Fuel Costs Rise: A 20-Cent Increase In Average Gas Prices
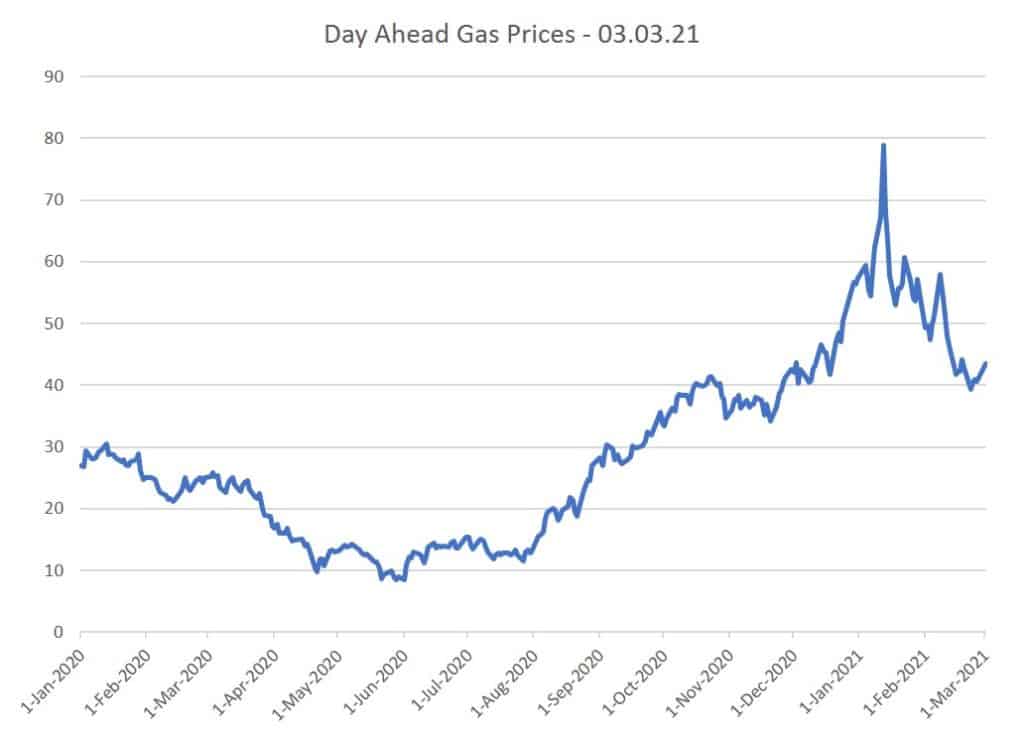
Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the 20-Cent Gas Price Increase
Several interconnected factors have contributed to this substantial 20-cent increase in the average gas price. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial to grasping the current situation and anticipating future trends in fuel costs.
- Increased Crude Oil Prices: Global crude oil prices have experienced a significant surge due to a complex interplay of supply and demand. Reduced oil production by OPEC+ nations, coupled with robust global demand, particularly from recovering economies, has pushed prices higher. This directly impacts the cost of refining gasoline.
- Reduced Refinery Capacity: A decrease in refinery capacity, resulting from maintenance, unexpected shutdowns, or a lack of investment, has limited the production of gasoline. This reduced supply, in the face of consistent demand, exerts upward pressure on prices.
- Increased Gasoline Demand: Seasonal factors, such as increased travel during summer months, along with a generally strong economy, have boosted gasoline demand, exacerbating the impact of reduced supply.
- Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical instability in various oil-producing regions creates uncertainty and volatility in global energy markets, often resulting in price spikes as investors react to potential supply disruptions. The ongoing war in Ukraine is a prime example of a geopolitical factor affecting fuel prices.
- Inflationary Pressures: Broader inflationary pressures are affecting the entire energy sector. Increased costs for transportation, labor, and raw materials used in refining fuel are all contributing to the higher pump prices. This means that even without changes in crude oil prices, the cost of getting gasoline to the consumer is increasing.
Impact of the Fuel Price Hike on Consumers
The 20-cent increase in the average gas price translates directly into a significant financial burden for many consumers. This impact is felt across various aspects of daily life.
