehavior while promoting positive outcomes.
Restorative Justice Practices
Restorative justice focuses on repairing harm and fostering understanding between students, victims, and the school community. It promotes reconciliation and accountability, empowering students to take responsibility for their actions.
- Conflict Resolution Circles: These circles provide a structured environment for students to discuss conflicts, express their perspectives, and find solutions together.
- Mediation: Mediation involves a neutral third party helping students work through disagreements and reach mutually agreeable resolutions.
- Community Service: Restorative justice may involve community service or other actions that allow students to make amends for their behavior.
- Focus on repairing harm: Unlike punitive suspensions, restorative practices aim to heal relationships and prevent future misbehavior.
Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (PBIS)
PBIS is a proactive framework that emphasizes teaching positive behaviors, providing support for struggling students, and using data to monitor effectiveness. It aims to create a positive school climate where students feel supported and empowered to make good choices.
- Teaching Positive Behaviors: PBIS programs teach students specific social and emotional skills, providing them with tools for managing their behavior effectively.
- Providing Support for Struggling Students: Students who are at risk for misbehavior receive early intervention and support to address the underlying causes of their behavior.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data on student behavior is collected and analyzed to identify trends and adjust interventions as needed.
- Emphasis on prevention: PBIS prioritizes preventing misbehavior in the first place, reducing the need for disciplinary actions like suspensions.
The Disproportionate Impact of Suspensions on Minority Students
School suspensions disproportionately affect minority students, particularly Black students. This disparity highlights systemic inequities and the impact of implicit bias in school discipline.
Racial Bias in School Discipline
- Higher Suspension Rates for Minority Students: Statistical data consistently shows that students of color are suspended at significantly higher rates than their white peers, even when controlling for factors like socioeconomic status and academic performance.
- Implicit Bias in Disciplinary Decisions: Implicit biases, unconscious biases that affect decision-making, play a significant role in the disproportionate suspension of minority students.
- Subjective Nature of Disciplinary Actions: The subjective nature of many disciplinary decisions leaves room for implicit bias to influence outcomes.
- Overrepresentation in Special Education: Minority students are often overrepresented in special education, which can lead to more frequent suspensions.
Addressing Systemic Inequities
Addressing the disproportionate impact of suspensions on minority students requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses on equity and inclusivity.
- Culturally Responsive Discipline Practices: Schools should implement culturally responsive discipline practices that take into account the diverse backgrounds and experiences of their students.
- Implicit Bias Training for School Staff: Training school staff on implicit bias and culturally responsive practices is essential to reduce the influence of unconscious biases on disciplinary decisions.
- Equity Audits of School Discipline Data: Regular equity audits of school discipline data can help identify and address systemic disparities.
- More equitable and inclusive school climates: Creating supportive school environments where all students feel valued and respected is a cornerstone of reducing suspension rates.
Conclusion
School suspensions, while seemingly a straightforward disciplinary tool, often inflict significant harm on students' academic progress, mental health, and future opportunities. The data overwhelmingly supports the argument that the negative consequences outweigh the intended benefits. Alternative approaches such as restorative justice and PBIS offer more effective and equitable ways to address student misbehavior, promoting positive school climates and fostering student success. It's time to rethink the widespread use of school suspensions. Let's advocate for alternatives like restorative justice and PBIS to create safer, more supportive, and equitable learning environments for all students, thereby reducing school suspensions and building a brighter future for every child. We must work towards reducing school suspensions and implementing more effective and just disciplinary strategies that create truly inclusive schools.
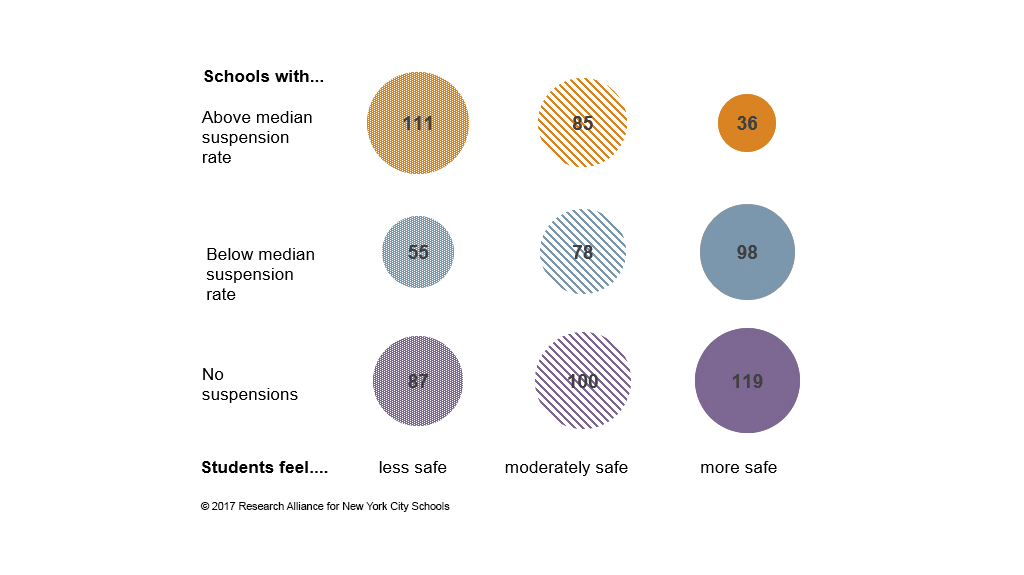
Featured Posts
-
 List Of Mental Health Courses From Indian Government Institutes Ignou Tiss Nimhans Etc
May 02, 2025
List Of Mental Health Courses From Indian Government Institutes Ignou Tiss Nimhans Etc
May 02, 2025 -
 How To Wear A High Waisted Suit Like Selena Gomez 80s Office Style
May 02, 2025
How To Wear A High Waisted Suit Like Selena Gomez 80s Office Style
May 02, 2025 -
 Ndcs Techiman South Election Petition Fails In High Court
May 02, 2025
Ndcs Techiman South Election Petition Fails In High Court
May 02, 2025 -
 Find Newsround On Bbc Two Hd The Ultimate Tv Guide
May 02, 2025
Find Newsround On Bbc Two Hd The Ultimate Tv Guide
May 02, 2025 -
 Miss Pacific Islands 2025 A Samoan Win
May 02, 2025
Miss Pacific Islands 2025 A Samoan Win
May 02, 2025
