Beyond BMW And Porsche: A Broader Look At Foreign Automakers' China Problems
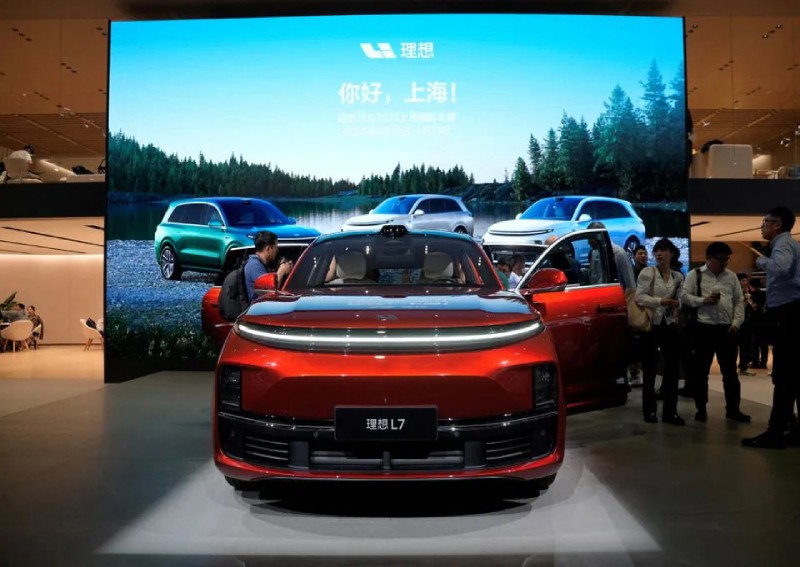

Table of Contents
Intense Domestic Competition
The Chinese automotive market is experiencing a dramatic shift, with domestic brands rapidly gaining ground on their foreign counterparts. This intense competition presents a significant hurdle for international players.
Rise of Chinese Auto Brands
The rise of Chinese auto brands like BYD, NIO, and Xpeng is nothing short of phenomenal. These companies are not only surviving but thriving, fueled by several key factors:
- Aggressive pricing strategies: Domestic brands often undercut foreign competitors, making their vehicles more accessible to a large segment of the Chinese market.
- Increasingly sophisticated technology: Chinese automakers are rapidly innovating, integrating cutting-edge features like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), connected car technology, and electric powertrains.
- Focus on features tailored to the Chinese market: Chinese brands prioritize features highly valued by local consumers, including large infotainment screens, advanced connectivity options, and integration with popular ride-sharing apps.
- Government support: The Chinese government actively supports the growth of domestic auto brands through subsidies, tax breaks, and favorable policies.
Market Share Erosion
The consequence of this rise is a noticeable erosion of market share for many foreign automakers. This isn't limited to the luxury segment; it's impacting brands across all categories.
- Statistical data: A recent study showed a 5% decrease in the combined market share of top 10 foreign automakers in China over the last five years, with a corresponding increase in the market share held by domestic brands. (Source needed - replace with actual data).
- Examples: Several well-established foreign brands have seen significant declines in sales and market position within the Chinese automotive industry. (Provide specific examples with data if possible).
- Analysis of consumer shift: Chinese consumers are increasingly confident in the quality and technological capabilities of domestic brands, leading to a notable shift in brand loyalty.
Regulatory Hurdles and Policy Changes
Navigating the regulatory landscape in China is another major challenge for foreign automakers. The rules are complex, constantly evolving, and often differ significantly from those in other global markets.
Navigating Complex Regulations
China imposes stringent regulations on various aspects of the automotive industry, including:
- Stricter emission standards: China's increasingly strict emission standards require significant investment in cleaner technologies, placing a greater burden on foreign automakers compared to some other regions.
- Complex import/export regulations: The import and export processes for vehicles and parts can be cumbersome and time-consuming, adding to operational costs and delays.
- Data localization requirements: Regulations mandating data storage within China present significant challenges for companies accustomed to global data management practices, requiring adaptation to new cybersecurity frameworks.
Adapting to Shifting Government Policies
The Chinese government frequently updates policies related to electric vehicles (EVs), fuel efficiency, and investment incentives, making long-term planning difficult.
- Examples of policy changes: Recent policy shifts have included increased incentives for electric vehicle adoption and stricter fuel efficiency targets for traditional combustion engine vehicles.
- Challenges of adaptation: Foreign automakers must constantly adapt their production strategies, investment plans, and product portfolios to align with evolving government mandates.
- Implications of China's EV push: China's aggressive push towards electric vehicle adoption requires significant investment in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and EV production capabilities.
Understanding Unique Consumer Preferences
Success in the Chinese market requires a deep understanding of unique consumer preferences, which differ significantly from those in other parts of the world.
Catering to Localized Demands
Chinese consumers prioritize certain vehicle features and attributes more than their counterparts in other regions:
- Specific features highly valued: Large touchscreens, advanced connectivity features, and driver assistance systems are highly valued. The importance of digital connectivity and mobile integration is critical.
- Differences in design preferences: Chinese consumers often prefer more opulent and visually striking designs compared to more minimalist aesthetics common in some Western markets.
- Importance of brand image: Brand image and cultural relevance play a critical role in consumer perception and purchasing decisions.
Building Strong Local Partnerships
Collaboration with local partners is crucial for navigating the complexities of the Chinese market.
- Benefits of joint ventures: Joint ventures and strategic partnerships provide access to local expertise, distribution networks, and regulatory knowledge.
- Challenges of managing partnerships: Managing partnerships effectively requires careful consideration of cultural differences and business practices.
- Examples of successful collaborations: (Include examples of successful joint ventures between foreign and Chinese companies).
Conclusion
The challenges faced by foreign automakers in China are multifaceted and require a nuanced understanding of the local market. Intense domestic competition, ever-evolving regulations, and unique consumer preferences create a complex landscape. To succeed, foreign automakers must prioritize localization, cultivate strong local partnerships, and adapt to the dynamic nature of the Chinese automotive market. Ignoring these challenges will hinder the success of foreign automakers in this dynamic market. Understanding these intricacies is key to navigating the Chinese automotive market successfully. Embrace these challenges and develop a robust strategy to thrive amongst the foreign automakers operating in this competitive landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 5 Key Dos And Don Ts To Succeed In The Private Credit Market
Apr 26, 2025
5 Key Dos And Don Ts To Succeed In The Private Credit Market
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Feeling The Mississippi Delta The Cinematography Of Sinners
Apr 26, 2025
Feeling The Mississippi Delta The Cinematography Of Sinners
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Will Chinese Vehicles Dominate The Global Car Market
Apr 26, 2025
Will Chinese Vehicles Dominate The Global Car Market
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Rural School 2700 Miles From Dc Feeling The Impact Of Trumps First 100 Days
Apr 26, 2025
Rural School 2700 Miles From Dc Feeling The Impact Of Trumps First 100 Days
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Congressional Stock Trading Ban Trumps Stance In Recent Time Interview
Apr 26, 2025
Congressional Stock Trading Ban Trumps Stance In Recent Time Interview
Apr 26, 2025
