Collaboration For Impact: Exploring Interdisciplinary And Transdisciplinary Methods
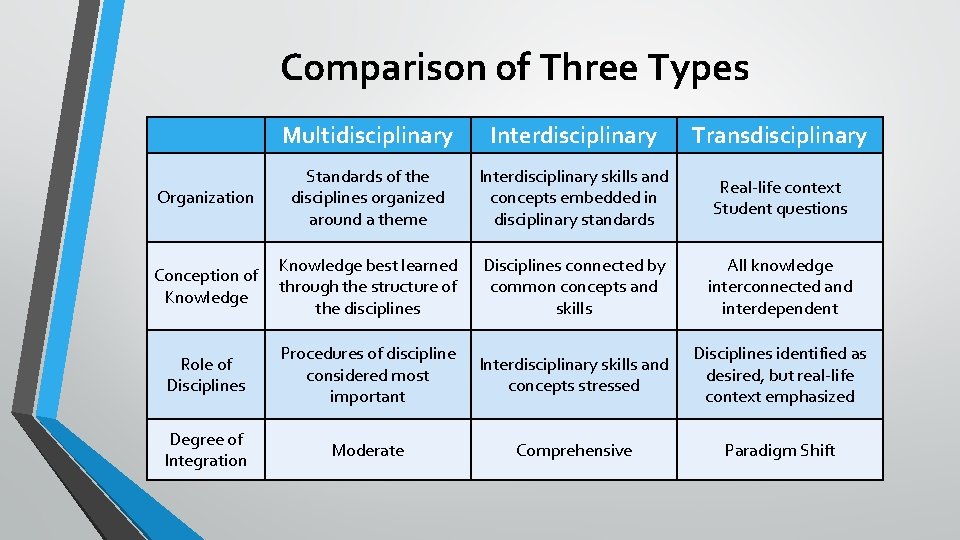
Table of Contents
Understanding Interdisciplinary Collaboration for Enhanced Problem Solving
Interdisciplinary collaboration involves integrating knowledge and methods from different academic disciplines to address a shared research question or problem. It's about bringing together experts from various fields – say, engineers, sociologists, and economists – to work towards a common goal. This synergistic approach leverages the unique perspectives and expertise of each discipline, leading to more comprehensive and innovative solutions.
Advantages of Interdisciplinary Teamwork:
- Broader Perspectives and Expertise: Diverse viewpoints enrich the problem-solving process, uncovering hidden assumptions and considering multiple angles.
- More Creative and Innovative Solutions: The fusion of different disciplinary approaches can spark unexpected insights and breakthroughs.
- Improved Problem-Solving Capabilities: Combining various skill sets and analytical tools leads to more robust and effective solutions.
- Increased Understanding of Complex Issues: Interdisciplinary research offers a holistic understanding of complex phenomena, going beyond the limitations of individual disciplines.
Challenges in Interdisciplinary Research:
- Communication Barriers: Differences in terminology, methodologies, and communication styles can hinder effective knowledge exchange.
- Conflicting Methodologies and Approaches: Integrating diverse research methods can be challenging and require careful planning and coordination.
- Difficulty in Integrating Diverse Perspectives: Synthesizing diverse viewpoints and reaching consensus can be a complex and time-consuming process.
- Challenges in Authorship and Credit Allocation: Fairly assigning credit and authorship can be a source of conflict in interdisciplinary projects.
Examples of Successful Interdisciplinary Projects: The development of effective public health interventions often requires the collaboration of epidemiologists, sociologists, and public health officials. Similarly, advancements in renewable energy technologies often involve cross-disciplinary research efforts between engineers, material scientists, and economists.
Exploring Transdisciplinary Collaboration: Bridging the Gap Between Disciplines and Stakeholders
Transdisciplinary collaboration extends beyond the integration of disciplines. It actively involves stakeholders – communities, policymakers, practitioners – in all phases of the research process. This approach prioritizes real-world application and ensures the research directly addresses the needs and concerns of those most affected. Transdisciplinary research methods prioritize collaboration and knowledge co-creation.
