Canadian Wildfires: 3°C New York Temperature Drop And Air Toxicant Trapping
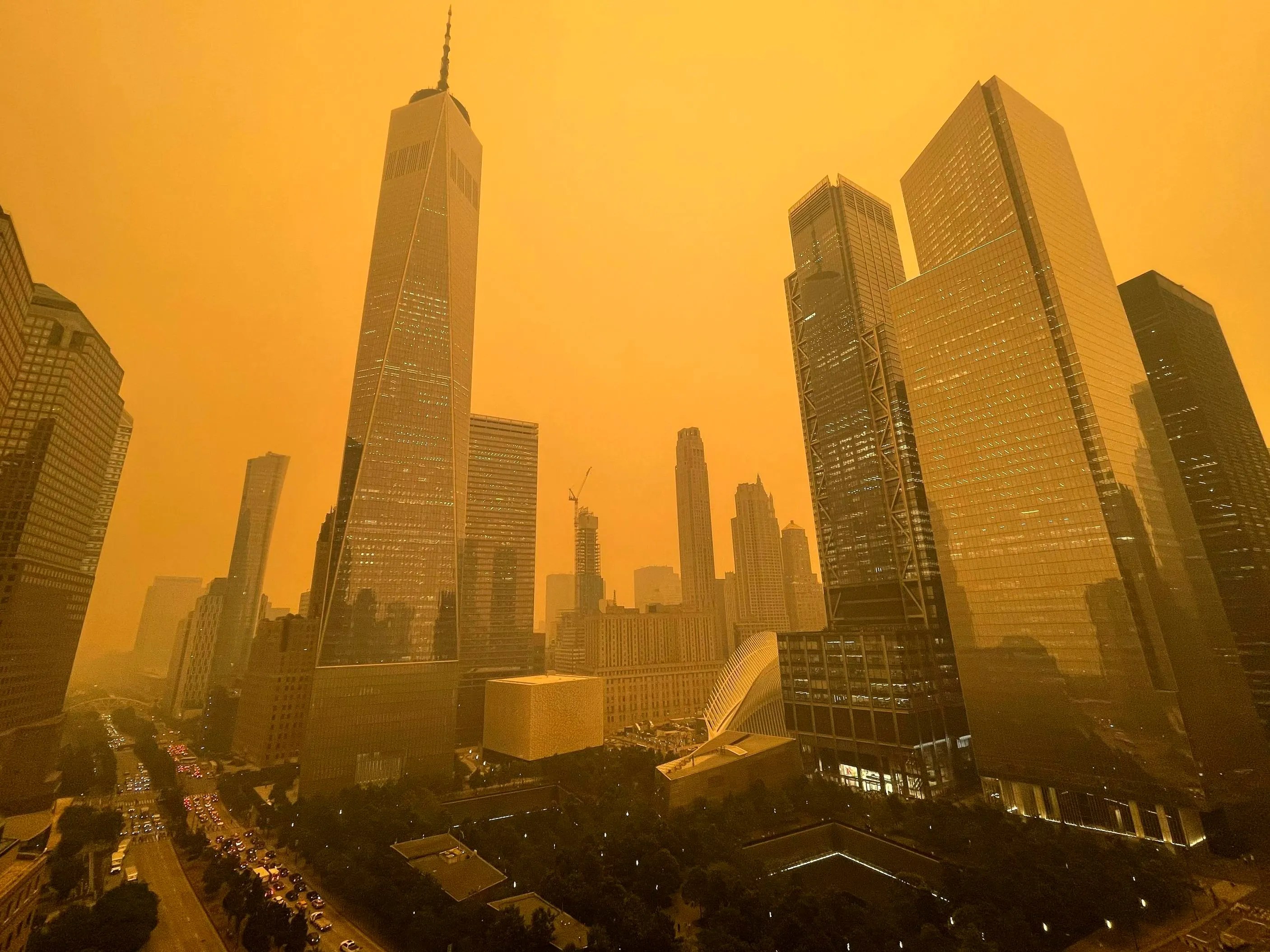

Table of Contents
The Unprecedented Scale and Intensity of Canadian Wildfires in 2023
The 2023 Canadian wildfire season has been described as the worst on record. The sheer number of wildfires, their intensity, and their geographic spread across vast swathes of the country are unprecedented. Factors contributing to this catastrophic season include:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and increasingly frequent heatwaves create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. The resulting drier vegetation acts as kindling, fueling larger and more intense blazes.
- Drought Conditions: Many regions in Canada experienced severe drought conditions leading up to the wildfire season, leaving forests exceptionally dry and vulnerable to ignition.
- Insect Infestations: Outbreaks of forest insects, such as the mountain pine beetle, have weakened vast tracts of forest, making them more susceptible to fire.
The scale of the devastation is staggering. Millions of hectares have burned, requiring massive deployments of firefighting resources and resulting in widespread evacuations. The sheer number of hectares burned and the intensity of the fires have overwhelmed firefighting capabilities in several provinces, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced wildfire management strategies and increased resource allocation. Keywords: Canadian wildfire season, hectares burned, climate change impacts, wildfire intensity.
