China Responds To Tariffs: Lower Interest Rates And Increased Bank Lending
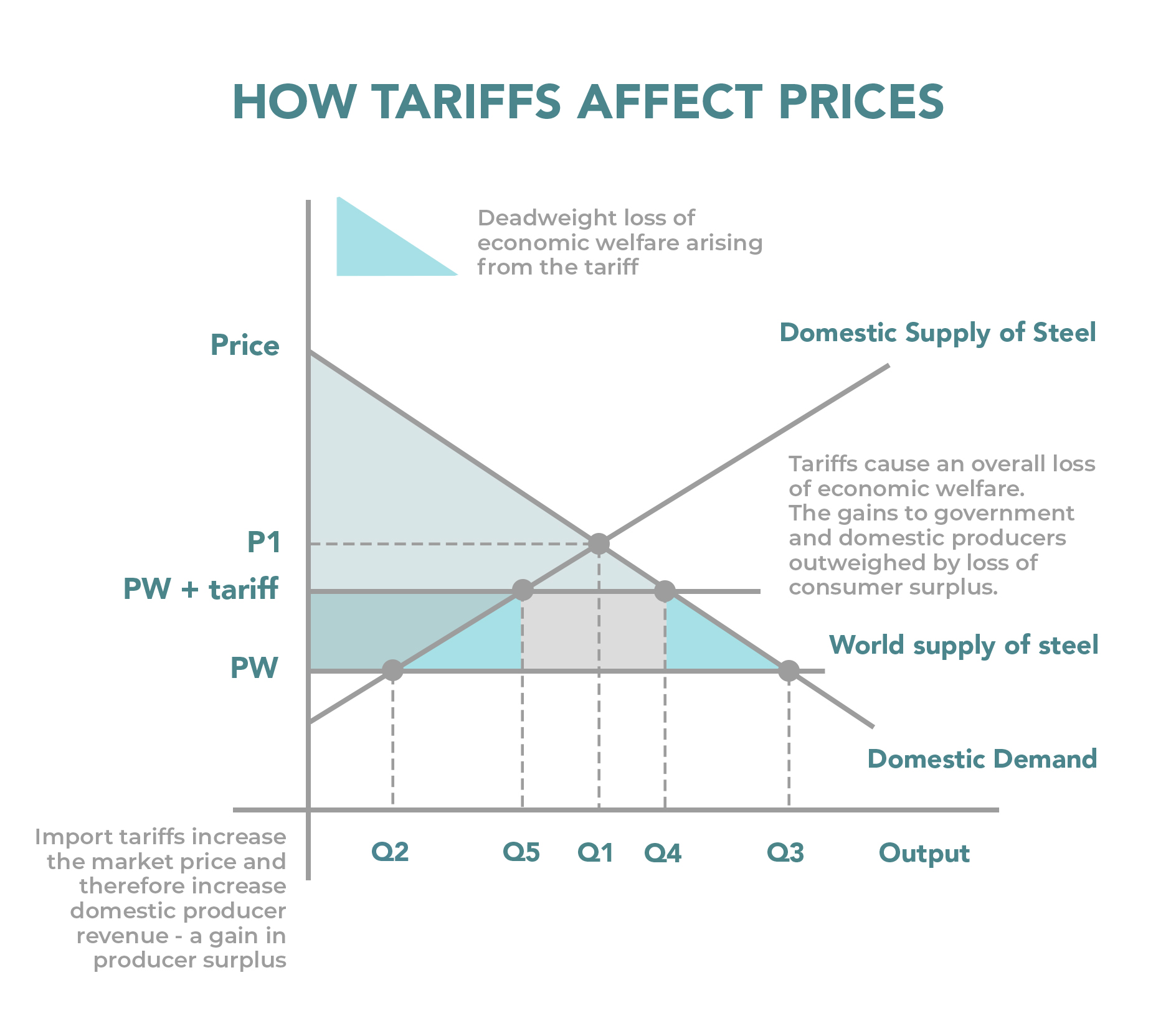
Table of Contents
The Impact of Tariffs on the Chinese Economy
Tariffs have dealt a significant blow to the Chinese economy, disrupting established trade flows and creating uncertainty across various sectors.
Disrupted Supply Chains and Reduced Exports
The imposition of tariffs has severely disrupted global supply chains, particularly impacting Chinese manufacturers and agricultural producers.
- Manufacturing: Sectors like electronics, textiles, and machinery have experienced reduced export orders due to increased costs and decreased global demand.
- Agriculture: Chinese agricultural exports, including soybeans and pork, have faced significant challenges due to retaliatory tariffs.
- Statistics: Reports from the Chinese customs authority show a noticeable decline in export volume and trade value since the implementation of tariffs, impacting overall GDP growth projections. (Specific data and source citations would be inserted here).
Foreign Investment Slowdown
The uncertainty created by escalating trade tensions and tariffs has led to a slowdown in foreign direct investment (FDI) into China.
- Decreased FDI: Businesses are hesitant to commit significant capital in an environment marked by trade uncertainty.
- Data Trends: (Insert data and source citations illustrating FDI trends before and after tariff implementation). This decline in FDI has had a ripple effect, hampering job creation and overall economic development.
Increased Inflationary Pressures
Tariffs contribute to higher prices for imported goods, increasing inflationary pressures within the Chinese economy.
