Grocery Inflation: A Three-Month Trend Of Price Increases
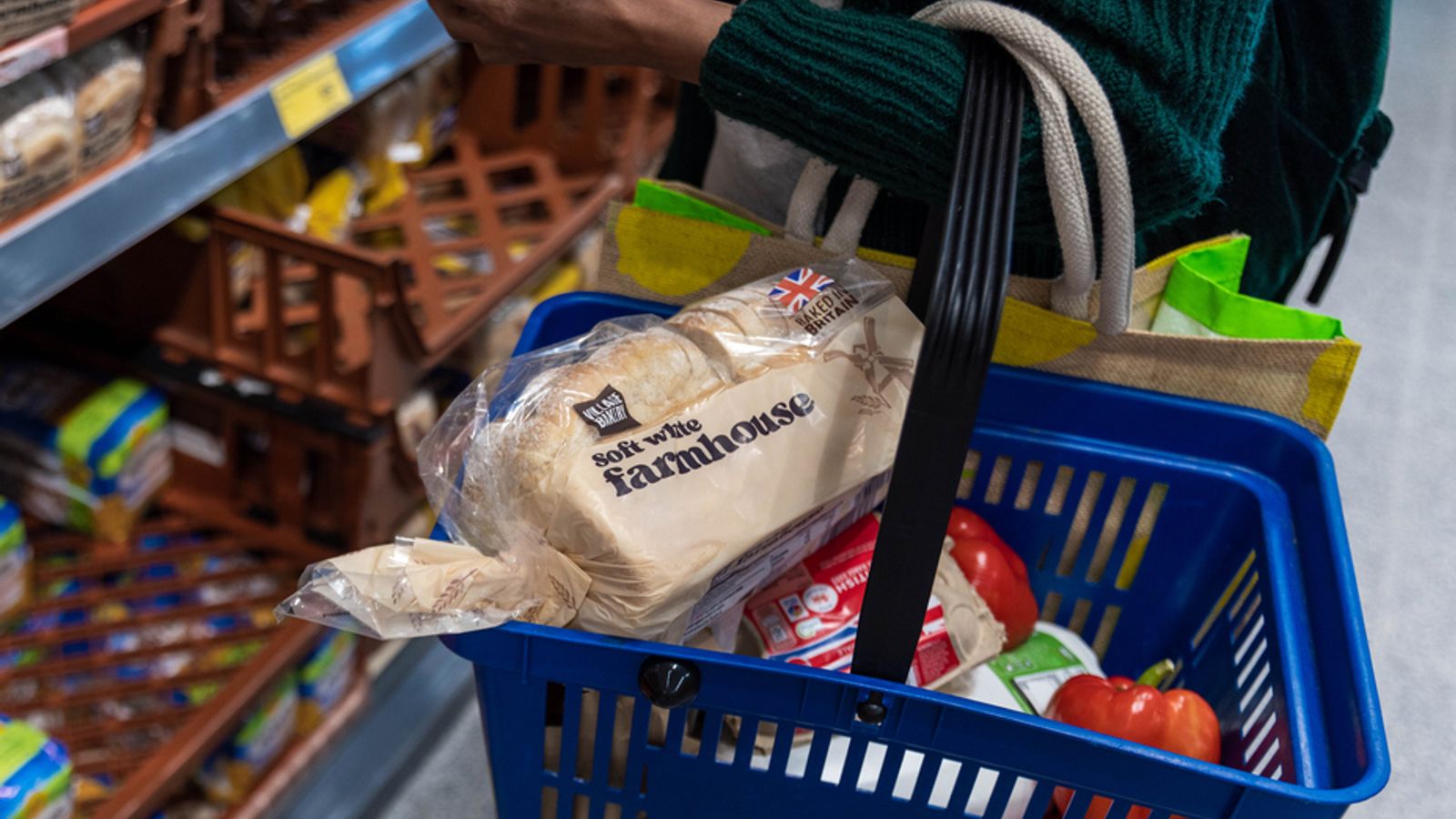

Table of Contents
Key Drivers of Grocery Inflation (past three months):
Several interconnected factors have contributed to the sharp increase in grocery prices over the last three months. Understanding these drivers is crucial to mitigating their impact on your finances.
Rising Energy Costs:
Increased fuel prices have rippled through the entire food system, significantly impacting grocery inflation. Higher energy costs affect every stage of food production and delivery.
- Increased fuel costs for farming equipment: Farmers rely heavily on fuel for tractors, harvesters, and other machinery. Higher fuel prices directly translate to higher production costs.
- Transportation of goods: Getting food from farms to processing plants and finally to grocery stores requires significant fuel consumption. The increase in fuel costs increases transportation costs, which are then passed on to consumers.
- Energy used in processing plants: Food processing plants are energy-intensive, using significant amounts of electricity and gas. Rising energy prices increase the cost of processing, adding to the final price of the goods.
- Impact on perishable goods: The increased cost of transportation especially impacts perishable goods with shorter shelf lives, as faster and more expensive transportation methods may be required to prevent spoilage.
Keywords: Energy prices, fuel costs, transportation costs, food production, supply chain disruptions, perishable goods
Supply Chain Disruptions:
Lingering effects from the pandemic and other global events continue to disrupt food supply chains, contributing to grocery inflation. These disruptions cause shortages and increased costs.
- Labor shortages: The food industry, like many others, faces labor shortages, impacting production, processing, and transportation.
