Economic Slowdown Under Biden: Causes, Consequences, And Solutions
Table of Contents
Causes of the Economic Slowdown Under the Biden Administration
Several interconnected factors have contributed to the perceived economic slowdown under President Biden. These include persistent inflation, global economic uncertainty, ongoing debates surrounding fiscal policy, and the Federal Reserve's response to rising prices.
Inflation and Rising Prices
Inflation has been a major driver of the economic slowdown. Soaring prices for essential goods and services have significantly reduced consumer purchasing power, hindering economic growth.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to shortages of various goods and increased transportation costs. This contributed significantly to inflation. The ongoing war in Ukraine has further exacerbated these issues, particularly regarding energy supplies.
- Increased Energy Costs: The price of oil and natural gas has surged, impacting transportation, manufacturing, and household energy bills. This surge is linked to geopolitical instability and reduced supply.
- Government Spending: Critics argue that expansive government spending under the Biden administration has fueled inflation by increasing aggregate demand without a corresponding increase in supply. Proponents, however, maintain that these investments are necessary for long-term economic growth and infrastructure improvement.
- Monetary Policy: The Federal Reserve's monetary policy plays a crucial role in managing inflation. While interest rate hikes aim to curb inflation, they can also slow down economic growth and potentially trigger a recession.
Global Economic Uncertainty
The US economy is not isolated from global events. Several international factors have contributed to the current economic slowdown.
- Geopolitical Instability: The war in Ukraine has created significant geopolitical uncertainty, disrupting global energy markets and supply chains. This instability increases market volatility and dampens investor confidence.
- Energy Crisis: The global energy crisis, partly fueled by the war in Ukraine, has driven up energy prices worldwide, impacting businesses and consumers alike. This has ripple effects across various sectors.
- Trade Wars: Ongoing trade tensions between countries can disrupt global trade flows and increase the cost of goods. This uncertainty impacts both import and export-oriented businesses.
- Global Recessionary Pressures: The possibility of a global recession further compounds the economic challenges facing the US. Interconnected global markets mean that a downturn in one major economy can easily spread.
Fiscal Policy Debates
The Biden administration's fiscal policies, including substantial investments in infrastructure and social programs, have been the subject of intense debate.
- Debate on Stimulus Effectiveness: The effectiveness of the various stimulus packages implemented during and after the pandemic remains a point of contention. Some argue that these measures were necessary to prevent a deeper economic downturn, while others contend that they fueled inflation.
- Government Debt: The increasing national debt raises concerns about the long-term fiscal sustainability of the country. This debt burden can limit the government’s ability to respond to future economic crises.
- Impact on Inflation: The relationship between government spending and inflation is complex and debated. While some argue that increased spending exacerbates inflation, others contend that targeted investments can boost productivity and long-term growth.
Monetary Policy Responses
The Federal Reserve's response to inflation has significant implications for the economy's trajectory.
- Interest Rate Hikes: The Fed has implemented a series of interest rate hikes to combat inflation. These hikes increase borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially slowing down economic activity.
- Quantitative Tightening: The Fed is also reducing its balance sheet through quantitative tightening, further impacting the money supply and credit conditions.
- Impact on Borrowing Costs: Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, impacting investment, business expansion, and consumer spending.
- Potential for Recession: Aggressive monetary policy tightening increases the risk of triggering a recession as economic growth slows sharply.
Consequences of the Economic Slowdown
The economic slowdown under the Biden administration carries several significant consequences.
Unemployment and Job Market Impacts
A slowing economy often leads to job losses and increased unemployment.
- Job Losses: Sectors sensitive to economic downturns, such as manufacturing and construction, may experience job losses.
- Wage Stagnation: Wage growth may stagnate or even decline as unemployment rises, impacting workers' purchasing power.
- Income Inequality: Economic slowdowns often disproportionately affect low-income households, potentially exacerbating income inequality.
Impact on Consumer Spending and Confidence
Reduced consumer spending and decreased confidence are key characteristics of an economic slowdown.
- Reduced Consumer Spending: High inflation and economic uncertainty lead to reduced consumer spending as people become more cautious.
- Decreased Investment: Businesses may postpone or cancel investment plans due to uncertainty, further dampening economic activity.
