Beijing's Trade War Pain: Hiding Economic Weakness From America?

Table of Contents
Weakening Economic Indicators Despite Official Claims
Official Chinese economic data, particularly GDP growth figures, often paint a picture of continued, albeit slowing, expansion. However, independent analyses and expert opinions frequently cast doubt on the accuracy and completeness of these reports. Discrepancies exist between the official narrative and the on-the-ground realities experienced by businesses and individuals.
-
Declining foreign investment despite government incentives: Despite significant government efforts to attract foreign direct investment (FDI), the inflow has shown a noticeable decline in recent years, indicating a loss of confidence in the Chinese market. This decrease is particularly pronounced in sectors heavily impacted by the trade war.
-
Rising corporate debt and non-performing loans: The level of corporate debt in China remains alarmingly high, with a significant portion classified as non-performing loans. This poses a considerable systemic risk, potentially destabilizing the financial system and hindering economic growth. The trade war has exacerbated this issue, increasing the financial strain on many businesses.
-
Slowdown in manufacturing and industrial production: Key indicators of manufacturing and industrial production have shown a marked slowdown, reflecting the impact of reduced exports and weakening global demand. This slowdown is particularly evident in export-oriented industries heavily targeted by US tariffs.
-
Increased reliance on domestic consumption which may not be sustainable: While the Chinese government is pushing for increased domestic consumption to offset the decline in exports, the sustainability of this strategy remains questionable. The long-term growth of domestic consumption may not be sufficient to compensate for the losses incurred in the export sector.
The Impact of Tariffs on Chinese Exports and Industries
US tariffs have targeted specific sectors of the Chinese economy, causing significant disruptions. Technology and agriculture have been particularly hard-hit, leading to job losses, reduced production, and a shift in export markets.
-
Decline in specific export categories following tariff imposition: The imposition of tariffs has led to a noticeable decline in exports of various goods, ranging from electronics and machinery to agricultural products. This has directly impacted the profitability of numerous Chinese businesses.
-
Job losses in affected industries: The decline in exports and production has inevitably resulted in job losses, particularly in sectors heavily reliant on the US market. This has contributed to social and economic unrest in some regions.
-
Shift in export markets towards other regions, potential challenges: China has attempted to mitigate the impact of US tariffs by diversifying its export markets, seeking new trade partners in Asia, Africa, and elsewhere. However, this strategy presents its own challenges, including differing market demands and logistical complexities.
-
Increased costs for Chinese businesses: Tariffs have increased the cost of goods for Chinese businesses, making them less competitive in both domestic and international markets. This has put added pressure on already struggling companies.
Strategic Data Concealment and Opacity
Obtaining accurate and reliable economic data from China remains a significant challenge. The lack of transparency and the limitations of publicly available information make it difficult to assess the true health of the Chinese economy.
-
Lack of transparency in government reporting: Government reports often present a rosy picture of the economy, downplaying or omitting negative indicators. This lack of transparency makes independent verification extremely difficult.
-
Difficulty in verifying independent economic assessments: Independent economic assessments are often hampered by restrictions on data access and the difficulty in verifying the accuracy of underlying data.
-
Restrictions on foreign access to data and research: Foreign researchers and analysts often face significant restrictions on access to crucial data and information, hindering their ability to conduct independent assessments of the Chinese economy.
-
Potential for intentional misrepresentation of economic performance: Some analysts believe there is a potential for intentional misrepresentation of economic performance to project an image of stability and strength.
The Role of State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) in Masking Economic Weakness
State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) play a significant role in the Chinese economy. Their continued operation, even in the face of market weakness, may be artificially propping up certain economic indicators.
-
SOE debt levels and their impact on overall economic stability: SOEs often carry substantial debt levels, which could pose a systemic risk to the economy if these debts were to default.
-
Government support for failing SOEs distorting market mechanisms: Government intervention to support failing SOEs can distort market mechanisms and prevent the efficient allocation of resources.
-
Lack of competition due to SOE dominance: The dominance of SOEs in many sectors limits competition and innovation, hindering overall economic efficiency.
Geopolitical Implications of China's Economic Vulnerability
China's economic challenges could have significant geopolitical implications, influencing its foreign policy decisions and potentially increasing its assertiveness.
-
Increased pressure on regional neighbors: Economic pressure could lead to increased pressure on regional neighbors, as China seeks to secure resources and markets.
-
Potential for escalation in trade disputes with other countries: Economic vulnerability may lead to a more assertive foreign policy, potentially escalating trade disputes with other countries.
-
Impact on global supply chains and investments: Economic instability in China could significantly impact global supply chains and investments, creating uncertainty for businesses worldwide.
Conclusion
The ongoing trade war with the US is undeniably putting significant pressure on the Chinese economy. While Beijing attempts to present a picture of resilience, a deeper look reveals potentially significant underlying economic weaknesses. The opacity surrounding China’s economic data makes it difficult to definitively assess the true extent of the damage, but the available evidence suggests that the impact of the trade war is far from insignificant. Understanding the true nature of Beijing’s trade war pain is crucial for navigating the complexities of the global economy. Further research and transparent data sharing are essential to accurately evaluate the long-term consequences of this ongoing conflict. Continued monitoring of Beijing’s trade war and its impact on the global economy is vital.

