Glacier Collapse In Switzerland: Mudslide Buries Village, One Missing
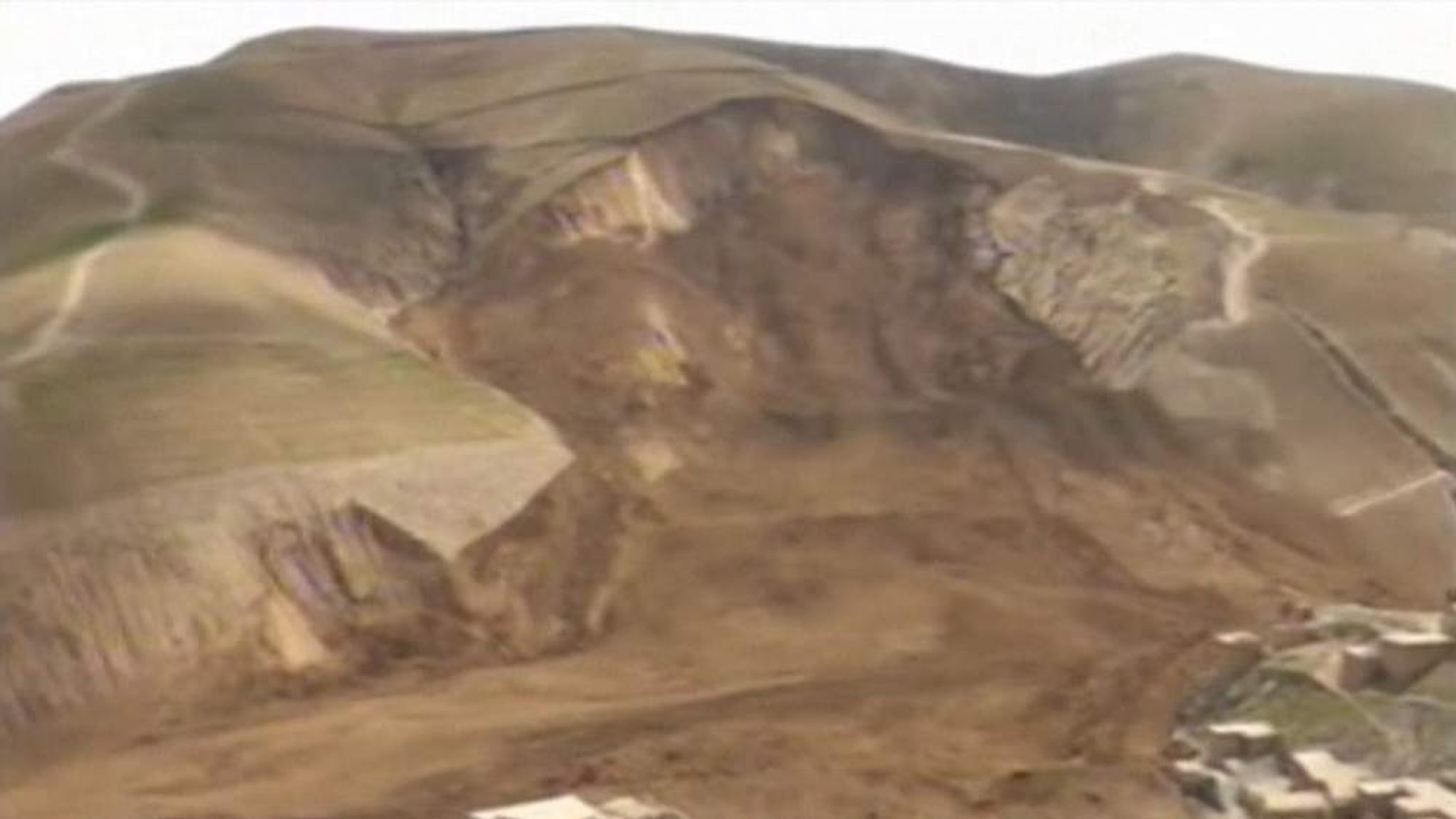

Table of Contents
The Impact of the Glacier Collapse
The immediate aftermath of the glacier collapse was catastrophic. A massive mudslide, a torrent of ice, rock, and water, surged down the mountainside, engulfing everything in its path. The force of the debris flow was immense, leaving behind a scene of utter devastation. The specific impacts included:
- Homes Destroyed: Numerous homes were completely destroyed or rendered uninhabitable, leaving many residents homeless and displaced.
- Roads and Bridges Impassable: Critical infrastructure, including roads and bridges, was severely damaged or completely destroyed, hindering rescue efforts and access to the affected area.
- Power Outages: The power grid suffered significant damage, leading to widespread power outages across the village and surrounding regions.
- Communication Disruptions: Communication lines were severed, hampering rescue coordination and the flow of information to the outside world.