- Higher Import Prices: Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported raw materials and finished goods.
- Consumer Impact: This increased cost is passed on to consumers, potentially dampening consumer spending and overall economic growth.
- Economic Indicators: (Insert relevant economic indicators and data, such as CPI, to demonstrate inflationary pressures).
China's Monetary Policy Response: Lowering Interest Rates
In response to the economic slowdown caused by tariffs, the Chinese government has implemented a series of monetary policy adjustments, primarily focusing on lowering interest rates.
Stimulating Economic Activity
Lower interest rates aim to stimulate borrowing and investment, thereby boosting economic activity.
- Increased Borrowing: Lower rates make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money for expansion and investment.
- Consumer Spending: Lower borrowing costs can also encourage consumers to spend more, increasing aggregate demand.
- PBoC Actions: The People's Bank of China (PBoC) has implemented several interest rate cuts (cite specific examples and dates).
Encouraging Investment in Infrastructure
Lower borrowing costs incentivize investment in large-scale infrastructure projects.
- Infrastructure Spending: Reduced interest rates make it more financially viable to undertake significant infrastructure development.
- Job Creation: These projects create numerous jobs, directly contributing to economic growth.
- Project Examples: (Provide examples of infrastructure projects stimulated by the lower interest rate policy).
Managing Exchange Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in managing exchange rates.
- Interest Rate & Currency: Lower interest rates can weaken the value of the yuan, making Chinese exports more competitive in the global market.
- Yuan Devaluation: While this can boost exports, it also carries risks, such as increased import costs. (Discuss potential benefits and drawbacks).
Increased Bank Lending and Credit Availability
Alongside lower interest rates, the Chinese government has encouraged increased bank lending to support businesses and stimulate the economy.
Supporting Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
SMEs are the backbone of the Chinese economy, and increased lending is crucial for their survival.
- SME Challenges: Tariffs have disproportionately impacted SMEs, creating financial challenges.
- Lending Support: Increased credit availability helps SMEs overcome these difficulties and continue operations.
- SME Statistics: (Provide statistics on SME lending and growth following the policy adjustments).
Promoting Consumption and Investment
Increased credit availability aims to stimulate both consumer spending and investment.
- Consumer Credit: Easier access to credit can boost consumer confidence and encourage purchases.
- Investment Growth: Increased credit can fuel investment in new businesses and expansion projects.
- Economic Correlation: (Provide data on credit growth and its correlation with economic activity).
Risks and Challenges of Increased Lending
While increased lending can stimulate the economy, it also carries potential risks.
- Asset Bubbles: Excessive credit growth can lead to the formation of asset bubbles and financial instability.
- PBoC Mitigation: The PBoC is implementing measures to manage these risks (mention specific measures).
- Long-Term Implications: The long-term consequences of this increased lending need careful monitoring and analysis.
Conclusion: China's Response to Tariffs: A Balancing Act
China's response to tariffs through lower interest rates and increased bank lending represents a strategic effort to mitigate the negative economic impacts. While these monetary policy adjustments have stimulated economic activity and supported businesses, particularly SMEs, they also present potential risks, including inflationary pressures and the possibility of asset bubbles. The effectiveness of this approach remains to be seen, requiring ongoing monitoring and evaluation. The future trajectory of the Chinese economy will depend on several factors, including the continued impact of tariffs, the government's ability to manage these risks, and the overall global economic environment. Stay informed about how China continues to respond to tariffs and the implications for global trade. Learn more about the intricacies of China's monetary policy and its effectiveness in navigating economic challenges.

Featured Posts
-
 Pierce Countys 160 Year Old Home Demolition And Park Conversion
May 08, 2025
Pierce Countys 160 Year Old Home Demolition And Park Conversion
May 08, 2025 -
 From Skimpy To Strong Examining The Evolution Of Rogues X Men Costume
May 08, 2025
From Skimpy To Strong Examining The Evolution Of Rogues X Men Costume
May 08, 2025 -
 Arsenal News Expert Collymore Questions Artetas Future
May 08, 2025
Arsenal News Expert Collymore Questions Artetas Future
May 08, 2025 -
 Latest News F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman In The Headlines
May 08, 2025
Latest News F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman In The Headlines
May 08, 2025 -
 X Men Rogue Channels Cyclops Powers
May 08, 2025
X Men Rogue Channels Cyclops Powers
May 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Colin Cowherds Continued Criticism Of Jayson Tatum
May 08, 2025
Colin Cowherds Continued Criticism Of Jayson Tatum
May 08, 2025 -
 Universal Credit Understanding And Reclaiming Hardship Payment Overpayments
May 08, 2025
Universal Credit Understanding And Reclaiming Hardship Payment Overpayments
May 08, 2025 -
 Celtics Vs Nets Latest Injury Report And Tatums Playing Status
May 08, 2025
Celtics Vs Nets Latest Injury Report And Tatums Playing Status
May 08, 2025 -
 Abc Promo Features Tnt Announcers Hilarious Take On Jayson Tatum
May 08, 2025
Abc Promo Features Tnt Announcers Hilarious Take On Jayson Tatum
May 08, 2025 -
 Dwp Universal Credit Claiming Back Overpaid Hardship Payments
May 08, 2025
Dwp Universal Credit Claiming Back Overpaid Hardship Payments
May 08, 2025
