Deadly Fungi: The Impact Of Global Warming On Human Health
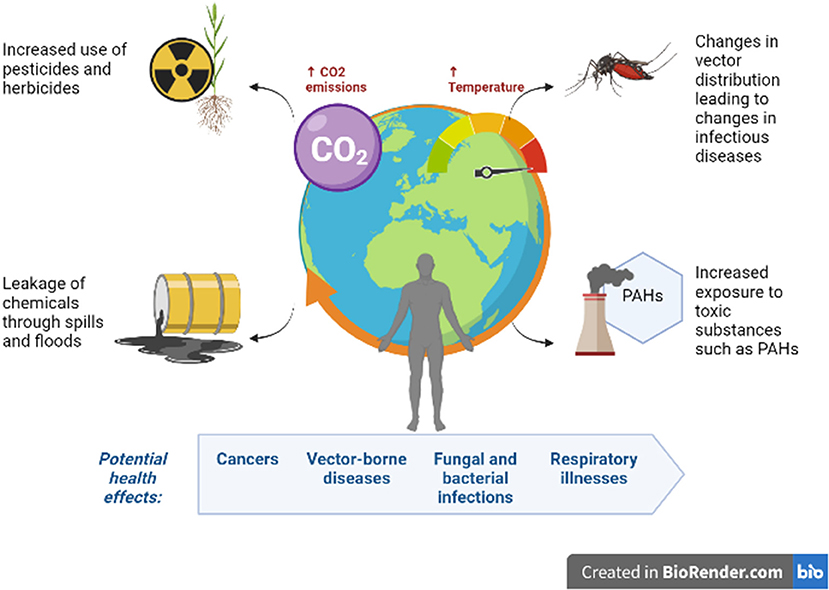
Table of Contents
H2: The Expanding Habitat of Deadly Fungi
Rising temperatures and increased humidity are creating ideal breeding grounds for a wider range of fungal species, allowing them to expand their geographic reach and impact more people. This expansion of deadly fungi is a significant consequence of global warming.
H3: Temperature and Humidity: Perfect Breeding Grounds
Many fungi thrive in warm, humid environments. Global warming provides these perfect conditions, leading to increased fungal growth and the spread of infections.
- Candida auris: This emerging fungal pathogen is highly resistant to antifungal drugs and is increasingly prevalent in warmer climates, posing a serious threat to hospital patients and immunocompromised individuals.
- Aspergillus fumigatus: This common mold can cause life-threatening infections, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. Warmer temperatures and increased humidity promote its growth and spore dispersal.
- The impact on immunocompromised individuals: People with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation, are particularly vulnerable to severe fungal infections. The expanding habitat of deadly fungi directly increases their risk.
H3: Shifting Ecosystems and Increased Exposure
Changes in our environment, driven by climate change, are increasing human contact with fungal spores.
- Flooded areas: Increased rainfall and flooding create moist environments perfect for fungal growth, leading to greater exposure for people living in these regions.
- Damaged forests: Deforestation and forest fires, often exacerbated by climate change, disrupt ecosystems and increase the release of fungal spores into the air.
- Altered weather patterns: More frequent and intense storms can disperse fungal spores over wider areas, leading to increased exposure for larger populations. These changes contribute to a significantly higher risk of fungal infections.
H2: The Evolution of Deadly Fungi
Warmer temperatures are not only expanding the habitat of deadly fungi but also accelerating their evolution, leading to more virulent and drug-resistant strains.
H3: Increased Virulence and Drug Resistance
Higher temperatures can speed up the mutation rate in fungi, leading to the development of strains that are more aggressive and resistant to antifungal medications.
- Mechanisms of evolution: Exposure to antifungal drugs selects for resistant strains, and warmer temperatures accelerate this process.
- Implications for treatment: The emergence of drug-resistant fungi makes treatment more challenging and increases the risk of mortality. This poses a significant public health challenge.
H3: Emergence of Novel Pathogens
Climate change could also facilitate the emergence of entirely new fungal pathogens, posing unpredictable health risks.
- Newly identified fungi: Researchers are constantly discovering new fungal species, some of which may possess pathogenic potential.
- Challenges of identification and treatment: Identifying and treating unknown pathogens can be difficult, delaying effective intervention and increasing mortality risk. This underscores the urgent need for proactive research and monitoring.
H2: The Impact on Human Health
The consequences of the expanding habitat and evolving nature of deadly fungi are already being felt globally.
H3: Increased Incidence of Fungal Infections
A correlation exists between rising global temperatures and humidity and the increasing incidence of fungal infections worldwide.
- Statistics on fungal diseases: Data show a clear upward trend in the number of cases of various fungal diseases, particularly in regions experiencing warmer climates.
- Healthcare system burden: The rise in fungal infections places a significant strain on healthcare systems, requiring more resources for diagnosis, treatment, and management.
H3: Vulnerable Populations and Health Disparities
The impact of deadly fungi is disproportionately felt by vulnerable populations.
- Elderly individuals: The elderly have weakened immune systems, making them more susceptible to severe fungal infections.
- Immunocompromised individuals: As previously mentioned, those with weakened immune systems are at increased risk.
- Low-income countries: Limited access to healthcare resources and sanitation further exacerbates the impact of fungal infections in these regions. Addressing these social determinants of health is crucial.
3. Conclusion
The link between global warming, the expansion of deadly fungi, and the increasing threat to human health is undeniable. The changing climate is creating a perfect storm for the proliferation of these dangerous pathogens, impacting vulnerable populations worldwide and straining healthcare systems. Addressing climate change is crucial to mitigate this risk. Understanding the relationship between deadly fungi and global warming is paramount. By taking action to reduce our carbon footprint, supporting research into fungal infections, and advocating for improved public health initiatives, we can safeguard our future and protect ourselves from this escalating health crisis. Learn more and get involved with organizations like [link to relevant organization 1] and [link to relevant organization 2].

Featured Posts
-
 Gerez Votre Equipe Cycliste Le Nouveau Jeu Rtbf Pour Le Tour De France
May 26, 2025
Gerez Votre Equipe Cycliste Le Nouveau Jeu Rtbf Pour Le Tour De France
May 26, 2025 -
 Dc Love Story From Thousands Of Miles Apart To Heartbreak
May 26, 2025
Dc Love Story From Thousands Of Miles Apart To Heartbreak
May 26, 2025 -
 Tour Of Flanders 2024 Pogacars Impressive Solo Triumph
May 26, 2025
Tour Of Flanders 2024 Pogacars Impressive Solo Triumph
May 26, 2025 -
 Wednesday Coastal Flood Warning Southeast Pa
May 26, 2025
Wednesday Coastal Flood Warning Southeast Pa
May 26, 2025 -
 Siaran Langsung Moto Gp Inggris 2025 Sprint Race Pukul 20 00 Wib Link Streaming
May 26, 2025
Siaran Langsung Moto Gp Inggris 2025 Sprint Race Pukul 20 00 Wib Link Streaming
May 26, 2025
