Grim Retail Sales Data: Implications For Bank Of Canada Interest Rates
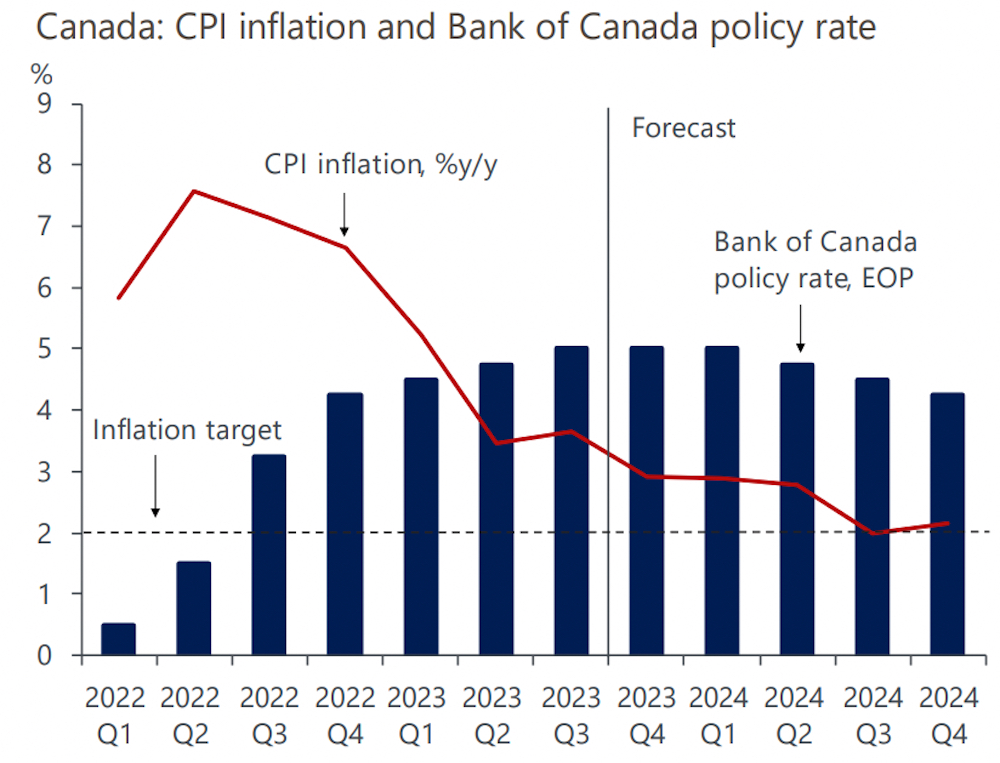
Table of Contents
Weak Retail Sales Indicate Slowing Economic Growth
The recent decline in retail sales figures points towards a slowing Canadian economy. Data released by Statistics Canada (replace with actual source and data) showed a [specific percentage]% drop in retail sales in [Month, Year], compared to [previous month/year]. This significant decrease follows a pattern of weakening consumer spending, raising concerns about overall economic health and GDP growth. The correlation between retail sales and GDP is strong; when consumer spending falters, it often reflects broader economic weakness.
- Specific percentage decline in retail sales: [Insert specific data from reliable source, e.g., a 1.5% decrease].
- Comparison to previous months/years: [Compare the current decline to previous periods, highlighting any significant changes].
- Impact on various retail sectors: The decline wasn't uniform across all sectors. [Mention specific sectors significantly impacted, e.g., a steeper drop in sales of big-ticket items like furniture and electronics compared to groceries].
- Factors contributing to the decline: Several factors contribute to this decline, including persistently high inflation, previous interest rate hikes by the Bank of Canada, and a general reduction in consumer confidence. The erosion of purchasing power is a key driver.
Inflation's Persistent Grip and its Influence on Consumer Spending
Persistent inflation continues to significantly impact consumer spending. Canada's current inflation rate stands at [insert current inflation rate and source], significantly impacting consumers' purchasing power. The rising cost of essential goods and services, like groceries and energy, forces consumers to cut back on discretionary spending. This reduction in spending across various retail sectors directly reflects the strain on household budgets caused by inflation.
