Eurovision Voting System Explained: From Jury To Televoting
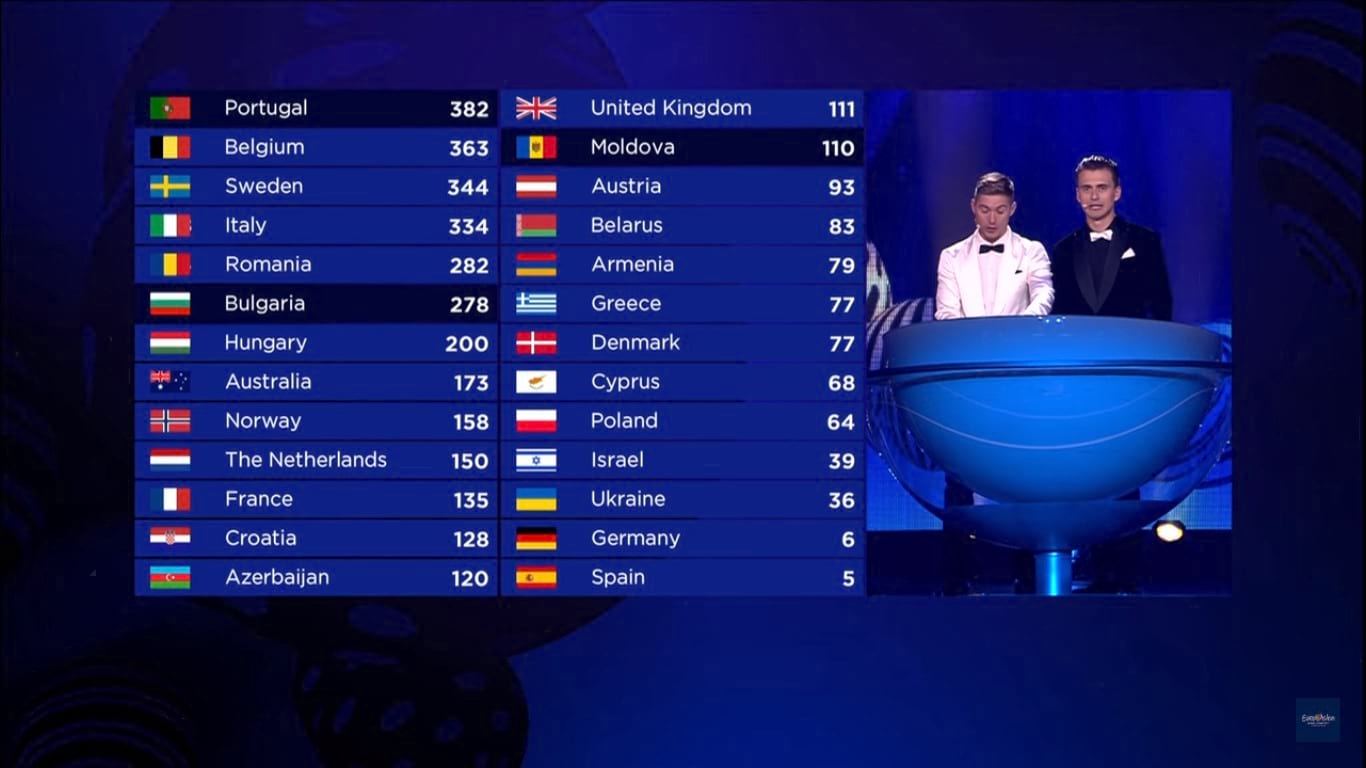
Table of Contents
The Two Pillars of Eurovision Voting: Jury and Televoting
The Eurovision Song Contest's voting system is built on two fundamental pillars: jury voting and televoting. This dual approach aims to balance professional musical opinion with the raw, unfiltered preferences of the viewing public. It's a unique blend designed to ensure a result that reflects both critical acclaim and widespread popularity.
- Jury voting: Brings the expertise of seasoned music professionals to the table, offering a critical evaluation of the performances.
- Televoting: Directly reflects the popularity and public appeal of the competing songs, representing the tastes of millions of viewers across Europe and beyond.
- Combined System: This combined system aims to create a fairer and more representative result than a system relying solely on one method. The intention is to avoid a situation where a critically acclaimed song fails to resonate with the public, or vice versa.
Understanding Jury Voting in the Eurovision Song Contest
Each participating country in the Eurovision Song Contest appoints a professional jury of five music industry experts. These individuals are carefully selected to ensure a diverse range of musical backgrounds and experiences. Their role is crucial in providing a balanced, professional assessment of each performance. The selection process emphasizes impartiality and aims to minimize potential bias or manipulation.