Advantages of Transdisciplinary Collaboration:
- Enhanced Relevance and Applicability of Research: Direct stakeholder involvement ensures the research addresses real-world problems and generates usable outcomes.
- Greater Stakeholder Engagement and Ownership: Involving stakeholders fosters a sense of ownership and increases the likelihood of successful implementation.
- Improved Dissemination and Implementation of Findings: Stakeholder participation facilitates the translation of research findings into actionable strategies.
- Increased Societal Impact and Benefits: Transdisciplinary research often leads to more significant and lasting positive societal impact.
Challenges in Transdisciplinary Initiatives:
- Power Imbalances: Differences in power dynamics between disciplines and stakeholders can create barriers to equitable participation.
- Managing Diverse Perspectives and Interests: Balancing the diverse perspectives and interests of multiple stakeholders can be challenging.
- Achieving Consensus and Agreement: Reaching consensus among diverse stakeholders with potentially conflicting priorities requires skilled facilitation.
- Increased Complexity in Project Management: Managing a large and diverse team necessitates robust project management strategies.
Examples of Successful Transdisciplinary Initiatives: Community-based participatory research (CBPR) projects empower communities to participate in research addressing their health and environmental concerns. Sustainable development projects often require transdisciplinary collaboration involving scientists, policymakers, and community members.
Strategies for Effective Interdisciplinary and Transdisciplinary Collaboration
Successfully navigating the complexities of interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary collaborations requires careful planning and execution. Several key strategies can enhance the effectiveness of these collaborative efforts.
Practical Strategies for Fostering Successful Collaboration:
- Establish Clear Goals and Objectives: Defining clear, shared goals and objectives from the outset is crucial for guiding the collaborative process.
- Develop Effective Communication and Collaboration Strategies: Establish clear communication protocols, regular meetings, and shared platforms for collaboration.
- Build Trust and Mutual Respect: Creating a supportive and inclusive environment where all participants feel valued and respected is vital.
- Manage Conflicts and Disagreements Constructively: Developing mechanisms for addressing conflicts and disagreements in a constructive manner is essential.
- Utilize Appropriate Tools and Technologies: Leveraging project management software and other collaborative tools can streamline the process.
Leadership and Facilitation are Key: Effective leadership and skilled facilitation are essential for navigating the complexities of these collaborative endeavors. A shared understanding and common vision are crucial for guiding the project. Effective collaboration techniques require deliberate effort and planning.
Maximizing Impact Through Meaningful Collaboration
In conclusion, interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary approaches offer powerful avenues for tackling complex challenges and achieving significant societal impact. While challenges exist, the potential benefits – broader perspectives, innovative solutions, increased relevance, and enhanced stakeholder engagement – far outweigh the obstacles. By implementing the strategies outlined above and fostering a culture of mutual respect and effective communication, we can harness the transformative power of collaborative methods.
To achieve greater impact in your work, actively embrace interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary collaboration. Explore resources on collaborative project management and effective teamwork strategies to further develop your collaborative skills. The future of impactful research and problem-solving lies in the power of meaningful collaboration.

Featured Posts
-
 The Fsu Clemson Settlement Four Reasons For Their Win
May 19, 2025
The Fsu Clemson Settlement Four Reasons For Their Win
May 19, 2025 -
 A Place In The Sun Top Locations For Retirement Overseas
May 19, 2025
A Place In The Sun Top Locations For Retirement Overseas
May 19, 2025 -
 Az Rbaycan S Fur 2025 Eurovisionun Soezcuesue
May 19, 2025
Az Rbaycan S Fur 2025 Eurovisionun Soezcuesue
May 19, 2025 -
 A Simple Guide To Eurovisions Voting Procedures
May 19, 2025
A Simple Guide To Eurovisions Voting Procedures
May 19, 2025 -
 Is Mobile Marketing The Future Of E Commerce A Comprehensive Guide
May 19, 2025
Is Mobile Marketing The Future Of E Commerce A Comprehensive Guide
May 19, 2025
