Investigation Into Persistent Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Following Ohio Train Derailment
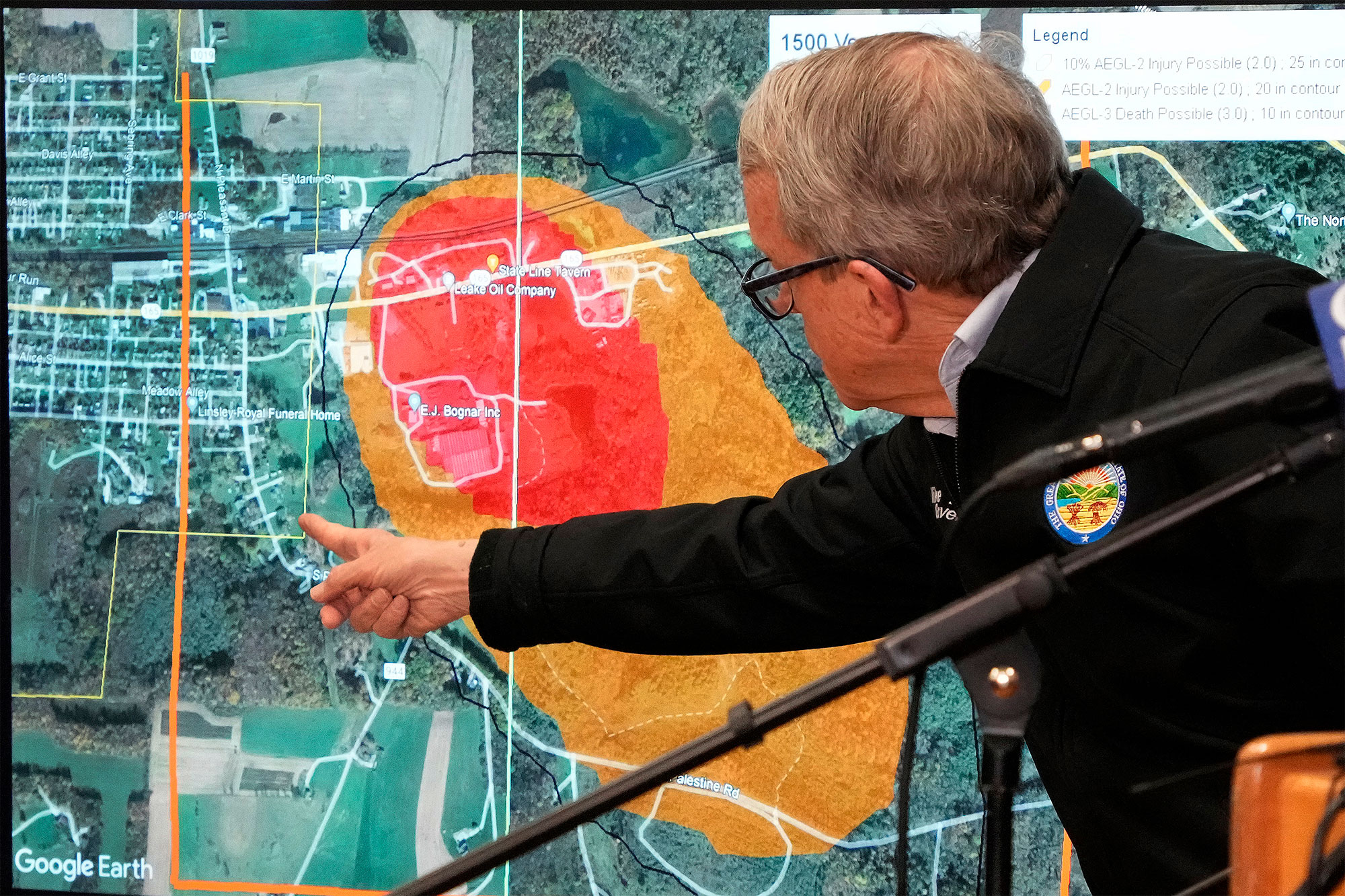
Table of Contents
Identifying Persistent Toxic Chemicals in the Aftermath
Types of Chemicals of Concern:
The Ohio train derailment involved the release of several hazardous materials, many of which are known persistent organic pollutants (POPs). These chemicals are particularly concerning due to their persistence in the environment and their potential for long-term health effects. Specific chemicals of concern include:
- Vinyl Chloride: A colorless gas used in the production of PVC plastics. Exposure can cause dizziness, headaches, and even liver cancer. [Link to SDS]
- Butyl Acrylate: A colorless liquid used in paints, adhesives, and coatings. It is a skin and respiratory irritant. [Link to SDS]
- Ethylhexyl Acrylate: Another liquid monomer used in paints and coatings. Similar to butyl acrylate, it presents skin and respiratory irritation risks. [Link to SDS]
- Other chemicals: Further investigation is needed to fully identify all chemicals released and their potential impact on building materials and the surrounding environment.
Methods for Detecting Chemical Contamination:
Detecting the presence of these persistent toxic chemicals in buildings requires a multi-pronged approach utilizing various testing methods:
- Air Quality Monitoring: Techniques include air sampling using specialized equipment followed by laboratory analysis using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to identify and quantify volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other airborne contaminants.