The Mechanics of the 3°C Temperature Drop in New York City
The unusual 3°C temperature drop in New York City was a direct consequence of the massive smoke plumes generated by the Canadian wildfires. These plumes, carrying vast quantities of smoke and particulate matter, travelled thousands of kilometers, impacting air quality across much of the eastern United States. The effect on temperature is multifaceted:
- Smoke Plume Effect: The dense smoke acted as a blanket, significantly reducing the amount of sunlight reaching the ground. This reduced solar radiation led to a decrease in daytime temperatures, a phenomenon known as atmospheric cooling.
- Temperature Anomaly: The resulting temperature drop was a significant anomaly for the time of year, demonstrating the powerful influence of large-scale wildfire events on regional weather patterns. The impact was far-reaching, affecting not only temperatures but also light levels and air visibility across several states.
- Canadian Wildfire Smoke: The unprecedented scale of the Canadian wildfire smoke plumes explains the magnitude of the temperature anomaly experienced in New York City and other areas.
Keywords: smoke plume effect, temperature anomaly, atmospheric cooling, Canadian wildfire smoke.
Air Toxicant Trapping and Health Impacts
Wildfires release a cocktail of harmful air toxicants, posing serious threats to public health. Key pollutants include:
- PM2.5 (Particulate Matter): These tiny particles penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory problems like asthma exacerbations, bronchitis, and even cardiovascular issues. The extremely high PM2.5 levels recorded across affected areas highlight the severity of the air pollution.
- Carbon Monoxide: This odorless, colorless gas can be lethal at high concentrations and can cause headaches, dizziness, and even death.
- Other Toxicants: Wildfires also release various other harmful pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides, and ozone.
These pollutants become trapped in the atmosphere, particularly in areas with temperature inversions, which prevent the dispersal of smoke and pollutants. Temperature inversions create a layer of warm air above a layer of cooler air, trapping pollutants near the ground. The resulting high concentrations of air toxicants cause significant health problems, leading to increased hospital admissions for respiratory illnesses and other health issues. Keywords: air pollution, PM2.5 levels, respiratory problems, air toxicant exposure, wildfire smoke health effects, carbon monoxide poisoning.
The Long-Term Environmental Consequences
The long-term consequences of the Canadian wildfires extend far beyond immediate health impacts. The environmental damage is extensive and multifaceted:
- Ecosystem Degradation: Wildfires destroy habitats, impacting biodiversity and potentially leading to long-term ecological changes. The loss of trees contributes to carbon emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Economic Impacts: The cost of fighting wildfires, property damage, and the economic disruption caused by evacuations and air quality issues are substantial. The long-term economic consequences, including impacts on tourism and forestry, could be significant.
- Air Quality Degradation: The persistent presence of wildfire smoke can degrade air quality for extended periods, impacting human health and the environment for months or even years after the fires are extinguished.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Investing in wildfire prevention, early detection systems, and community preparedness strategies are crucial for mitigating future wildfire risks and reducing the severity of their impact.
Keywords: environmental impact, economic cost of wildfires, climate change mitigation, wildfire prevention.
Conclusion: Understanding and Mitigating the Risks of Canadian Wildfires
The 2023 Canadian wildfires serve as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of these events, extending far beyond their immediate geographic location. The 3°C temperature drop in New York City, the trapping of air toxicants, and the significant impact on air quality underscore the urgent need to understand and mitigate the risks associated with Canadian wildfires. The scale of these wildfires and their cascading effects on weather patterns, air quality, and public health demand a comprehensive response.
Stay informed about Canadian Wildfire updates through official government channels and monitor air quality reports regularly. Protect yourself from wildfire smoke by limiting outdoor activities during high pollution periods and using appropriate respiratory protection. Learn about wildfire preparedness and take steps to protect your home and family. By understanding the intricate relationship between Canadian wildfires and air quality, we can work collectively to reduce risks and protect our communities.

Featured Posts
-
 Dragon Den Puppy Toilet Innovation Leads To Copyright Infringement Lawsuit
May 31, 2025
Dragon Den Puppy Toilet Innovation Leads To Copyright Infringement Lawsuit
May 31, 2025 -
 Netflixs Black Mirror 5 Real World Parallels To The Dystopian Series
May 31, 2025
Netflixs Black Mirror 5 Real World Parallels To The Dystopian Series
May 31, 2025 -
 Bodensee Katastrophenuebung In Hard Vorbereitung Auf Den Ernstfall
May 31, 2025
Bodensee Katastrophenuebung In Hard Vorbereitung Auf Den Ernstfall
May 31, 2025 -
 Jaime Munguia Avenges Loss To Bruno Wins By Decision
May 31, 2025
Jaime Munguia Avenges Loss To Bruno Wins By Decision
May 31, 2025 -
 City Of Estevan Releases 2024 Street Sweeping Dates
May 31, 2025
City Of Estevan Releases 2024 Street Sweeping Dates
May 31, 2025
