NATO Allies Progressing Towards 2% Defense Spending Goal
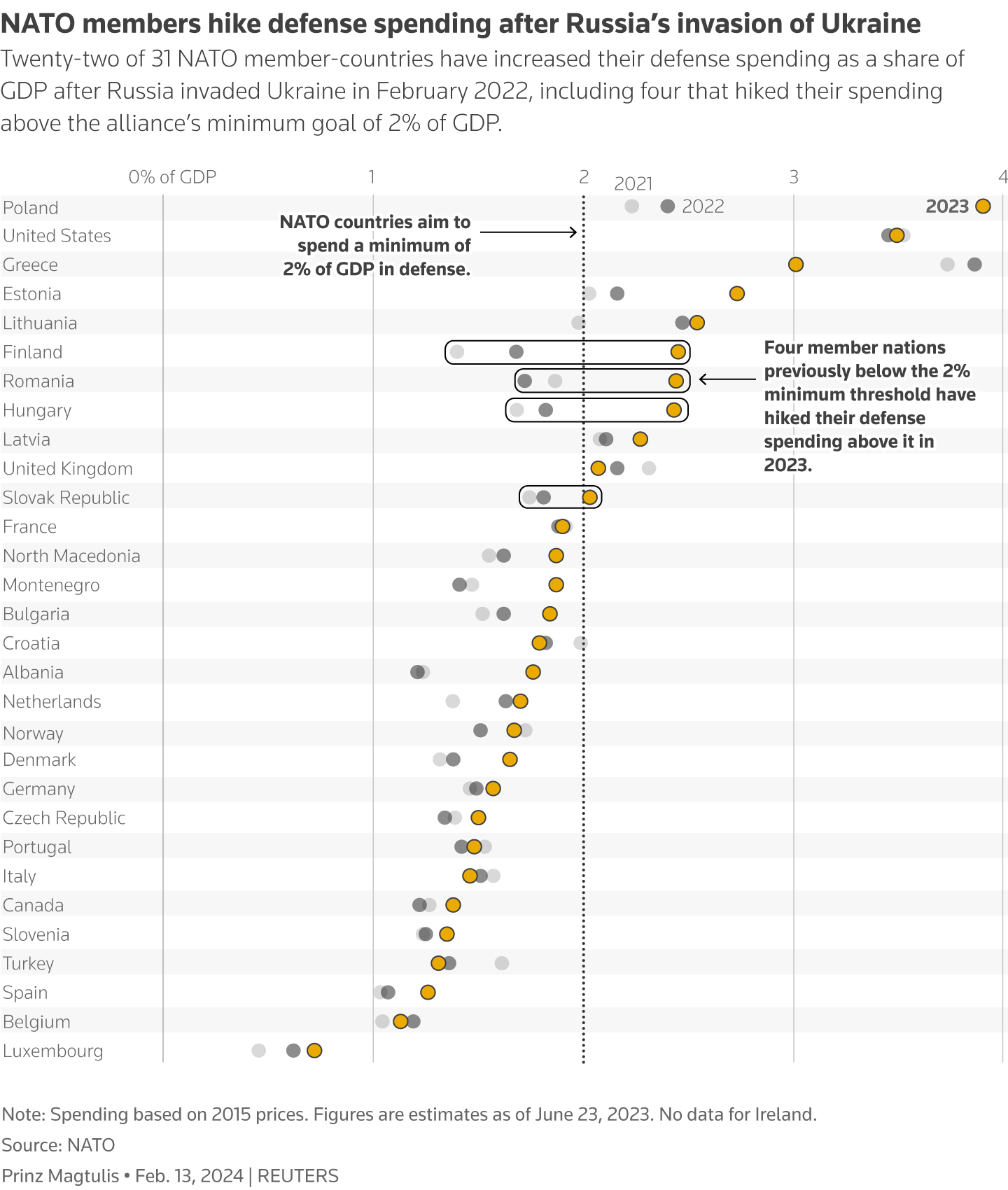
Table of Contents
Current Status of 2% GDP Defense Spending Goal
The 2% GDP defense spending target, while aspirational for all NATO members, reflects a significant disparity in commitment and capacity across the alliance. Analyzing defense expenditure as a percentage of GDP provides a standardized metric for comparison, despite variations in economic size and military structures.
-
Overview of Achievers: While the exact number fluctuates year to year based on reporting and economic adjustments, a select group of NATO allies consistently exceed the 2% benchmark. These nations often cite a heightened sense of security threat or a commitment to regional stability as driving factors. The United States, for example, has historically been a major contributor, significantly exceeding the 2% target.
-
Average NATO Spending: The average defense spending percentage across all NATO members is consistently below the 2% target. This average masks significant variations, however, highlighting the uneven distribution of military burden-sharing within the alliance.
-
High Achievers and Motivations: Countries like Greece, Poland, and the United Kingdom consistently surpass the 2% mark. Their motivations often stem from specific geopolitical concerns, regional instability, and perceived threats. These nations are actively modernizing their militaries and increasing their defense capabilities.
-
Low Achievers and Reasons for Under-Spending: Many European NATO members remain significantly below the 2% target. Reasons for this under-spending are multifaceted and often interconnected:
- Economic Constraints: Budgetary limitations and competing domestic priorities (healthcare, education, infrastructure) often constrain defense spending.
