How Climate Change Impacts Your Ability To Buy A Home: Understanding Credit Risk
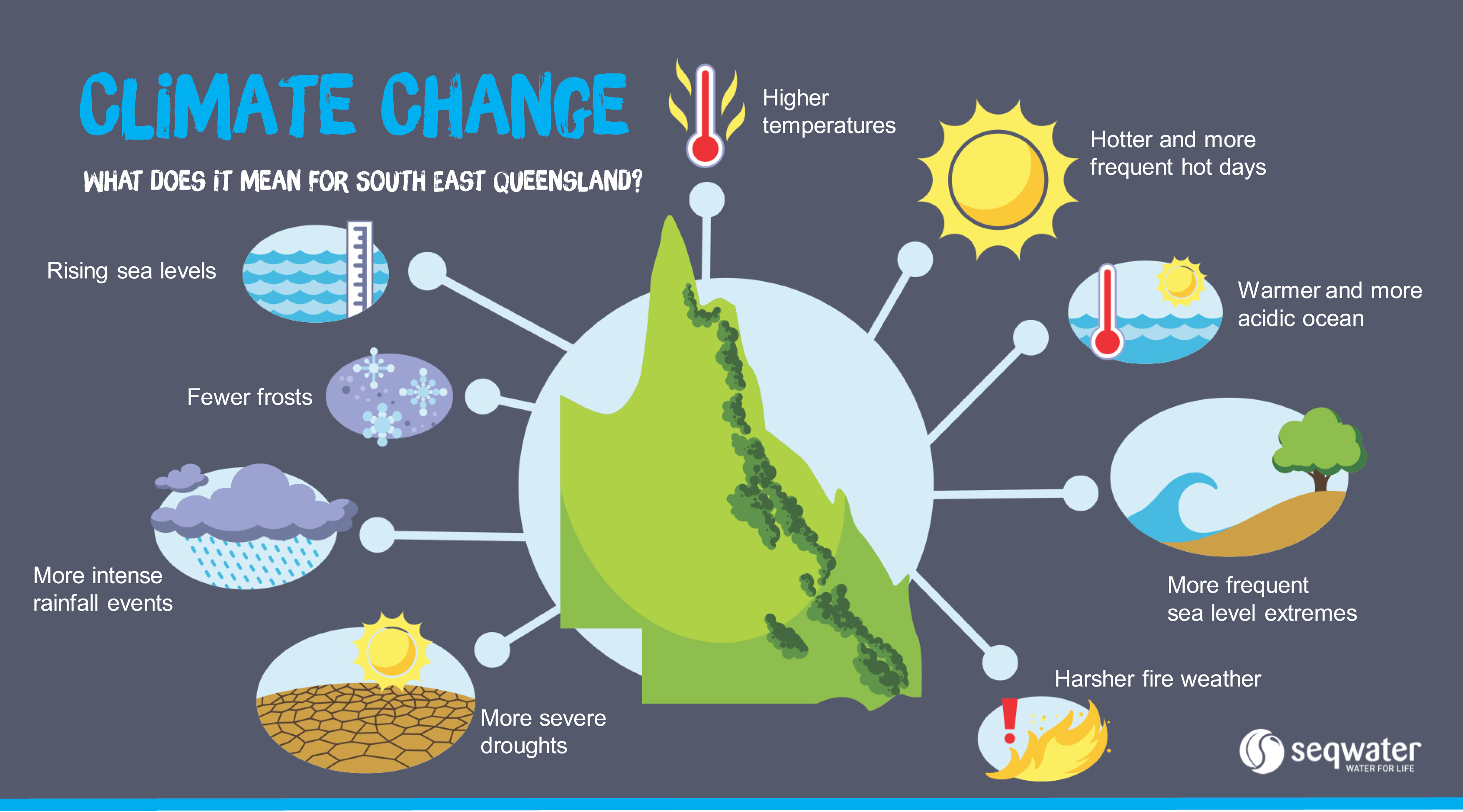
Table of Contents
Increased Home Insurance Premiums & Credit Scores
Climate change significantly increases the risk of damage to properties. More frequent and intense flooding, wildfires, hurricanes, and other extreme weather events directly translate to higher risks for insurers. In response, insurers are raising premiums in areas deemed high-risk, often dramatically so. This increase in home insurance premiums has a direct impact on a borrower's ability to secure a mortgage.
- Higher premiums directly increase monthly housing costs. This impacts your debt-to-income ratio (DTI), a crucial factor lenders use to assess your ability to repay a loan. A higher DTI reduces your chances of approval.