Featured Posts
-
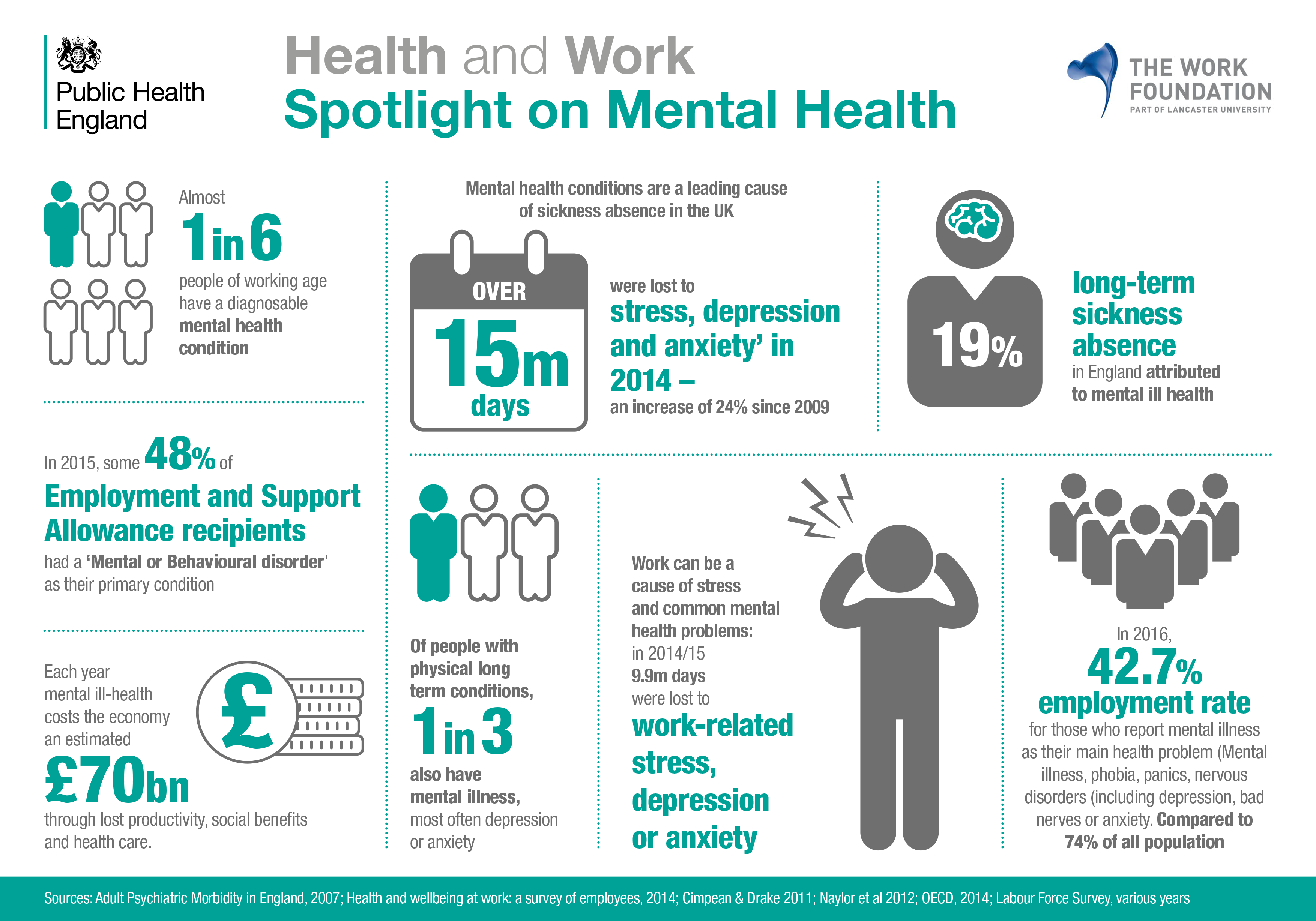 Ignou Tiss Nimhans And Other Government Mental Health Training Programs A Comprehensive List
May 03, 2025
Ignou Tiss Nimhans And Other Government Mental Health Training Programs A Comprehensive List
May 03, 2025 -
 Play Station Showcase Imminent Speculation Mounts For Ps 5 Gamers
May 03, 2025
Play Station Showcase Imminent Speculation Mounts For Ps 5 Gamers
May 03, 2025 -
 Arsenals Title Near Miss Souness Explains The Crucial Factor
May 03, 2025
Arsenals Title Near Miss Souness Explains The Crucial Factor
May 03, 2025 -
 Retro Office Chic Selena Gomezs High Waisted Suit
May 03, 2025
Retro Office Chic Selena Gomezs High Waisted Suit
May 03, 2025 -
 Revised Energy Policies Guido Fawkes Perspective On The Change Of Direction
May 03, 2025
Revised Energy Policies Guido Fawkes Perspective On The Change Of Direction
May 03, 2025
