Building Contamination Following Ohio Train Derailment: The Long-Term Presence Of Toxic Chemicals
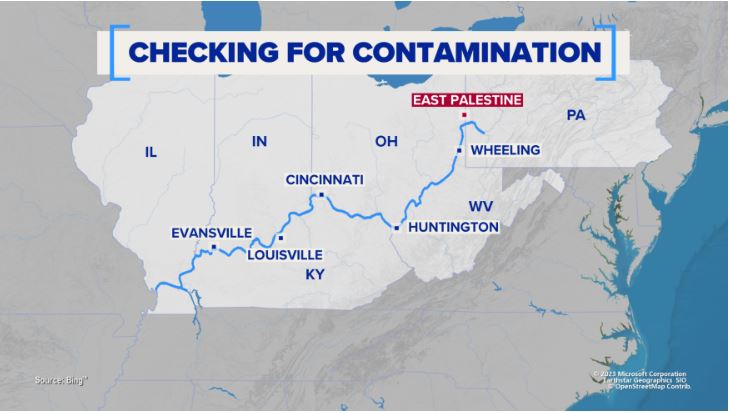
Table of Contents
H2: Types of Toxic Chemicals Released and Their Impact on Building Materials
The derailment resulted in the release of a cocktail of hazardous chemicals, with vinyl chloride being a primary concern. Understanding the properties and effects of these chemicals is paramount to addressing building contamination following Ohio train derailment.
H3: Vinyl Chloride:
Vinyl chloride, a colorless gas used in the production of PVC plastics, is highly volatile and carcinogenic. Its long-term persistence in the environment poses a serious threat to building materials and human health.
- Damage to Building Materials: Vinyl chloride can degrade various building materials, including plastics, paints, and insulation, causing discoloration, weakening, and potential structural damage.
- Health Risks: Exposure to vinyl chloride is linked to an increased risk of liver cancer, brain cancer, and other serious health problems. Long-term exposure, even at low levels, can have cumulative effects.
- Remediation Challenges: Removing vinyl chloride contamination from building materials can be complex and expensive, often requiring specialized techniques and equipment.
H3: Other Toxic Chemicals:
Beyond vinyl chloride, other toxic chemicals released during the derailment, such as butyl acrylate, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, and others, also pose significant risks.
- Butyl Acrylate: This acrylic monomer is highly reactive and can cause respiratory irritation and skin sensitization. Its presence in building materials could lead to long-term health hazards.
- Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether: This solvent can cause skin and eye irritation, as well as potential respiratory and nervous system effects. Its infiltration into building materials can pose significant health risks.
- Synergistic Effects: The combined impact of multiple chemicals present could exacerbate the overall health and environmental consequences, increasing the severity of building contamination following Ohio train derailment.
H2: Pathways of Contamination: How Toxic Chemicals Enter Buildings
Understanding how toxic chemicals enter buildings is critical to effectively addressing building contamination following Ohio train derailment. Several pathways exist, demanding a multi-pronged approach to remediation.
H3: Airborne Contamination:
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during the derailment can easily infiltrate buildings through various pathways.
- Ventilation Systems: Inadequate or damaged ventilation systems can allow contaminated air to enter and circulate within buildings.
- Cracks and Gaps: Small cracks in walls, windows, and foundations can serve as entry points for airborne contaminants.
- Wind Direction: Prevailing wind patterns can influence the spread of airborne contaminants, potentially exposing buildings downwind of the derailment site to higher levels of contamination.
H3: Water Contamination:
Contaminated groundwater or surface water can seep into building foundations, affecting structural integrity and indoor air quality.
- Foundation Issues: Cracks or leaks in building foundations can provide direct pathways for contaminated water to enter.
- Well Water Contamination: Private wells in the vicinity of the derailment may have been contaminated, leading to indirect exposure through contaminated drinking water.
- Long-term Impacts: Groundwater contamination can persist for years, necessitating long-term monitoring and remediation efforts.
H3: Soil Contamination:
Toxic chemicals can migrate into the soil surrounding buildings, entering through cracks in foundations or via vapor intrusion.
- Vapor Intrusion: Volatile chemicals can migrate from contaminated soil into buildings through cracks in the foundation or other openings, contaminating indoor air.
- Foundation Damage: Soil contamination can weaken building foundations, compromising structural integrity.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Regular soil testing is crucial to monitor the extent of contamination and assess the effectiveness of remediation efforts.
H2: Long-Term Health and Environmental Consequences of Building Contamination
The long-term consequences of building contamination following Ohio train derailment are far-reaching and demand immediate attention.
H3: Human Health Impacts:
Exposure to contaminated buildings can result in various adverse health effects.
- Cancer: Many of the chemicals released are known carcinogens, increasing the risk of various cancers over time.
- Respiratory Issues: Exposure to VOCs and other airborne contaminants can cause respiratory problems, including asthma and other lung diseases.
- Legal Recourse: Affected residents may have legal recourse to seek compensation for health damages and remediation costs.
