Endowment Tax Changes: Harvard And Yale To Bear The Brunt Of New House Plan
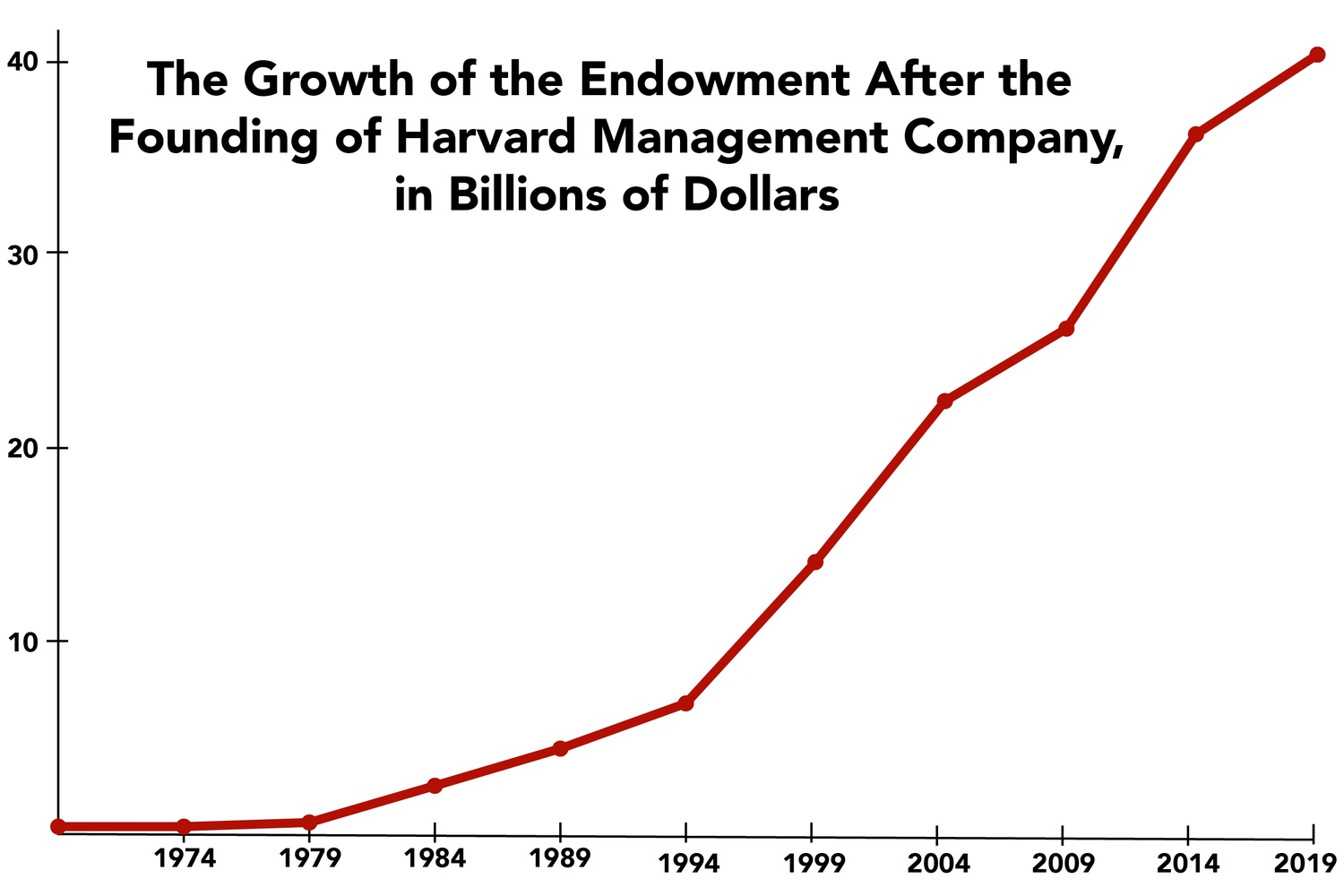
Table of Contents
The Proposed Changes to Endowment Taxation
The proposed endowment tax reform involves significant alterations to how universities are taxed on their investment income. Currently, many universities enjoy tax-exempt status for a significant portion of their endowment earnings. The new plan, however, suggests altering this status, introducing new tax brackets and thresholds specifically targeting large endowments. These changes fall under the broader umbrella of higher education tax reform and specifically address the taxation of non-profit endowments.
- Increased Tax Rates on Investment Income: The proposed plan increases the tax rate on endowment investment income exceeding a certain threshold. This threshold is significantly lower than the current levels, meaning a larger portion of endowment earnings will be subject to taxation.