- High premiums can lead to loan denial due to exceeding DTI limits. Lenders have strict DTI thresholds; exceeding them due to inflated insurance costs can disqualify you from a mortgage.
- Some lenders may consider high insurance premiums a credit risk factor. The increased financial burden suggests a higher likelihood of default, making lenders more hesitant to approve your application. This is particularly true for properties in areas frequently affected by climate-related disasters. Your credit score, while not directly affected by the insurance premiums themselves, can be indirectly impacted by the resulting loan application denial.
Property Value Depreciation Due to Climate Risk
The perceived risk of climate-related damage significantly impacts property values. Properties in areas prone to flooding, wildfires, or extreme heat waves may depreciate faster than those in safer locations. This depreciation is a serious concern for lenders, as property value serves as collateral for the mortgage.
- Properties in high-risk areas may lose value faster than others. This decrease in value is reflected in appraisals, potentially impacting your loan-to-value (LTV) ratio.
- Lenders are more cautious when lending on properties with depreciating values. A lower property value increases the lender's risk, potentially leading to stricter lending requirements.
- Lower LTV ratios can lead to higher down payment requirements or loan denials. To mitigate their risk, lenders may require a larger down payment or deny the loan altogether if the LTV ratio is too high. Understanding this climate-driven devaluation is critical to your home-buying strategy.
Increased Frequency of Natural Disasters and Loan Defaults
The increasing frequency and severity of climate-related disasters directly increase the likelihood of loan defaults. When a natural disaster strikes, homeowners may be unable to make mortgage payments due to damage, displacement, or job loss. This trend is forcing lenders to reassess their risk profiles.
- More frequent disasters lead to higher claims and increased lender losses. This directly impacts the cost of lending and encourages a more conservative approach to mortgage approvals.
- Lenders are developing more sophisticated risk assessment models. These models incorporate climate data and risk assessments to better understand the long-term implications of lending in vulnerable areas.
- Borrowers in high-risk areas may face stricter lending requirements or higher interest rates. Lenders might require larger down payments, higher credit scores, or charge higher interest rates to offset the increased risk associated with properties in climate-vulnerable zones.
Government Regulations and Climate-Related Disclosure
Government regulations concerning climate risk disclosure in the mortgage industry are evolving rapidly. This means increased transparency about climate risks for both lenders and borrowers. This transparency should help borrowers make informed decisions.
- Increased transparency about climate risks helps borrowers make informed decisions. This includes access to flood maps, wildfire risk assessments, and other crucial data related to climate vulnerability.
- New regulations may lead to stricter lending practices in vulnerable areas. This might include more stringent underwriting criteria or limitations on lending in certain high-risk zones.
- Understanding climate-related disclosures is crucial for responsible homeownership. It's essential to actively research and understand the climate risks associated with a property before making a purchase.
Conclusion
Climate change is significantly impacting the ability to buy a home. The increased insurance premiums, property value depreciation, and stricter lending practices resulting from climate-related disasters represent major hurdles in the home-buying process. Understanding how climate change impacts your ability to buy a home is crucial. Increased insurance costs, potential property devaluation, and stricter lending criteria all stem from escalating climate risks. Before you begin your home search, research climate risks in your desired location thoroughly. Consult flood maps, wildfire risk assessments, and other relevant resources to make an informed decision. Take the time to assess your climate risk and plan accordingly.

Featured Posts
-
 Sezon Baslamadan Sok Ayrilik Tadic Fenerbahce Ye Veda Etti
May 20, 2025
Sezon Baslamadan Sok Ayrilik Tadic Fenerbahce Ye Veda Etti
May 20, 2025 -
 Dusan Tadic In Sueper Lig Yolculugu 100 Macin Hikayesi
May 20, 2025
Dusan Tadic In Sueper Lig Yolculugu 100 Macin Hikayesi
May 20, 2025 -
 Henriksen The Mainz Manager Charting A New Course After Klopp And Tuchel
May 20, 2025
Henriksen The Mainz Manager Charting A New Course After Klopp And Tuchel
May 20, 2025 -
 1 Reason To Buy This Ai Quantum Computing Stock Now
May 20, 2025
1 Reason To Buy This Ai Quantum Computing Stock Now
May 20, 2025 -
 Complete Answers Nyt Mini Crossword March 31
May 20, 2025
Complete Answers Nyt Mini Crossword March 31
May 20, 2025
