G-7 To Debate Lowering De Minimis Tariffs On Chinese Imports
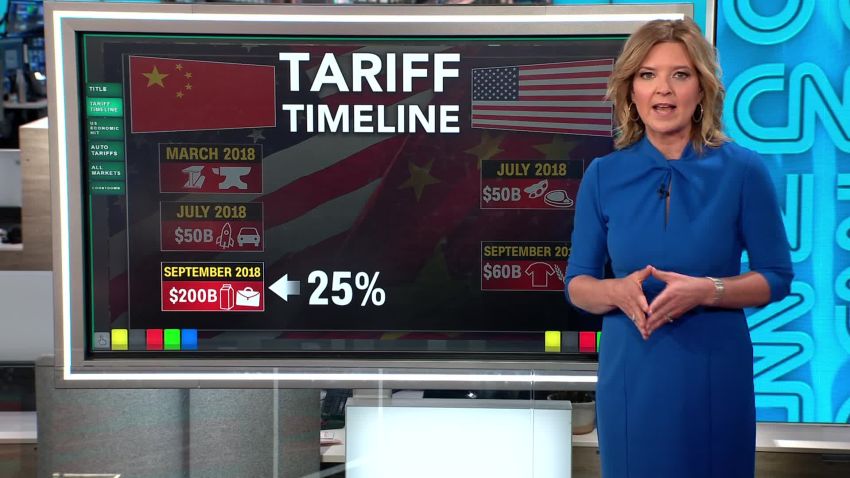
Table of Contents
Current State of De Minimis Tariffs on Chinese Imports
Currently, G7 nations maintain varying levels of de minimis tariffs on goods imported from China. These tariffs, which exempt small shipments from customs duties, significantly impact the flow of goods, particularly for smaller businesses engaging in e-commerce. The current system often results in unpredictable costs and administrative burdens, especially for those dealing with a high volume of smaller shipments.
- Current tariff rates for different product categories: Rates vary considerably depending on the product category, with some goods facing higher tariffs than others. This inconsistency creates complexity for importers and exporters.
- Examples of businesses affected by the current system: E-commerce businesses, small retailers importing goods from China, and individual consumers ordering goods online are all significantly affected by the current de minimis tariff structure.
- Statistics illustrating the volume of imports affected: A significant portion of consumer goods and smaller business imports from China fall under the de minimis threshold. Precise figures vary between G7 nations, but the volume is substantial.
Arguments for Lowering De Minimis Tariffs
Advocates for lowering de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports argue that the change would unlock significant economic benefits. Reduced tariffs are projected to stimulate economic activity and increase overall trade.
- Increased consumer choice and lower prices for consumers: Lower tariffs could translate to lower prices for consumers, offering them access to a wider range of goods from China. This increased competition benefits consumers directly.
- Boost to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) importing from China: Lowering tariffs removes a significant barrier to entry for SMEs, allowing them to compete more effectively with larger businesses and access cheaper goods for resale or production.
- Enhanced competitiveness for businesses operating within the G7 nations: Access to cheaper imported goods could reduce businesses’ input costs, boosting their competitiveness in the global marketplace.
- Potential for increased trade volume between G7 and China: Simplified import processes and reduced tariffs incentivize increased trade between the G7 and China, benefiting both economies.
Concerns Regarding Lowering Tariffs
Despite the potential benefits, concerns remain about the potential drawbacks of reducing de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods.
- Impact on domestic industries and potential job losses: Lowering tariffs could lead to increased competition from Chinese imports, potentially impacting domestic industries and leading to job losses in certain sectors.
- Concerns about unfair trade practices and intellectual property theft: Reducing tariffs without addressing concerns about unfair trade practices and intellectual property rights could exacerbate existing issues and harm G7 businesses.
- Risks associated with increased reliance on Chinese imports: An over-reliance on Chinese imports could create vulnerabilities in global supply chains and increase economic dependence on a single nation.
- Potential for increased trade deficits: Lowering tariffs could lead to an increase in imports from China, potentially widening trade deficits for some G7 nations.
Potential Impacts on Global Trade
The G7's decision on de minimis tariffs will have significant ripple effects on global trade.
- Ripple effects on other trading partners: Other countries may respond to the G7's decision, potentially leading to a wider shift in global trade policies.
- Possible responses from other nations: Competitor nations might adjust their own tariff policies in response to the G7's actions, triggering a chain reaction across the global trade system.
- Influence on global supply chains: The change could significantly reshape global supply chains, influencing sourcing decisions for businesses worldwide.
- Impact on international trade negotiations: The G7's decision will likely influence future international trade negotiations and agreements.
The G7’s Decision-Making Process
The G7's decision-making process will involve extensive discussions and negotiations among member nations.
- Timeline for discussions and potential outcomes: The timeline for reaching a decision is uncertain, but the implications are significant, requiring careful consideration.
- Key players involved in the decision-making process: Various government agencies, trade representatives, and economic advisors will play crucial roles in shaping the final decision.
- Factors that will likely influence the final decision: Economic forecasts, domestic political pressures, and concerns about fair trade practices will all play a significant role.
Conclusion
The G7's debate on lowering de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports presents a complex balancing act between economic benefits and potential risks. While reduced tariffs could lead to lower prices and increased trade, concerns about domestic industries and fair trade practices remain significant. The outcome will have major implications for global trade dynamics.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the G7's decision regarding de minimis tariffs on Chinese imports. Understanding the implications of changes to these tariffs is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. Further research into the potential effects of altering de minimis tariffs is essential for informed decision-making. The impact of any adjustments to de minimis tariff levels will be substantial, demanding careful consideration of all potential consequences.

Featured Posts
-
 Kazuo Ishiguro An Exploration Of Memory And Forgetting
May 26, 2025
Kazuo Ishiguro An Exploration Of Memory And Forgetting
May 26, 2025 -
 The Naomi Campbell Anna Wintour Rift Will It Impact The 2025 Met Gala
May 26, 2025
The Naomi Campbell Anna Wintour Rift Will It Impact The 2025 Met Gala
May 26, 2025 -
 Rtl Laurence Melys Et L Avenir Du Cyclisme Feminin
May 26, 2025
Rtl Laurence Melys Et L Avenir Du Cyclisme Feminin
May 26, 2025 -
 Delaware Governors Warning Identifying And Confronting Fascism In A Post Trump Era
May 26, 2025
Delaware Governors Warning Identifying And Confronting Fascism In A Post Trump Era
May 26, 2025 -
 Guide Pour Comprendre Les Gens D Ici
May 26, 2025
Guide Pour Comprendre Les Gens D Ici
May 26, 2025
