Bank Of Canada Rate Cuts: Economists Predict Renewed Rate Reduction Amidst Tariff Job Losses
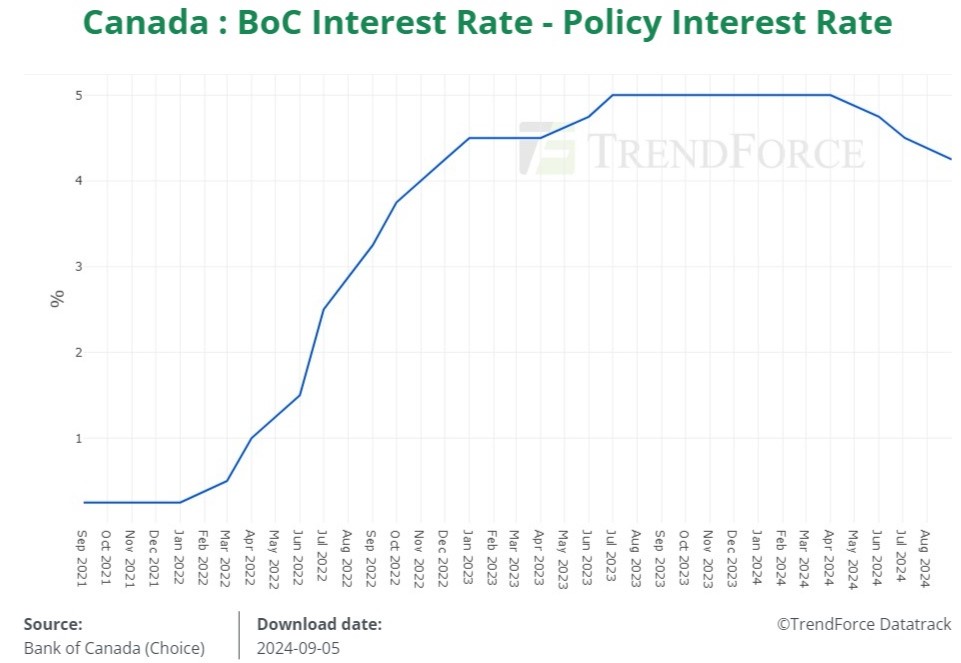
Table of Contents
Rising Unemployment Due to Tariffs
The escalating trade war has dealt a significant blow to the Canadian economy, disproportionately impacting key sectors. This has led to substantial job losses and a reduction in overall economic activity, creating a compelling case for Bank of Canada intervention via interest rate adjustments.
Impact on Key Sectors
Canadian industries like agriculture, manufacturing, and forestry have been particularly hard hit by the trade war. The resulting job losses are substantial and far-reaching.
- Agriculture: Farmers are facing reduced export opportunities and lower prices for their goods, leading to farm closures and rural job losses. Statistics Canada data shows a [Insert percentage]% decline in agricultural exports in [Insert timeframe].
- Manufacturing: Increased tariffs on Canadian goods have made them less competitive in international markets, resulting in factory closures and layoffs. For example, the manufacturing sector experienced a loss of [Insert number] jobs in [Insert timeframe], according to [Source].
- Forestry: The lumber industry, a significant contributor to the Canadian economy, has been severely impacted by trade disputes, leading to mill closures and unemployment in forestry-dependent communities. [Insert relevant statistic on job losses in the forestry sector].
These losses are not isolated incidents; they represent a significant drag on GDP growth, contributing to the overall economic slowdown and necessitating a response from the Bank of Canada.
Consumer Confidence and Spending
The uncertainty surrounding the trade situation has significantly dampened consumer confidence. This decreased confidence translates directly into reduced consumer spending, further slowing economic growth. This creates a vicious cycle, demanding action from the Bank of Canada to stimulate demand.
- Consumer Confidence Indices: The Conference Board of Canada's Consumer Confidence Index has fallen to [Insert current value], indicating a decline in consumer optimism.
- Retail Sales: Retail sales figures have shown [Insert percentage]% decline in [Insert timeframe], reflecting reduced consumer spending.
- Impact on Economic Growth: The decrease in consumer spending directly impacts economic growth, as consumer spending accounts for a significant portion of Canada's GDP.
This decreased consumer spending underscores the urgency for intervention, reinforcing the argument for Bank of Canada rate cuts to boost economic activity.