- Impact on Business Growth: Reduced consumer demand and investment can significantly hamper business growth and expansion.
Potential for Recession
The current economic conditions raise concerns about the possibility of a recession.
- Definition of a Recession: A recession is typically defined as two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth.
- Leading Indicators: Various leading economic indicators, such as consumer confidence and manufacturing activity, can provide clues about the likelihood of a recession.
- Potential Duration and Impact: The duration and severity of a potential recession depend on the interplay of various economic factors and policy responses.
Potential Solutions and Policy Recommendations
Addressing the economic slowdown requires a multi-pronged approach involving both fiscal and monetary policy adjustments, as well as strategies to improve supply chain efficiency.
Fiscal Policy Adjustments
Targeted fiscal policy adjustments can help stimulate economic growth while addressing inflationary pressures.
- Targeted Tax Cuts: Carefully designed tax cuts can boost consumer spending and investment, but need to avoid exacerbating inflation.
- Infrastructure Investments: Continued investment in infrastructure can enhance productivity and create jobs in the long run.
- Social Safety Net Programs: Maintaining adequate social safety nets is essential to protect vulnerable populations during economic downturns.
Monetary Policy Strategies
The Federal Reserve needs to carefully calibrate its monetary policy to combat inflation while minimizing the risk of a recession.
- Gradual Interest Rate Increases: A more gradual approach to interest rate increases can help mitigate the risk of triggering a recession.
- Targeted Inflation Control Measures: Focusing on specific factors driving inflation, rather than broad interest rate increases, might prove more effective.
Addressing Supply Chain Issues
Improving the efficiency of global supply chains is crucial to reduce inflationary pressures.
- Investments in Infrastructure: Investing in transportation infrastructure can improve the flow of goods and reduce transportation costs.
- Trade Agreements: Strengthening international trade agreements can help diversify supply chains and reduce reliance on single sources.
- Diversification of Supply Chains: Businesses should strive to diversify their supply chains to mitigate risks associated with disruptions.
Conclusion
The economic slowdown under the Biden administration is a multifaceted challenge stemming from inflation, global uncertainty, fiscal policy debates, and monetary policy responses. The consequences, including potential job losses and a possible recession, necessitate a comprehensive and carefully calibrated approach. Understanding the economic slowdown and its causes is paramount for formulating effective economic policies and ensuring a sustainable economic future. We must remain informed about economic developments, engage in constructive dialogue, and advocate for policies that promote sustainable economic growth and alleviate the challenges facing American families and businesses. By navigating these economic challenges effectively, we can work towards strengthening the American economy and building a more resilient and prosperous future – a future where understanding the economic slowdown translates into proactive and effective solutions.

Featured Posts
-
 April 16 2025 Lotto Results
May 03, 2025
April 16 2025 Lotto Results
May 03, 2025 -
 Havertz Underwhelms Sounesss Verdict On Arsenals Epl Signing
May 03, 2025
Havertz Underwhelms Sounesss Verdict On Arsenals Epl Signing
May 03, 2025 -
 Is Riot Platforms Stock A Buy At 52 Week Lows
May 03, 2025
Is Riot Platforms Stock A Buy At 52 Week Lows
May 03, 2025 -
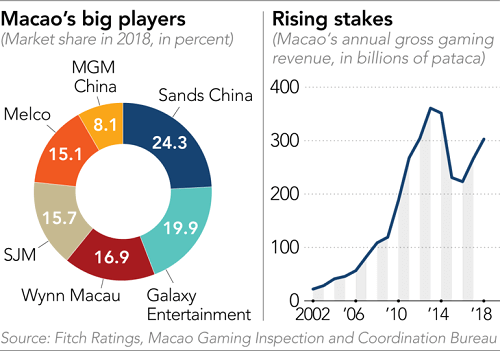 Stronger Than Predicted Macaus Gaming Revenue Before Golden Week
May 03, 2025
Stronger Than Predicted Macaus Gaming Revenue Before Golden Week
May 03, 2025 -
 Recent Fortnite Refunds Precursor To Cosmetic Overhaul
May 03, 2025
Recent Fortnite Refunds Precursor To Cosmetic Overhaul
May 03, 2025
