Insufficient Rainfall In March: Water Deficit Continues
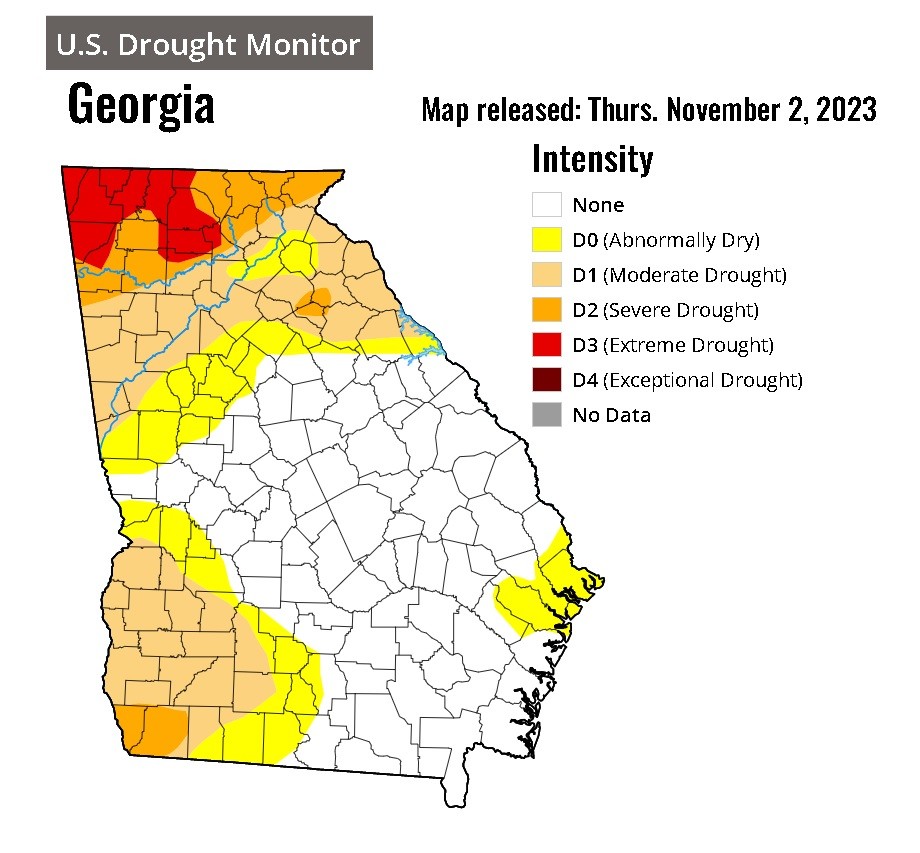
Table of Contents
Impact on Agriculture
The lack of rainfall in March has severely impacted agricultural production, creating a ripple effect throughout the food system. Many crops are experiencing significant water stress, leading to reduced yields and potential food shortages. This agricultural drought is placing immense pressure on farmers and threatens food security across affected regions.
-
Decreased crop yields in major producing regions: Preliminary reports suggest a substantial decline in yields for key crops like wheat, corn, and soybeans in several regions. The impact varies depending on the specific crop, soil type, and existing water infrastructure.
-
Increased reliance on expensive irrigation methods: Farmers are forced to rely heavily on irrigation to compensate for the lack of rainfall, leading to increased costs and potentially unsustainable water usage. This added expense further strains already tight profit margins.
-
Potential for food price increases and food insecurity: Reduced crop yields directly translate to higher food prices, affecting consumers and particularly vulnerable populations who may face food insecurity. Market instability and supply chain disruptions are likely to amplify these effects.
-
Damage to livestock due to lack of pasture: The drought also impacts livestock, with reduced pastureland leading to feed shortages and potentially impacting animal health and productivity. This further compounds the economic burden on farmers.
Specific Examples of Agricultural Impact
For instance, wheat production in the Central Plains is projected to be down by 15% due to the March drought, while preliminary data suggests a 10% reduction in corn yields in the Southern agricultural belt. These figures represent significant economic losses and underscore the urgency of the situation. Further detailed assessments are ongoing to fully understand the extent of the damage.
Implications for Water Resources
The persistent lack of rainfall has had a devastating impact on water resources. Reservoir levels are critically low, and groundwater depletion is accelerating, creating a dire situation for many communities. This necessitates immediate action, including water rationing and restrictions.
-
Significantly reduced reservoir storage capacity: Many reservoirs are operating at dangerously low levels, raising concerns about the ability to meet future water demands for both human consumption and industrial uses.