- Jury Composition: Each national jury consists of five members with significant experience in the music industry. This can include composers, singers, producers, and music journalists.
- Scoring Criteria: Juries score each performance based on pre-determined criteria, usually encompassing elements like vocal performance, stage presence, artistic impression, and overall composition. These criteria are designed to be as objective as possible.
- Secrecy and Impartiality: Jury scores are kept strictly confidential until the official announcement, preventing any potential influence or pressure on the results. Strict rules and procedures are in place to address potential conflicts of interest and maintain the integrity of the process. This includes detailed regulations on the jury members’ backgrounds and relationships with participating artists.
Decoding Televoting in the Eurovision Song Contest
Televoting allows viewers in participating countries to directly contribute to the final result, expressing their preference for their favorite acts. This is a significant part of the Eurovision Voting System, reflecting the popularity of each song with the general public. Robust security measures are implemented to ensure fairness and prevent fraudulent voting.
- Voting Methods: Viewers typically vote via telephone, SMS text message, or dedicated Eurovision apps.
- Vote Weighting: Each vote carries equal weight towards the final score, ensuring that every viewer has an equal voice in determining the winner.
- Fraud Prevention: National broadcasters employ various methods to prevent and detect fraudulent voting, including systems to identify and block bulk voting attempts and rigorous monitoring of voting patterns. These measures are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the televoting results.
- Eligibility and Limits: Specific rules regarding eligibility and voting limits (such as the number of votes permitted per phone number) vary by participating country but are designed to prevent undue influence and ensure fair participation.
Regional Voting Patterns in the Eurovision Song Contest
Geographic proximity and cultural affinities often play a significant role in shaping televoting patterns. This is a fascinating aspect of the Eurovision voting system.
- Neighborly Voting: Neighboring countries tend to show a higher propensity to vote for each other, reflecting geographical and cultural ties.
- Cultural Similarities: Songs with similar musical styles or cultural references often receive support from countries with shared cultural backgrounds.
- Bloc Voting: While not explicitly against the rules, instances of bloc voting (where multiple countries coordinate their votes) have been observed and occasionally discussed as a potential strategic element.
Calculating the Final Eurovision Score: The Point System Explained
The final Eurovision score is determined by combining the jury and televoting results for each participating country. This ensures a balanced outcome, reflecting both critical assessment and public opinion.
- Point Allocation: Each country awards points to the top ten performing countries based on a combined ranking from the jury and televoting scores. The points awarded are 12, 10, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1.
- Overall Ranking: The country accumulating the highest total points from all participating countries is declared the winner.
- Rank-Based Points: It's crucial to understand that points are awarded based on the rank of each song in the combined results, not on a numerical score. This means the difference between the first and second-placed songs could vary greatly in terms of points.
Changes and Controversies in the Eurovision Voting System
The Eurovision Voting System has undergone several changes throughout its history. These revisions often aimed to improve fairness, transparency, and the overall integrity of the process.
- System Evolution: Modifications have been introduced over time to address potential issues, enhancing the process's robustness and reliability.
- Past Controversies: While the system aims for objectivity, various controversies concerning specific voting results have arisen over the years, sparking discussions and improvements.
Conclusion
Understanding the Eurovision Voting System, from its jury and televoting components to the final point calculation, enhances the enjoyment of the contest. The combination of professional judgment and popular opinion aims to create a fair and engaging competition. By grasping the intricacies of this system, you can fully appreciate the drama and excitement leading to the crowning of the Eurovision champion. So, delve deeper into the intricacies of the Eurovision Voting System and become a true Eurovision expert!

Featured Posts
-
 Royal Mail Announces 1 70 Price For First Class Stamps
May 19, 2025
Royal Mail Announces 1 70 Price For First Class Stamps
May 19, 2025 -
 Why Interdisciplinary And Transdisciplinary Approaches Matter
May 19, 2025
Why Interdisciplinary And Transdisciplinary Approaches Matter
May 19, 2025 -
 Breeze Airways Announces Two New Routes
May 19, 2025
Breeze Airways Announces Two New Routes
May 19, 2025 -
 Erling Haaland And Man City Mascot Incident Police Statement Expected
May 19, 2025
Erling Haaland And Man City Mascot Incident Police Statement Expected
May 19, 2025 -
 Conoce A Los Aspirantes A Diputados De Nueva Corriente En Las Proximas Elecciones
May 19, 2025
Conoce A Los Aspirantes A Diputados De Nueva Corriente En Las Proximas Elecciones
May 19, 2025
