Congo's Cobalt Export Ban: Market Impact And The Anticipated Quota Plan
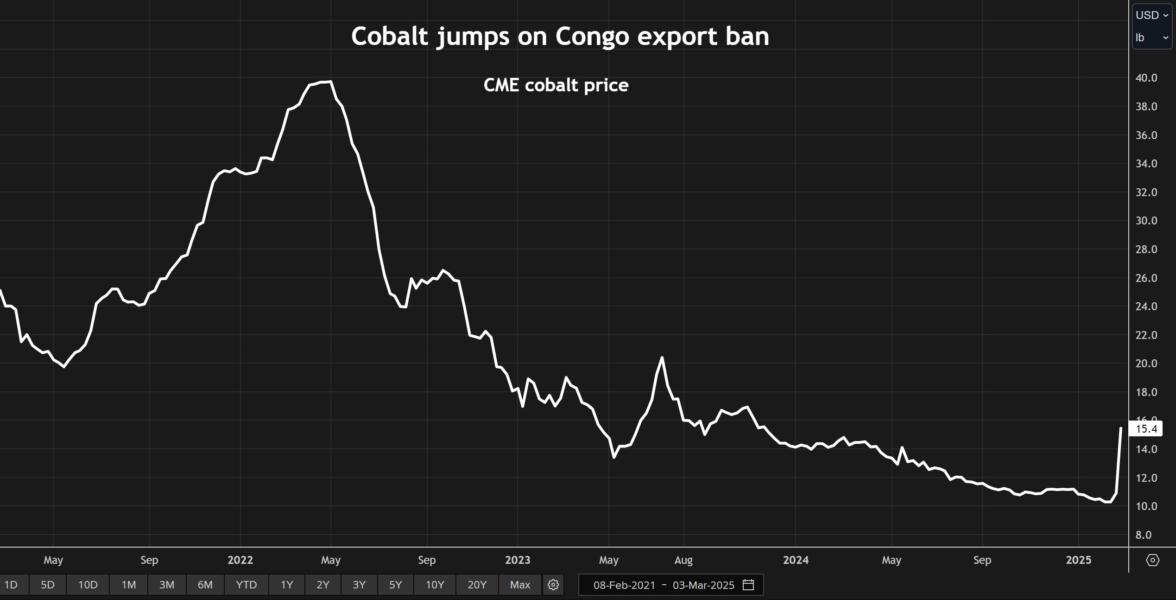
Table of Contents
The Current State of Cobalt Production in the DRC
The DRC's dominance in global cobalt production is undeniable. It accounts for over 70% of the world's cobalt supply, making it a critical player in the global economy. However, this dominance is intertwined with significant challenges. A substantial portion of cobalt production originates from the artisanal mining sector, characterized by informal operations lacking safety regulations and environmental protections. This artisanal cobalt mining poses significant environmental risks, including deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution. Furthermore, human rights concerns, such as child labor and unsafe working conditions, are prevalent within this sector.
Existing export regulations in the DRC have proven largely ineffective in addressing these issues. Lack of transparency and enforcement mechanisms have allowed illegal mining and unethical practices to persist.
- Percentage of global cobalt production sourced from the DRC: Over 70%
- Key regions in the DRC where cobalt is mined: Katanga province is the primary source.
- Challenges related to traceability and responsible sourcing: Lack of transparency makes it difficult to trace cobalt from mine to end product, hindering efforts for responsible sourcing.
- Current export taxes and duties: These are currently in place but haven't effectively controlled the market or addressed the environmental and social issues.
Potential Market Impacts of a Cobalt Export Ban
A Congo cobalt export ban would have profound consequences for the global market. The most immediate impact would be felt in the electric vehicle (EV) battery industry, which relies heavily on cobalt for its energy density and performance. A significant reduction or complete halt in cobalt exports from the DRC could trigger severe supply chain bottlenecks, potentially delaying EV production and increasing prices.
The impact extends beyond the EV sector. Various industries, including electronics and aerospace, utilize cobalt in their manufacturing processes. A ban would lead to significant price volatility, potentially causing substantial price hikes. This price increase would affect the profitability of numerous industries reliant on this crucial metal.
Finding alternative cobalt sources presents challenges. While other countries produce cobalt, they lack the DRC's scale and readily available resources. These alternative sources might not be able to compensate for the shortfall, leading to prolonged supply disruptions and price instability.