-
Increased reliance on groundwater, leading to depletion: As surface water sources dwindle, communities and industries are increasingly reliant on groundwater, leading to unsustainable depletion of this precious resource. Over-extraction leads to long-term ecological damage.
-
Implementation of water rationing and restrictions in affected areas: Many regions are implementing water rationing and restrictions to conserve remaining supplies, impacting daily life and creating significant challenges for residents and businesses.
-
Potential for future water shortages and conflicts over water resources: The continuing water deficit raises concerns about future water shortages and the potential for conflicts between different user groups competing for limited resources. This requires proactive and collaborative water management solutions.
Regional Variations in Water Scarcity
The severity of the water scarcity varies across regions, with some areas experiencing more acute impacts than others. Areas with less developed water infrastructure are particularly vulnerable. Detailed regional analysis is crucial to target interventions effectively.
The Role of Climate Change
The insufficient rainfall in March is consistent with broader climate change trends, including altered precipitation patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events. This underscores the urgent need for sustainable water management strategies that consider the long-term impacts of climate change.
-
Increased frequency of droughts due to climate change: Climate change models predict an increase in the frequency and intensity of droughts in many regions, making water scarcity a persistent and growing threat.
-
Shifting rainfall patterns affecting water availability: Changes in rainfall patterns are impacting the timing and distribution of water resources, making it more challenging to manage water supplies effectively.
-
The need for proactive adaptation strategies to mitigate drought impacts: Adapting to the changing climate requires proactive strategies, such as developing more resilient infrastructure, improving water storage capacity, and implementing drought-resistant farming practices.
-
The importance of investing in climate-resilient infrastructure: Investing in climate-resilient infrastructure, such as improved water storage and distribution systems, is crucial to enhance water security in the face of increasingly unpredictable weather patterns.
Mitigating the Water Deficit
Addressing the ongoing water deficit requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating both short-term and long-term solutions. Water conservation, rainwater harvesting, and sustainable agricultural practices are paramount to building water security for the future.
-
Implementing water-efficient irrigation techniques: Adopting modern, water-efficient irrigation techniques can significantly reduce water consumption in agriculture while maintaining crop yields.
-
Promoting rainwater harvesting and storage solutions: Rainwater harvesting can help supplement water supplies, particularly in areas with limited access to surface water. Investment in improved storage infrastructure is needed.
-
Encouraging water conservation measures at the household level: Individual actions, such as reducing water consumption in homes and gardens, collectively make a significant contribution to water conservation.
-
Investing in drought-resistant crops and farming practices: Shifting towards drought-resistant crops and adopting sustainable agricultural practices can enhance the resilience of the agricultural sector to future droughts.
-
Implementing stricter water management policies: Effective water management policies are critical to ensure responsible and equitable use of water resources, addressing potential conflicts and promoting sustainability.
Conclusion
March's insufficient rainfall has significantly worsened the existing water deficit, impacting agriculture, straining water resources, and highlighting the urgent need to address climate change. The situation necessitates immediate action to mitigate the short-term consequences and prevent future crises. Understanding the implications of insufficient rainfall is crucial for building a more resilient future. We need collective action to conserve water, invest in sustainable water management strategies, and address the root causes of this growing water deficit. Let's work together to ensure water security for the future. Learn more about water conservation and drought mitigation strategies today.

Featured Posts
-
 Did Elon Musks Daughter Vivians Modeling Debut Signal A Break From Family
May 30, 2025
Did Elon Musks Daughter Vivians Modeling Debut Signal A Break From Family
May 30, 2025 -
 Maye Musk On Elon Musks Family Wealth Years Of Hard Work And Perseverance
May 30, 2025
Maye Musk On Elon Musks Family Wealth Years Of Hard Work And Perseverance
May 30, 2025 -
 Why Your Weather Forecast Might Not Include An Excessive Heat Warning
May 30, 2025
Why Your Weather Forecast Might Not Include An Excessive Heat Warning
May 30, 2025 -
 Future Of Des Moines Central Campus Agriscience Program Uncertain After Pause
May 30, 2025
Future Of Des Moines Central Campus Agriscience Program Uncertain After Pause
May 30, 2025 -
 Subvention Pour Medine La Region Grand Est Face A La Colere Du Rn
May 30, 2025
Subvention Pour Medine La Region Grand Est Face A La Colere Du Rn
May 30, 2025
