Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Outlook: Job Losses And The Potential For Further Cuts
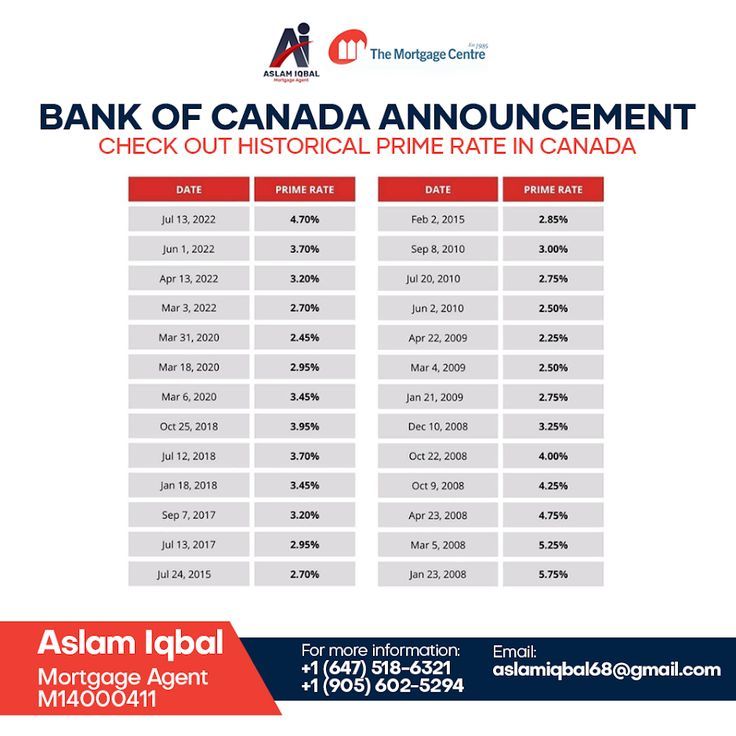
Table of Contents
The Current State of the Canadian Economy and Rising Job Losses
The Canadian economy is facing headwinds. While GDP growth remains positive, it's showing signs of deceleration. Inflation, although easing, remains above the Bank of Canada's target range. Consumer confidence is wavering, reflecting uncertainty about the future. Coupled with this economic slowdown are significant job losses across various sectors, painting a concerning picture for the labor market. Statistics Canada's employment reports consistently highlight this trend.
Recent unemployment figures paint a worrying picture. Specific sectors are experiencing particularly sharp declines:
- Manufacturing sector job losses: Automation and global competition have led to significant layoffs in this sector.
- Construction industry layoffs: A slowdown in housing starts and infrastructure projects has resulted in widespread job losses.
- Retail sector downsizing: E-commerce competition and changing consumer habits are contributing to downsizing and reduced hiring in the retail sector.
Inflation and the Bank of Canada's Mandate
The Bank of Canada operates under a dual mandate: maintaining price stability and achieving full employment. The current inflation rate, while declining, remains a key concern. The Bank faces a difficult trade-off: lowering interest rates to stimulate employment and risk fueling inflation further, or keeping rates higher to curb inflation and potentially exacerbating job losses. This delicate balancing act is at the heart of their decision-making process.
Current inflationary pressures include:
- Rising energy prices: Global energy markets remain volatile, pushing up the cost of energy for consumers and businesses.
- Supply chain disruptions: Lingering supply chain bottlenecks continue to impact the availability and cost of goods.
- Increased demand for goods and services: Pent-up demand following the pandemic continues to contribute to inflationary pressures.
The Impact of Job Losses on Inflation
High unemployment can actually curb inflation. With fewer jobs and less disposable income, consumer spending decreases, leading to reduced demand and potentially lower price increases. This is a crucial factor the Bank of Canada will consider when making interest rate decisions. The interplay between unemployment and inflation is complex and requires careful analysis.
Predicting Future Bank of Canada Interest Rate Decisions
Predicting future Bank of Canada interest rate decisions is challenging, but analyzing expert opinions and economic forecasts offers valuable insight. Various economic forecasters have differing views:
-
Prediction 1: Some economists predict further interest rate cuts to stimulate economic growth and combat rising unemployment, even if it means accepting a slightly higher inflation rate in the short term. Their reasoning is based on the belief that the current economic slowdown warrants a more aggressive stimulus.
-
Prediction 2: Other experts believe the Bank of Canada will hold steady, prioritizing the fight against inflation. They argue that further rate cuts could reignite inflationary pressures and ultimately harm the economy in the long run.
-
Prediction 3: A more conservative view anticipates that the Bank will wait to assess the impact of previous rate changes before implementing further adjustments. They emphasize the need for careful data analysis before making further monetary policy decisions.
The Implications of Further Interest Rate Cuts
Further interest rate cuts by the Bank of Canada would likely have a multifaceted impact on the Canadian economy.
Potential positive effects:
- Economic stimulus: Lower interest rates can incentivize borrowing and spending, potentially boosting economic activity.
- Increased consumer spending: Reduced borrowing costs can encourage consumers to spend more, stimulating demand and supporting businesses.
- Business investment: Lower borrowing rates can make it more attractive for businesses to invest in expansion and job creation.
Potential negative effects:
- Increased inflation: Lower interest rates can fuel inflation if demand increases significantly faster than supply.
- Asset bubbles: Lower interest rates can inflate asset prices, potentially leading to unsustainable booms and busts.
Conclusion:
The relationship between job losses and the Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions is complex and intertwined with inflation concerns. The Bank faces a difficult balancing act between stimulating economic growth and controlling inflation. The uncertainty surrounding future interest rate movements underscores the need for continued monitoring of economic indicators and Bank of Canada statements. Experts offer various predictions, but the ultimate decision hinges on the evolving economic data. Stay informed about the Bank of Canada interest rate outlook and its implications for the Canadian economy by regularly checking our website for updates on interest rate changes and their potential impact on your financial situation. Understanding the Bank of Canada interest rates is crucial for making informed financial decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Tennessee Edges Lsu In Late Inning Rally Series Tied
May 12, 2025
Tennessee Edges Lsu In Late Inning Rally Series Tied
May 12, 2025 -
 Is Black Gold Within Reach Uruguays Offshore Drilling Prospects
May 12, 2025
Is Black Gold Within Reach Uruguays Offshore Drilling Prospects
May 12, 2025 -
 Payton Pritchards Historic Year Earns Him Sixth Man Of The Year Award
May 12, 2025
Payton Pritchards Historic Year Earns Him Sixth Man Of The Year Award
May 12, 2025 -
 Colombia Vs Uruguay En Vivo Minuto A Minuto Del Sudamericano Sub 20
May 12, 2025
Colombia Vs Uruguay En Vivo Minuto A Minuto Del Sudamericano Sub 20
May 12, 2025 -
 Lowrys Valspar Championship Performance A Contender Emerges
May 12, 2025
Lowrys Valspar Championship Performance A Contender Emerges
May 12, 2025