- Domestic Political Opposition: Public and political resistance to increased military budgets can limit government action.
- Historical Context: Some nations have deeply ingrained pacifist sentiments or a legacy of prioritizing social welfare programs over defense.
-
Visual Representation: [Insert a table or chart here visually representing the data on defense spending percentages for various NATO members. This should clearly show which countries are above and below the 2% target.]
Factors Driving Increases in Defense Spending
The recent geopolitical landscape, particularly Russia's aggression in Ukraine, has profoundly impacted defense spending decisions across NATO. This conflict has served as a stark reminder of the enduring need for robust collective defense capabilities.
-
The Ukraine Conflict's Impact: The invasion of Ukraine has been a watershed moment, prompting many allies to re-evaluate their defense postures and dramatically increase military investment. The conflict underscored the need for enhanced conventional warfare capabilities, as well as modernizing cyber defense and missile defense systems.
-
Increased Investment in Specific Capabilities: Defense modernization is a key element of increased spending. This includes investments in:
- Cyber Warfare: Protecting critical infrastructure and countering cyberattacks.
- Missile Defense: Strengthening defenses against ballistic and cruise missile threats.
- Air and Naval Power: Modernizing fleets and enhancing air superiority capabilities.
-
Geopolitical Uncertainty and Perceived Threats: The rise of revisionist powers, territorial disputes, and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction contribute to a climate of geopolitical uncertainty, motivating increased defense spending.
-
Public Opinion and Political Pressure: Growing public awareness of security threats, coupled with political pressure from within and between nations, is pushing for increased military budgets and a strengthened collective defense.
Challenges and Obstacles to Achieving the 2% Goal
Despite the increased awareness of the need for enhanced defense capabilities, several challenges persist in achieving the 2% target across all NATO members.
-
Budgetary Constraints: Many European nations face significant budgetary constraints due to economic downturns, high national debt, and competing demands on public funds.
-
Competing National Priorities: Healthcare, education, and infrastructure development frequently compete for budgetary resources with defense spending. Balancing these priorities remains a considerable challenge.
-
Domestic Political Opposition: Political parties and public opinion can oppose increased military spending, particularly in countries with pacifist traditions or a strong emphasis on social welfare programs. This opposition can significantly hinder government efforts to meet the 2% target.
The Importance of Meeting the 2% Defense Spending Target
The 2% GDP defense spending target is not merely an arbitrary number; it's a crucial element of maintaining the credibility and effectiveness of the NATO alliance.
-
Collective Security: Meeting the 2% target strengthens collective defense by ensuring that each member contributes its fair share to the common defense effort. This enhances the alliance's ability to deter aggression and respond effectively to threats.
-
Deterrence and Alliance Credibility: Adequate defense spending demonstrates a commitment to collective security, enhancing NATO's credibility as a deterrent to potential adversaries. This dissuades aggression and contributes to regional stability.
-
Burden Sharing: The 2% target promotes fair burden-sharing among allies, preventing any single nation from carrying an undue share of the defense burden. This ensures a more equitable and sustainable collective security framework.
-
Effective Response to Threats: Sufficient defense spending provides the resources necessary to maintain modern military capabilities, ensuring the alliance's ability to respond effectively to various security threats.
Conclusion
The progress of NATO allies towards the 2% defense spending goal is a complex and evolving issue. While some members consistently exceed the target, many others face significant challenges in achieving it. Factors such as economic constraints, competing national priorities, and domestic political opposition all contribute to this uneven distribution of military burden-sharing. However, the recent geopolitical climate, especially Russia's war in Ukraine, has highlighted the critical importance of maintaining a strong collective defense. The pursuit of the 2% defense spending goal remains crucial for ensuring the continued strength and security of the NATO alliance. Understanding the progress, challenges, and underlying factors is paramount for maintaining a robust collective defense. Further research and analysis into NATO defense spending and the 2% GDP target are essential for informed policymaking and ensuring the alliance's future effectiveness. Learn more about the complexities of NATO's 2% defense spending goal and its impact on global security.

Featured Posts
-
 El Equipo Espanol Para El Mundial De Atletismo En Pista Cubierta De Nanjing Convocatoria Completa
May 28, 2025
El Equipo Espanol Para El Mundial De Atletismo En Pista Cubierta De Nanjing Convocatoria Completa
May 28, 2025 -
 Pirates Vs Braves Recap Triolos Impact Bullpen Performance In Close Game
May 28, 2025
Pirates Vs Braves Recap Triolos Impact Bullpen Performance In Close Game
May 28, 2025 -
 Shein Ordered To Comply With Eu Consumer Laws Or Face Penalties
May 28, 2025
Shein Ordered To Comply With Eu Consumer Laws Or Face Penalties
May 28, 2025 -
 Jennifer Lopez Host Of The 2025 American Music Awards On Cbs
May 28, 2025
Jennifer Lopez Host Of The 2025 American Music Awards On Cbs
May 28, 2025 -
 Nadal Bids Tearful Adieu To Roland Garros Sabalenka Claims Victory
May 28, 2025
Nadal Bids Tearful Adieu To Roland Garros Sabalenka Claims Victory
May 28, 2025