Inflation Remains Low
Despite the economic slowdown, inflation in Canada remains stubbornly low, below the Bank of Canada's target range. This low inflation rate provides the central bank with considerable leeway to implement further monetary easing through interest rate reductions.
Below Target Inflation Rate
The current inflation rate in Canada is [Insert current inflation rate], which is significantly below the Bank of Canada's target range of [Insert Bank of Canada's inflation target range]. This low inflation provides the central bank with the opportunity to stimulate the economy without the risk of fueling inflationary pressures.
- Contributing Factors: The low inflation rate can be attributed to various factors, including weak consumer demand, low oil prices, and increased competition.
Potential for Deflationary Pressures
The prolonged period of low inflation raises concerns about the potential for deflation, a situation where prices consistently decline. Deflation can be extremely detrimental to an economy, discouraging spending and investment as consumers expect prices to fall further. Rate cuts are a crucial tool to proactively counter this risk.
- Risks of Deflation: Deflation can lead to a vicious cycle of decreased spending, lower production, and job losses, potentially resulting in a prolonged economic recession.
- Historical Examples: [Insert examples of historical deflationary periods and their negative consequences].
- Rate Cuts as a Preventative Measure: By lowering interest rates, the Bank of Canada aims to encourage borrowing and spending, thus stimulating demand and preventing deflationary pressures.
Economists' Predictions and Market Reactions
A growing consensus among economists points towards further Bank of Canada rate cuts in the coming months. This expectation is largely driven by the economic challenges outlined above.
Consensus View on Rate Cuts
Many prominent economists are forecasting additional interest rate reductions by the Bank of Canada. Their reasoning centers on the need to stimulate the economy amidst rising unemployment and persistently low inflation.
- Expert Opinions: [Insert quotes from prominent economists and their predictions regarding Bank of Canada rate cuts].
- Market Forecasts: Financial markets are reflecting this expectation, with [Insert data on bond yields or other market indicators].
Impact on the Canadian Dollar
Further rate cuts are likely to weaken the Canadian dollar. While a weaker dollar could boost exports, making Canadian goods more competitive internationally, it also presents potential drawbacks.
- Exchange Rate Dynamics: Lower interest rates typically lead to a weaker currency as investors seek higher returns elsewhere.
- Benefits of a Weaker Dollar: Increased competitiveness for Canadian exporters could help offset some of the negative impacts of the trade war.
- Drawbacks of a Weaker Dollar: A weaker dollar can lead to higher import costs, potentially increasing inflation and impacting the cost of living for Canadians.
Conclusion
The combination of rising unemployment caused by tariffs, persistently low inflation, and the widespread expectation among economists strongly suggests a high probability of further Bank of Canada rate cuts. While these cuts are intended to stimulate economic activity and mitigate the negative effects of trade tensions, careful monitoring of their effectiveness and potential side effects is essential. Staying informed about future Bank of Canada rate cuts and their implications is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. Understanding the driving forces behind these decisions empowers you to make better financial choices during these uncertain economic times. Continue to follow news and analysis regarding Bank of Canada rate cuts and related economic indicators to stay ahead of the curve and make informed decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Captain America Brave New Worlds Box Office Flop Analysis And Reasons
May 14, 2025
Captain America Brave New Worlds Box Office Flop Analysis And Reasons
May 14, 2025 -
 Startup Stalling Before Ipo Exploring All Options In The Forerunner Long Game
May 14, 2025
Startup Stalling Before Ipo Exploring All Options In The Forerunner Long Game
May 14, 2025 -
 Saint Pierre Et Miquelon L Humour Face Aux Propositions De Wauquiez Sur Les Oqtf
May 14, 2025
Saint Pierre Et Miquelon L Humour Face Aux Propositions De Wauquiez Sur Les Oqtf
May 14, 2025 -
 Israel Eurovision 2024 Yuval Raphael Impresses At Second Rehearsal
May 14, 2025
Israel Eurovision 2024 Yuval Raphael Impresses At Second Rehearsal
May 14, 2025 -
 Uskomaton Eurojackpot Voitto 4 8 Miljoonaa Euroa Suomeen
May 14, 2025
Uskomaton Eurojackpot Voitto 4 8 Miljoonaa Euroa Suomeen
May 14, 2025
