Measles Cases In The U.S.: An Update On The Current Outbreak
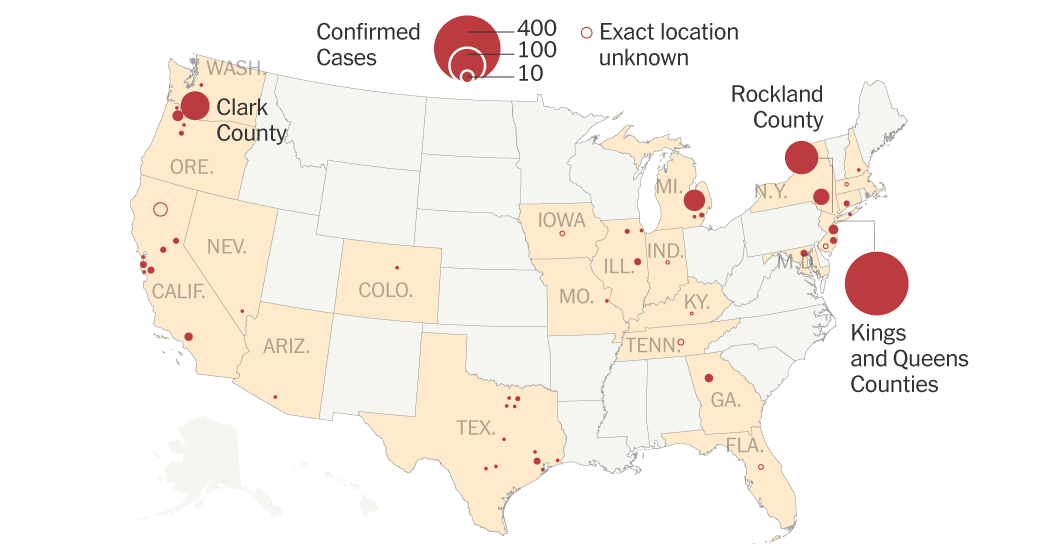
Table of Contents
Recent Measles Outbreaks and Their Locations
The geographic distribution of recent measles outbreaks in the U.S. paints a concerning picture. Several states have experienced significant increases in measles cases, underscoring the widespread nature of this problem.
Geographic Distribution
Several states, including Ohio, Texas, and New York, have reported clusters of measles cases. These outbreaks highlight a worrying trend across the nation. Location-specific keywords are essential here, and further research could reveal the most affected areas. Using data from the CDC, we can further refine the location-based analysis and provide more specific examples of the areas hit hardest by recent outbreaks.
- Ohio: Reports indicate a significant number of confirmed measles cases linked to unvaccinated individuals within specific communities.
- Texas: A measles outbreak in a large urban area demonstrated the rapid spread of the virus in densely populated settings with low vaccination rates.
- New York: Specific counties in New York experienced clusters of measles cases, often tied to religious communities with low vaccination rates. More granular data regarding specific counties within New York would enhance the accuracy and usefulness of this information.
The contributing factors for each location are often interconnected, but frequently involve low vaccination rates within specific communities. The lack of herd immunity leaves these populations vulnerable to outbreaks. These outbreaks of measles cases underscore the need for improved vaccination coverage and targeted public health interventions.
Factors Contributing to the Rise in Measles Cases
The increase in measles cases in the U.S. is multifaceted, stemming from a complex interplay of factors. Two primary issues contribute to this alarming trend.
Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
The spread of misinformation surrounding the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is a significant driver of the recent outbreaks. Anti-vaccine sentiment, fueled by unsubstantiated claims and conspiracy theories, leads many parents to forgo vaccinating their children.
- Effectiveness of the MMR Vaccine: The MMR vaccine is highly effective, preventing the vast majority of measles cases. It's considered safe and has a long history of success in protecting populations.
- The Dangers of Misinformation: The spread of misinformation through social media and other platforms hinders public health efforts and undermines confidence in established medical practices. Fact-checking and effective communication are vital to combat these narratives.
- Combating Misinformation: Public health organizations and medical professionals are actively engaged in counteracting misinformation campaigns, using evidence-based information to address public concerns and clarify misconceptions.
Gaps in Vaccination Coverage
Low vaccination rates, particularly among specific age groups and populations, significantly increase the risk of measles outbreaks. This reflects broader gaps in access to healthcare and public health services.
- Vaccination Coverage Rates: National vaccination rates for the MMR vaccine may not be consistently high across all states or communities, leading to pockets of vulnerability.
- Reasons for Low Vaccination Rates: Access to healthcare, cost, religious beliefs, and parental concerns are factors that can influence vaccination decisions.
- Consequences of Insufficient Coverage: Low vaccination rates result in reduced herd immunity, making communities more susceptible to outbreaks and increasing the risk for severe complications from measles.
Public Health Response and Prevention Measures
The public health response to measles outbreaks in the U.S. involves multifaceted strategies aimed at controlling the spread of the virus and protecting vulnerable populations.
CDC and Public Health Initiatives
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a crucial role in coordinating the national response.
- Public Health Interventions: Contact tracing is vital to identify and isolate individuals who have been exposed to the measles virus. Quarantine measures may be implemented to prevent further spread.
- Public Health Education Campaigns: Raising awareness about the importance of vaccination and the risks of measles through targeted campaigns is crucial.
- Improving Vaccination Rates: Public health initiatives focus on increasing vaccination rates, addressing barriers to access, and countering misinformation.
Protecting Vulnerable Populations
Infants, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems are particularly susceptible to severe complications from measles.
- Vulnerability of Specific Groups: These groups often cannot receive the MMR vaccine (infants) or have compromised immune systems, making them especially vulnerable.
- Specific Recommendations: Measures to protect these populations include avoiding contact with individuals who may be infected and ensuring that those around them are vaccinated.
Conclusion
The resurgence of measles cases in the U.S. underscores the critical importance of vaccination. This article has highlighted the geographic distribution of recent outbreaks, the underlying factors driving the increase, and the public health response. Misinformation and low vaccination rates significantly contribute to the problem. Public health agencies are working to control outbreaks, but individual responsibility is crucial. Protect yourself and your community from measles – learn more about measles prevention and get vaccinated if you haven't already. Stay informed about current measles cases in the U.S., and encourage others to do the same. Get vaccinated against measles today! Understanding and addressing the factors contributing to measles cases in the U.S. is essential for preventing future outbreaks and protecting public health.

Featured Posts
-
 Everything We Know Top 10 Questions About Btss Future
May 30, 2025
Everything We Know Top 10 Questions About Btss Future
May 30, 2025 -
 Dwytshh Bnk Ywse Ntaq Aemalh Fy Alimarat Alerbyt Almthdt
May 30, 2025
Dwytshh Bnk Ywse Ntaq Aemalh Fy Alimarat Alerbyt Almthdt
May 30, 2025 -
 Savvato 15 3 Plires Programma Tileoptikon Metadoseon
May 30, 2025
Savvato 15 3 Plires Programma Tileoptikon Metadoseon
May 30, 2025 -
 Bc Lng Projects Progress Challenges And The Future
May 30, 2025
Bc Lng Projects Progress Challenges And The Future
May 30, 2025 -
 Katastrofa Odry Czy Powtorka Jest Nieunikniona
May 30, 2025
Katastrofa Odry Czy Powtorka Jest Nieunikniona
May 30, 2025