Beyond the immediate human cost, the environmental impact is also severe. The mudslide has significantly altered the local ecosystem, damaging precious flora and fauna in the Alpine region. The long-term consequences for the delicate balance of this mountain environment remain to be seen. This natural disaster underscores the fragility of these ecosystems in the face of climate change.
Search and Rescue Efforts
Following the glacier collapse, a massive search and rescue operation was immediately launched. Helicopters, search dogs, and numerous emergency service personnel from across Switzerland have been deployed to locate the missing person and assist those affected. However, the treacherous terrain, unstable conditions, and the sheer volume of debris pose significant challenges to rescuers. The ongoing efforts are hampered by:
- Unstable Terrain: The risk of further landslides and the unstable nature of the debris field make rescue efforts extremely dangerous.
- Hazardous Conditions: The mudslide has created hazardous conditions, including potential hazards such as unstable ground and submerged debris.
- Difficult Access: The damaged roads and bridges are severely limiting access to the affected areas, hindering the delivery of supplies and personnel.
While many have been rescued and treated for injuries, the focus remains on locating the one missing individual. The unwavering dedication of the rescue teams provides a glimmer of hope amidst the devastation. This disaster relief effort showcases the resilience and commitment of the Swiss emergency services.
Causes and Contributing Factors
The devastating glacier collapse in Switzerland raises serious questions about the underlying causes and contributing factors. While investigations are ongoing, several factors strongly suggest a link to climate change:
- Climate Change and Global Warming: Rising global temperatures are accelerating glacial melt, destabilizing the mountains and increasing the risk of glacier collapses and landslides.
- Increased Glacial Melt: The accelerated melting of glaciers weakens their structure, making them more prone to collapse.
- Permafrost Thaw: The thawing of permafrost, the permanently frozen ground that anchors glaciers, removes crucial support and contributes to instability.
- Geological Instability: The inherent geological instability of the Alpine region further compounds the risk, creating a perfect storm for such catastrophic events.
Scientific research clearly links these factors to an increased frequency and severity of glacial hazards in the Alps. Understanding these causes is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Long-Term Impacts and Prevention
The long-term impacts of this Swiss glacier disaster will be far-reaching. The affected village faces a lengthy recovery process, requiring substantial investment in rebuilding homes, infrastructure, and restoring the local economy. Beyond immediate recovery, long-term prevention strategies are critical:
- Early Warning Systems: Developing advanced early warning systems to detect signs of glacial instability is crucial for mitigating future risks.
- Improved Infrastructure: Building more resilient infrastructure, capable of withstanding extreme events, is vital for protecting communities in high-risk areas.
- Land-Use Planning: Careful land-use planning can help minimize development in high-risk zones and protect vulnerable communities.
- Increased Monitoring: Regular and comprehensive monitoring of glaciers in the region is essential to identify potential hazards early on.
These preventative measures will be crucial in enhancing climate resilience and building a safer future for communities living in the shadow of the Alps. Investing in disaster preparedness and risk mitigation is not just a matter of cost but a moral imperative.
Conclusion: Learning from the Swiss Glacier Collapse
The devastating glacier collapse in Switzerland serves as a stark reminder of the impact of climate change and the urgent need for action. The scale of the destruction, the human cost, and the environmental consequences highlight the critical need for improved disaster preparedness, proactive risk assessment, and sustained efforts to mitigate the effects of global warming. This event, a catastrophic example of Swiss glacier disasters, should galvanize us all to confront the challenges posed by a changing climate. Stay informed about the ongoing situation surrounding the devastating glacier collapse in Switzerland and consider supporting organizations dedicated to disaster relief and climate change mitigation. Understanding the impact of glacier collapse is crucial for building a more resilient future.

Featured Posts
-
 Hanouna Et Le Pen Verdict D Appel Attendu En 2026 Jacobelli S Exprime
May 30, 2025
Hanouna Et Le Pen Verdict D Appel Attendu En 2026 Jacobelli S Exprime
May 30, 2025 -
 Affaire Rn Le Jugement En Appel Et La Rapidite De La Justice
May 30, 2025
Affaire Rn Le Jugement En Appel Et La Rapidite De La Justice
May 30, 2025 -
 Is A Single Unknown Respiratory Virus The Cause Of Kawasaki Disease New Data Suggests A Link
May 30, 2025
Is A Single Unknown Respiratory Virus The Cause Of Kawasaki Disease New Data Suggests A Link
May 30, 2025 -
 Madrid Open Draper Through To First Clay Court Final
May 30, 2025
Madrid Open Draper Through To First Clay Court Final
May 30, 2025 -
 19 Mars 2025 Ecouter L Integrale D Europe 1 Soir
May 30, 2025
19 Mars 2025 Ecouter L Integrale D Europe 1 Soir
May 30, 2025