- Water Testing: Water samples from wells, municipal supplies, and building plumbing need to be collected and analyzed for the presence of dissolved chemicals. Laboratory analysis, again using techniques like GC-MS, is crucial for identifying and quantifying contaminants.
- Soil and Surface Testing: Soil samples from around buildings and surface samples from building interiors (e.g., flooring, walls) should be collected and analyzed for chemical residues. Techniques like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) are often employed.
- Limitations of Testing: It’s crucial to acknowledge that testing methods have limitations. Some chemicals may be difficult to detect at low concentrations, and the presence of multiple chemicals can complicate analysis.
Assessing the Extent of Building Contamination
Impact on Indoor Air Quality:
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) can accumulate indoors, leading to poor indoor air quality (IAQ). Building materials can act as reservoirs for these chemicals, slowly releasing them into the air over time. This can lead to:
- Short-term effects: Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat; headaches; dizziness.
- Long-term effects: Increased risk of respiratory illnesses, including asthma and lung cancer; potential neurological damage.
- Building Materials: Porous materials like drywall, insulation, and carpeting can absorb and retain chemicals, exacerbating indoor air contamination.
Potential for Water Contamination:
Groundwater and surface water contamination pose a significant risk to building water supplies. Chemicals released during the derailment can leach into the groundwater, potentially contaminating wells and municipal water sources that supply buildings. This contaminated water can lead to:
- Health risks: Ingestion of contaminated water can cause gastrointestinal distress, neurological problems, and long-term health issues.
- Water Filtration Systems: While water filtration systems can remove some contaminants, their effectiveness varies depending on the type and concentration of chemicals present. Regular testing and maintenance are essential.
Remediation and Cleanup Strategies
Decontamination Procedures:
Effective remediation strategies are crucial for removing persistent toxic chemicals from buildings and the surrounding environment. These strategies include:
- Air Scrubbing: Utilizing specialized air filtration systems to remove airborne contaminants.
- Surface Cleaning: Cleaning and decontaminating surfaces using appropriate cleaning agents and procedures.
- Soil Remediation: Removing and treating contaminated soil, potentially using techniques like bioremediation or thermal desorption.
- Challenges: Large-scale remediation efforts can be complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized expertise and resources.
Long-Term Monitoring and Prevention:
Long-term monitoring is vital to assess the effectiveness of remediation efforts and to identify any potential re-contamination. This includes:
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular testing of air, water, and soil samples to track chemical levels over time.
- Prevention Strategies: Implementing measures to prevent future contamination incidents, including improved transportation safety regulations and enhanced emergency response protocols.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Strong regulatory frameworks are crucial for ensuring responsible handling and transportation of hazardous materials.
Health Risks and Public Health Response
Short-term Health Effects:
Exposure to the released chemicals can cause a range of short-term health effects, including:
- Respiratory problems: Coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath.
- Eye and skin irritation: Burning, redness, itching.
- Headaches, dizziness, nausea: Symptoms related to central nervous system effects.
- Immediate Response: Providing immediate medical care to those experiencing acute health effects is crucial.
Long-term Health Concerns:
Long-term exposure to persistent toxic chemicals presents significant health risks, including:
- Increased cancer risk: Certain chemicals released in the derailment are known carcinogens.
- Chronic respiratory illnesses: Long-term respiratory problems such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Neurological damage: Potential for long-term neurological effects.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Long-term health monitoring programs for exposed populations are crucial to identify and manage long-term health consequences. Public health agencies play a critical role in overseeing these efforts.
Conclusion:
The Ohio train derailment highlights the severe risks associated with the release of persistent toxic chemicals and their potential for long-term building contamination. Thorough investigation, effective remediation, and comprehensive monitoring are crucial for safeguarding public health. Understanding the types of chemicals involved, the methods for detection, and appropriate cleanup strategies are vital for preventing future health crises.
Further research and comprehensive analysis are needed to fully understand the extent of the contamination from the Ohio train derailment and to develop effective strategies for preventing similar incidents. Continued monitoring and vigilant action are crucial to mitigate the long-term effects of persistent toxic chemicals in buildings and protect public health. Stay informed about the ongoing investigation into the persistent toxic chemicals impacting buildings following the Ohio train derailment.

Featured Posts
-
 Nuit Des Musees 2025 Une Nocturne Cinematographique A La Fondation Seydoux Pathe
May 14, 2025
Nuit Des Musees 2025 Une Nocturne Cinematographique A La Fondation Seydoux Pathe
May 14, 2025 -
 Dean Huijsen Arsenal And Chelsea Battle For Young Star
May 14, 2025
Dean Huijsen Arsenal And Chelsea Battle For Young Star
May 14, 2025 -
 Mark Wahlberg Returning For Ted Series On Peacock
May 14, 2025
Mark Wahlberg Returning For Ted Series On Peacock
May 14, 2025 -
 La Discussione Tra Alessia Marcuzzi E Mara Venier Cosa E Davvero Successo
May 14, 2025
La Discussione Tra Alessia Marcuzzi E Mara Venier Cosa E Davvero Successo
May 14, 2025 -
 Banned Candle Sales In Canada A Look At Etsy Walmart And Amazon
May 14, 2025
Banned Candle Sales In Canada A Look At Etsy Walmart And Amazon
May 14, 2025