- Increased Transportation Costs: Commuters face higher daily expenses, impacting their disposable income. Businesses also experience increased transportation costs, potentially affecting profitability and pricing strategies.
- Reduced Disposable Income: Higher fuel expenses leave less money for other essential goods and services, potentially impacting consumer spending and overall economic activity. This can lead to a decreased quality of life for many families.
- Shift in Consumer Spending Habits: Consumers may adjust their spending patterns, prioritizing essential needs over discretionary purchases. This can have a ripple effect throughout the economy.
- Exacerbation of Inflation: The increased fuel costs contribute to broader inflationary pressures, creating a vicious cycle of rising prices across various sectors.
- Disproportionate Impact on Low-Income Households: Lower-income households are disproportionately affected, as a larger percentage of their income is allocated to transportation costs. This fuel price increase can create significant financial strain.
Strategies for Managing Increased Fuel Costs
While the rising fuel costs are a challenge, consumers can adopt strategies to mitigate their impact.
- Improve Fuel Efficiency: Maintaining proper tire inflation, ensuring regular car maintenance (including timely oil changes and tune-ups), and avoiding aggressive driving habits (such as rapid acceleration and braking) can significantly improve fuel efficiency and reduce fuel consumption.
- Explore Alternative Transportation: Consider using public transportation, carpooling, cycling, or walking whenever feasible. This can substantially reduce reliance on personal vehicles and associated fuel expenses.
- Cost-Effective Driving Habits: Plan routes efficiently to minimize mileage, avoid unnecessary trips, and consolidate errands to reduce overall fuel consumption.
- Smart Fuel Purchases: Utilize fuel reward programs, compare prices at different gas stations, and refuel when prices are lower to save money. Consider using gas station apps to locate the cheapest fuel in your area.
Government Response and Future Outlook on Gas Prices
Governments are closely monitoring the situation and may implement policies to address the impact of rising fuel costs. The future outlook on gas prices remains uncertain.
- Potential Government Interventions: Governments might consider measures like fuel subsidies, tax relief, or strategic reserves to stabilize prices and alleviate the burden on consumers.
- Future Supply and Demand Projections: Analysts will be closely monitoring global crude oil production, economic growth, and geopolitical factors to project future supply and demand dynamics.
- Expert Opinions: Energy experts and economists offer varying predictions on the long-term trajectory of gas prices, influenced by factors like technological advancements in renewable energy and global political developments.
Conclusion
The 20-cent increase in average gas prices represents a significant challenge for consumers and the economy. Understanding the underlying causes—from rising crude oil prices and reduced refinery capacity to geopolitical instability and inflation—is key to navigating this situation. By implementing fuel-saving strategies and staying informed about government policies and future price predictions, individuals can better manage their fuel budgets and prepare for potential future fluctuations in gas prices. Stay informed about fluctuating gas prices and take control of your fuel budget by implementing the fuel-saving tips outlined above. [Link to a relevant resource, e.g., a fuel price tracking website]

Featured Posts
-
 Occasionmarkt Bloeit Abn Amro Registreert Aanzienlijke Verkoopstijging
May 22, 2025
Occasionmarkt Bloeit Abn Amro Registreert Aanzienlijke Verkoopstijging
May 22, 2025 -
 Watercolor Themed Play Script Review Promising New Talent
May 22, 2025
Watercolor Themed Play Script Review Promising New Talent
May 22, 2025 -
 Employee Quits Pub Landlord Unleashes Profanity Filled Tirade
May 22, 2025
Employee Quits Pub Landlord Unleashes Profanity Filled Tirade
May 22, 2025 -
 El Virus Fifa Agota A La Real Sociedad Calendario Infernal Sin Respiro
May 22, 2025
El Virus Fifa Agota A La Real Sociedad Calendario Infernal Sin Respiro
May 22, 2025 -
 Abn Amro Sterke Stijging Occasionverkopen Door Toename Autobezit
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Sterke Stijging Occasionverkopen Door Toename Autobezit
May 22, 2025