- Modified Tax-Exempt Status: The plan proposes to limit or modify the tax-exempt status currently enjoyed by universities, particularly those with endowments exceeding a specific size. This could mean a loss of significant tax benefits for large institutions.
- Limited Exemptions: While some exemptions may remain for specific charitable activities or financial aid programs, the proposed changes significantly restrict the availability of these exceptions, placing a greater tax burden on institutions.
Impact on Harvard and Yale's Endowments
The potential financial impact of these Harvard endowment tax and Yale endowment tax changes is substantial. Harvard, boasting an endowment exceeding $50 billion, and Yale, with an endowment in the tens of billions, are uniquely vulnerable. These Ivy League endowment tax implications dwarf the impact on smaller institutions.
- Size Disparity: The sheer size of Harvard and Yale’s endowments means that even a small percentage increase in taxation translates to billions of dollars in lost revenue. This contrasts sharply with smaller universities whose endowment tax burdens would be comparatively less severe.
- Disproportionate Impact: The proposed changes are structured in a way that disproportionately impacts institutions with large endowments. The larger the endowment, the greater the percentage of investment income that will become taxable.
- Consequences for Operations: This substantial loss of revenue could significantly impact financial aid programs, research funding, and crucial campus operations. Reductions in these areas could affect student access, faculty research capabilities, and the overall quality of education.
Arguments For and Against the Proposed Tax Changes
The debate surrounding endowment tax policy is complex, with compelling arguments on both sides. The endowment tax debate centers on fundamental questions of wealth distribution and the role of higher education in society.
- Arguments for Increased Taxes: Proponents argue that taxing large university endowments addresses wealth inequality, makes resources available for public services, and levels the playing field for less-affluent institutions. The argument is that these vast sums of money could be better used to address societal needs.
- Arguments Against Increased Taxes: Opponents argue that taxing endowments undermines academic research, negatively impacts student financial aid, and could stifle innovation. They highlight the importance of these endowments in supporting vital university functions. The pros and cons of endowment tax are intensely debated, highlighting the multifaceted nature of this issue.
Potential Alternatives and Future Implications
The proposed endowment tax changes are not without alternatives. Instead of directly taxing endowments, policymakers could explore alternative solutions to address wealth inequality and fund public services. The future of endowment taxation is likely to involve ongoing debate and potential adjustments.
- Alternative Funding Mechanisms: Exploring alternative funding sources for public services, such as targeted taxes or increased government funding for education, could mitigate the need to directly tax university endowments.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects on university budgets and student access are a critical concern. Reduced funding could lead to increased tuition fees, reduced financial aid, and a potential decrease in the overall quality of education.
- Legal and Political Ramifications: The proposed changes may face legal challenges and could spark significant political debate, potentially altering the final legislation. Understanding the endowment tax alternatives and their ramifications is essential.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Endowment Tax Changes
The proposed endowment tax changes will have a significant impact on institutions like Harvard and Yale, potentially leading to billions of dollars in lost revenue. While some argue that these changes are necessary to address wealth inequality and fund public services, others warn of potential negative consequences for academic research, financial aid, and overall educational quality. The debate surrounding these changes is far from over and will continue to shape the landscape of higher education funding. Stay informed about the evolving landscape of endowment tax changes and advocate for policies that support both equitable wealth distribution and the vitality of higher education. The long-term consequences of these changes will profoundly affect the future of higher education for generations to come.

Featured Posts
-
 Market Rally S And P 500 Up Over 3 Following Trade Deal Progress
May 13, 2025
Market Rally S And P 500 Up Over 3 Following Trade Deal Progress
May 13, 2025 -
 Finansovaya Pomosch Veteranam V Eao V Chest 80 Letiya Pobedy
May 13, 2025
Finansovaya Pomosch Veteranam V Eao V Chest 80 Letiya Pobedy
May 13, 2025 -
 She The Reverse Engineer Of A Trophy Wife Ali Larter Teases Angelas Season 2 Journey
May 13, 2025
She The Reverse Engineer Of A Trophy Wife Ali Larter Teases Angelas Season 2 Journey
May 13, 2025 -
 Refining Credit Processes Walleye Cuts And Core Commodity Group Prioritization
May 13, 2025
Refining Credit Processes Walleye Cuts And Core Commodity Group Prioritization
May 13, 2025 -
 Jay Idzes Tampil Sepanjang Pertandingan Venezia Tahan Imbang Atalanta
May 13, 2025
Jay Idzes Tampil Sepanjang Pertandingan Venezia Tahan Imbang Atalanta
May 13, 2025