H3: Environmental Impacts:
The environmental consequences extend beyond immediate impacts, requiring ongoing monitoring and remediation.
- Soil and Water Pollution: Long-term contamination of soil and water resources can have devastating consequences for local ecosystems.
- Ecological Damage: The effects on local plant and animal life require careful assessment and potential mitigation strategies.
- Long-term Monitoring: Continuous environmental monitoring is critical to assessing the long-term effects and guiding remediation efforts.
H2: Remediation Strategies and Best Practices
Effective remediation is vital to mitigate the long-term consequences of building contamination following Ohio train derailment.
H3: Assessment and Monitoring:
A comprehensive assessment is the first step in addressing contamination.
- Air Quality Testing: Measuring VOC levels and other airborne contaminants is essential to determine the extent of contamination.
- Water Testing: Testing groundwater and well water is critical to assess potential contamination sources.
- Soil Sampling: Soil sampling identifies the extent of soil contamination and guides remediation strategies.
H3: Remediation Techniques:
Various remediation techniques may be necessary.
- Decontamination: Cleaning and treating contaminated surfaces to remove or neutralize hazardous substances.
- Demolition: In cases of severe contamination, demolition and rebuilding may be necessary.
- Soil Excavation: Removal and replacement of contaminated soil is often required to remediate the underlying source of contamination.
H3: Prevention Strategies:
Preventing future incidents requires a multi-pronged approach.
- Improved Safety Regulations: Stricter regulations for the transportation and handling of hazardous materials are crucial.
- Enhanced Emergency Response: Improved training and resources for emergency response teams are essential.
- Better Transportation Practices: Investing in safer transportation technologies and practices can significantly reduce the risk of future derailments.
3. Conclusion:
The Ohio train derailment underscores the long-term risks of building contamination following Ohio train derailment, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive assessments, effective remediation strategies, and robust long-term monitoring. The human health and environmental consequences are significant, demanding a concerted effort from all stakeholders. We must advocate for stricter regulations, support affected communities, and demand accountability from responsible parties to prevent future disasters and address existing contamination. Resources for further information on environmental remediation and the ongoing effects of the Ohio train derailment can be found through the EPA and relevant state agencies. Let’s work together to address this critical issue and prevent future cases of building contamination. Addressing building contamination from train derailments requires immediate and sustained action, including implementing effective long-term building contamination solutions.

Featured Posts
-
 Reduced Tesla Q1 Profits A Look At The Underlying Causes
Apr 24, 2025
Reduced Tesla Q1 Profits A Look At The Underlying Causes
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Pope Franciss Signet Ring Its Fate After His Death Explained
Apr 24, 2025
Pope Franciss Signet Ring Its Fate After His Death Explained
Apr 24, 2025 -
 My 77 Inch Lg C3 Oled Tv A Detailed Review
Apr 24, 2025
My 77 Inch Lg C3 Oled Tv A Detailed Review
Apr 24, 2025 -
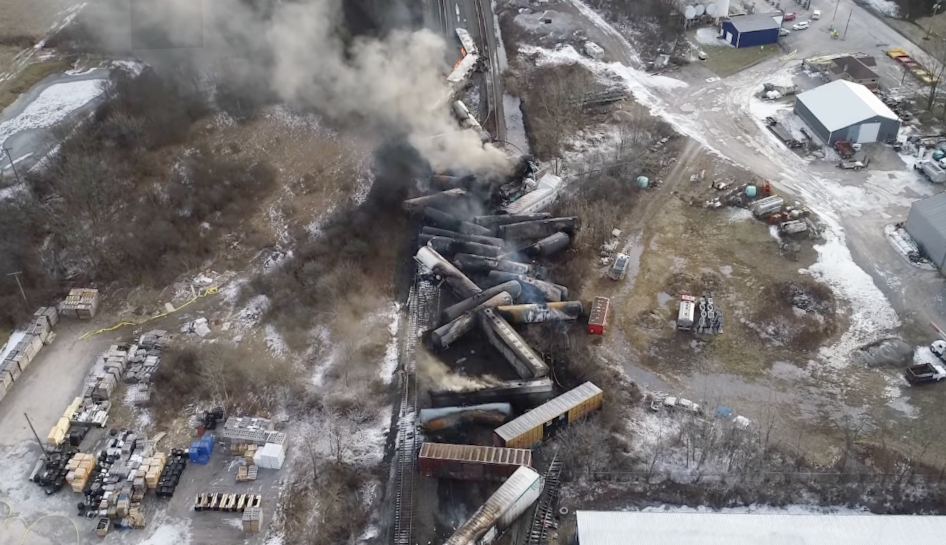 Ohio Train Derailment Persistent Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Months After The Disaster
Apr 24, 2025
Ohio Train Derailment Persistent Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Months After The Disaster
Apr 24, 2025 -
 New Business Hot Spots Across The Nation An Interactive Map
Apr 24, 2025
New Business Hot Spots Across The Nation An Interactive Map
Apr 24, 2025