- Current inflation rate in Canada: [Insert current CPI data with source].
- Impact of inflation on specific goods and services: [Give specific examples, e.g., the increased price of gasoline, food, and housing].
- How inflation affects consumer confidence and spending habits: High inflation erodes consumer confidence, leading to a more cautious approach to spending. Consumers delay major purchases and prioritize essential goods, further depressing retail sales.
The Bank of Canada's Dilemma: Inflation vs. Economic Growth
The Bank of Canada faces a difficult balancing act. While aiming to curb inflation, it must also avoid triggering a significant economic slowdown or recession. The grim retail sales data complicates this task. Further interest rate hikes, while potentially effective in controlling inflation, risk further dampening consumer spending and potentially pushing the economy into a recession. Conversely, pausing or cutting rates risks allowing inflation to become entrenched.
- Possible scenarios for future interest rate adjustments: The Bank of Canada might opt for a smaller interest rate hike, a pause, or even a rate cut, depending on upcoming economic data and inflation trends.
- Risks of further interest rate hikes: Aggressive rate hikes could exacerbate the economic slowdown, leading to job losses and a potential recession.
- Potential for a pause or even a rate cut: A pause or rate cut would signal a shift towards supporting economic growth, but risks allowing inflation to persist at elevated levels.
- Discussion of the "soft landing" scenario and its likelihood: The Bank of Canada aims for a "soft landing," where inflation is controlled without triggering a significant recession. The likelihood of achieving this soft landing, given the current economic indicators, is uncertain and debated among economists.
Potential Future Impacts of Grim Retail Sales Data
The weak retail sales data has far-reaching consequences beyond simply impacting retailers. The ripple effects could significantly impact various sectors of the Canadian economy.
- Potential impact on employment and job losses: A prolonged slowdown in consumer spending could lead to job losses across various sectors, particularly in retail, hospitality, and related industries.
- Effects on the housing market: Reduced consumer confidence and higher interest rates could further depress the housing market, potentially leading to further price declines and impacting mortgage rates.
- Influence on the Canadian dollar's exchange rate: A weakening economy can lead to a depreciation of the Canadian dollar against other major currencies.
Conclusion
The grim retail sales data underscores a slowing Canadian economy, presenting a significant challenge for the Bank of Canada. The interplay between inflation control and economic growth necessitates careful consideration in upcoming interest rate decisions. The Bank's actions will significantly shape the future trajectory of the Canadian economy. Stay informed about the evolving situation by regularly checking for updates on grim retail sales data and its implications for Bank of Canada interest rates. Understanding these economic indicators is vital for making informed financial decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 From Railroad To Overwater Highway A Florida Keys Road Trip
Apr 28, 2025
From Railroad To Overwater Highway A Florida Keys Road Trip
Apr 28, 2025 -
 The Red Sox 2025 Outfield A Deep Dive Into Espns Projection
Apr 28, 2025
The Red Sox 2025 Outfield A Deep Dive Into Espns Projection
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Open Ais Chat Gpt An Ftc Investigation And Its Potential Consequences
Apr 28, 2025
Open Ais Chat Gpt An Ftc Investigation And Its Potential Consequences
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Unexpected Encounter Trump And Zelensky Meet Before Popes Funeral
Apr 28, 2025
Unexpected Encounter Trump And Zelensky Meet Before Popes Funeral
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Deportation Case Of Harvard Researcher Headed To Louisiana Court
Apr 28, 2025
Deportation Case Of Harvard Researcher Headed To Louisiana Court
Apr 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 75
Apr 28, 2025
75
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Universal Tone Tecno
Apr 28, 2025
Universal Tone Tecno
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Tecno Universal Tone
Apr 28, 2025
Tecno Universal Tone
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Boston Red Sox Lineup Modifications For Doubleheaders First Game
Apr 28, 2025
Boston Red Sox Lineup Modifications For Doubleheaders First Game
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Red Sox Game 1 Lineup Coras Minor Adjustments
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Game 1 Lineup Coras Minor Adjustments
Apr 28, 2025