- Projected cobalt price increases under different ban scenarios: Experts predict drastic price increases, potentially doubling or tripling current market values.
- Potential supply chain bottlenecks for EV manufacturers: Delays in EV production and potential shortages are highly likely.
- Impact on the profitability of cobalt-dependent industries: Reduced profitability and potentially plant closures are possible outcomes.
- Countries that could become alternative cobalt suppliers: Australia, Canada, and Zambia are potential alternatives, but their production capacity is significantly lower.
The Anticipated Quota Plan: Details and Implications
Instead of a complete ban, the DRC might implement a quota system for cobalt exports. This plan aims to increase domestic processing of cobalt before export, generating more revenue within the country and potentially leading to more sustainable mining practices. The rationale behind this approach is to add value to the raw material before export, stimulating economic growth within the DRC.
However, a quota system presents its own set of challenges. The limited supply under a quota system could still cause price volatility and supply chain disruptions. The allocation of quotas to mining companies raises concerns about potential corruption and unfair distribution. Effective monitoring and enforcement mechanisms are crucial to ensure the system's transparency and effectiveness.
- Proposed cobalt export quotas: The specific quota amounts remain uncertain, but they are expected to significantly restrict exports.
- Mechanism for allocating quotas to mining companies: The process for allocation is yet to be fully defined, raising concerns about transparency and fairness.
- Potential for corruption and unfair allocation: The risk of corruption is high if the allocation process is not transparent and robust.
- Government's plan for monitoring and enforcement: The DRC government needs a strong monitoring and enforcement strategy to prevent illegal activities.
International Response and Geopolitical Implications
The potential Congo cobalt export ban or quota has already elicited reactions from major cobalt consumers, including China, Europe, and the USA. These countries are exploring various options, from seeking alternative suppliers to negotiating agreements with the DRC. The geopolitical implications are substantial. The ban or quota could lead to trade disputes and retaliatory measures, straining relationships between the DRC and its major trading partners.
International cooperation is essential to address the complex challenges surrounding the cobalt supply chain. This involves fostering responsible mining practices, promoting transparency, and ensuring ethical sourcing. Collaborative efforts can help mitigate the risks associated with the Congo cobalt export ban and create a more sustainable and equitable cobalt market.
- Statements from key governments and international organizations: Many have expressed concerns about the potential impact on global supply chains.
- Potential trade negotiations and agreements: Discussions are likely to intensify between the DRC and its major trading partners.
- Impact on bilateral relations between the DRC and major trading partners: The situation could strain diplomatic ties.
- Potential for collaborative efforts on responsible mining practices: International cooperation is crucial for sustainable and ethical cobalt mining.
Conclusion
The potential implementation of a Congo cobalt export ban or a strict quota system presents significant challenges and opportunities for the global market. While the DRC aims to leverage its cobalt resources for greater domestic economic benefit and improved environmental and social practices, the move carries substantial risks of price volatility, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. Understanding the implications of the Congo cobalt export ban and the details of the anticipated quota plan is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. Staying informed about developments related to the Congo cobalt export ban is vital for navigating this evolving situation and mitigating potential negative consequences. Further research and engagement in dialogue regarding responsible sourcing and sustainable cobalt mining practices are critical to ensuring a stable and ethical supply chain for this crucial resource.

Featured Posts
-
 Warriors And Grizzlies Clash In Crucial Nba Play In Game
May 16, 2025
Warriors And Grizzlies Clash In Crucial Nba Play In Game
May 16, 2025 -
 Boston Celtics Gear Shop The Latest Styles At Fanatics For The Playoffs
May 16, 2025
Boston Celtics Gear Shop The Latest Styles At Fanatics For The Playoffs
May 16, 2025 -
 Athletic Club De Bilbao Match Schedules Results And More On Vavel United States
May 16, 2025
Athletic Club De Bilbao Match Schedules Results And More On Vavel United States
May 16, 2025 -
 Jalen Brunsons Wife Ali Marks Life And Relationship With The Nba Player
May 16, 2025
Jalen Brunsons Wife Ali Marks Life And Relationship With The Nba Player
May 16, 2025 -
 Watch Ottawa Senators Vs Toronto Maple Leafs Game 5 Online Free Nhl Playoffs Live Stream
May 16, 2025
Watch Ottawa Senators Vs Toronto Maple Leafs Game 5 Online Free Nhl Playoffs Live Stream
May 16, 2025