- Port congestion: Delays in shipping and port congestion lead to increased costs and potential shortages of imported food products.
- Packaging material shortages: Shortages of essential packaging materials like cardboard and plastic increase production costs.
- Impact on import/export of food products: Global supply chain issues affect the availability and price of imported foods. For example, delays in importing certain fruits or spices can lead to price hikes.
Keywords: Supply chain issues, logistics, labor shortages, global supply chain, import/export, food shortages
Increased Demand & Consumer Behavior:
Changes in consumer behavior and increased demand for certain products have also contributed to grocery inflation.
- Shifting consumer preferences: Increased demand for specific items, perhaps driven by trends or changing dietary habits, can lead to price increases for those goods.
- Impact of inflation on overall purchasing power: As overall inflation increases, consumers may stockpile certain items, leading to temporary shortages and increased prices.
Keywords: Consumer demand, purchasing power, consumer behavior, food trends, inflation impact
Impact of the War in Ukraine:
The ongoing war in Ukraine has had a significant global impact on food prices. Ukraine and Russia are major exporters of several key food commodities.
- Ukraine and Russia as major exporters of wheat, corn, and sunflower oil: The disruption of exports from these countries has led to global shortages and price increases for these essential food products.
- Impact on global food security and prices: The conflict has created significant uncertainty in global food markets, affecting prices worldwide.
- Alternative sourcing strategies and their limitations: Countries are seeking alternative sources for these commodities, but these alternatives often come at a higher cost and may not fully compensate for the shortfall.
Keywords: Geopolitical instability, Ukraine conflict, food security, grain prices, vegetable oil prices, global food markets
Specific Examples of Price Increases (past three months):
Over the past three months, consumers have witnessed significant price hikes in various grocery staples. While specific percentages vary by region and retailer, some notable examples include:
- Eggs: Egg prices have seen dramatic increases due to a combination of avian flu outbreaks and rising feed costs. Increases of 30-50% have been reported in some areas.
- Meat: Beef, pork, and poultry prices have all increased due to rising feed costs, labor shortages, and transportation issues.
- Dairy: Milk and cheese prices have also risen, reflecting increased feed costs and transportation expenses.
- Bread: The cost of wheat, a primary ingredient in bread, has increased, leading to higher bread prices.
- Vegetable Oils: Prices for sunflower oil, a major cooking oil, have increased significantly due to the disruption of exports from Ukraine.
Keywords: Grocery prices, food price increases, specific food item inflation (e.g., egg prices, meat prices), dairy prices, bread prices
Strategies for Managing Grocery Inflation:
While you can't control rising grocery prices, you can control how you respond to them. Implementing these strategies can help you mitigate the impact on your budget.
Budget Planning and Meal Planning:
Creating a detailed grocery budget and meal planning are essential tools for managing grocery inflation.
- Tips for creating a grocery budget: Track your spending for a few weeks to identify areas where you can cut back. Set a realistic budget and stick to it.
- Meal planning strategies: Plan your meals for the week to avoid impulse purchases and reduce food waste.
- Utilizing leftovers: Get creative with leftovers to minimize food waste and stretch your grocery budget further.
- Utilizing coupons and loyalty programs: Take advantage of store coupons and loyalty programs to save money.
Keywords: Budget planning, meal planning, grocery budget, couponing, food waste, saving money on groceries
Smart Shopping Habits:
Implementing smart shopping habits can help you maximize your grocery budget.
- Comparison shopping: Compare prices at different stores before making purchases.
- Buying in bulk (consider storage): Buying in bulk can sometimes save money, but only if you have adequate storage space and will use the items before they expire.
- Choosing store brands: Store brands often offer similar quality at a lower price than name brands.
- Utilizing sales and discounts: Take advantage of sales and discounts to save money on your groceries.
- Avoiding impulse buys: Stick to your shopping list to avoid unnecessary purchases.
Keywords: Smart shopping, grocery shopping tips, saving money, comparison shopping, bulk buying, store brands
Conclusion:
Grocery inflation continues to impact household budgets significantly. The past three months have shown a concerning trend of rising food prices driven by a complex interplay of factors, from soaring energy costs and supply chain disruptions to geopolitical instability. By understanding these drivers and adopting smart shopping strategies and budget planning, consumers can better navigate this challenging economic landscape. Stay informed about grocery inflation trends and adjust your spending accordingly to manage your grocery budget effectively. Don't let grocery inflation control your finances; take control with proactive planning and smart shopping habits.

Featured Posts
-
 Adam Ramey Dropout Kings Vocalist Dies Aged 31
May 22, 2025
Adam Ramey Dropout Kings Vocalist Dies Aged 31
May 22, 2025 -
 Vybz Kartel Opens Up Skin Bleaching And The Search For Self Acceptance
May 22, 2025
Vybz Kartel Opens Up Skin Bleaching And The Search For Self Acceptance
May 22, 2025 -
 Nyt Wordle Solution For March 26 How To Solve Todays Wordle
May 22, 2025
Nyt Wordle Solution For March 26 How To Solve Todays Wordle
May 22, 2025 -
 Cwd Found In Jackson Hole Elk Understanding The Risks
May 22, 2025
Cwd Found In Jackson Hole Elk Understanding The Risks
May 22, 2025 -
 Wordle 370 Solution Hints And Clues For Thursday March 20th
May 22, 2025
Wordle 370 Solution Hints And Clues For Thursday March 20th
May 22, 2025
