NATO Defense Spending: Progress And Challenges
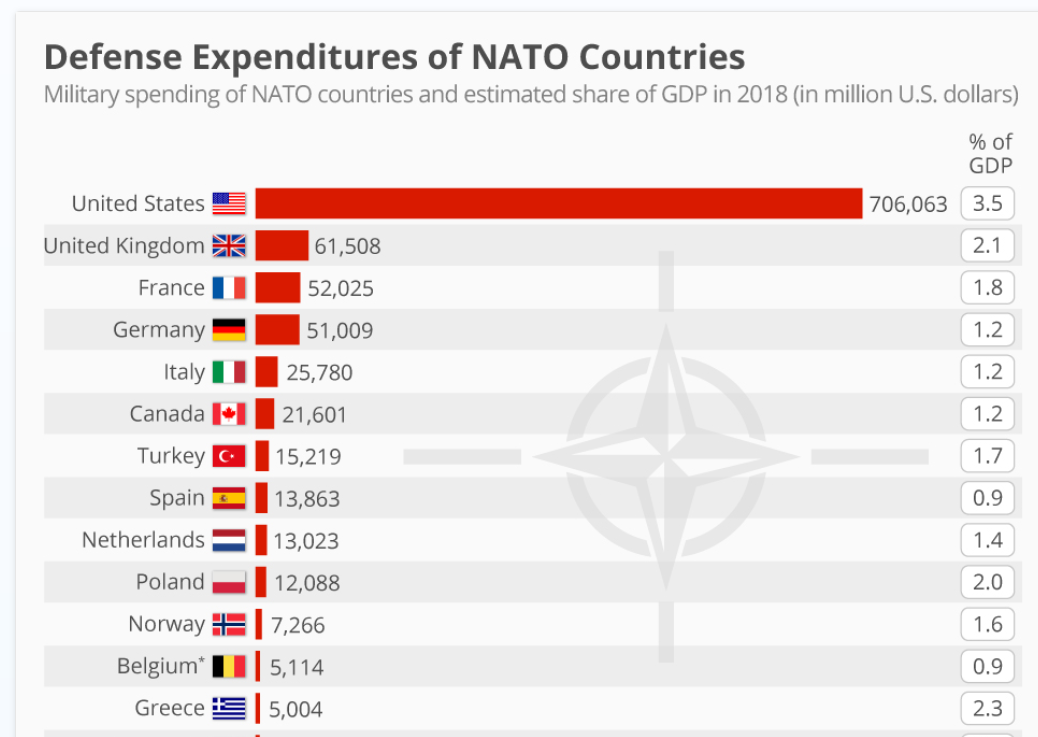
Table of Contents
Progress in NATO Defense Spending
Increased Spending Since 2014
Since the Wales Summit's pledge for nations to move toward spending 2% of their GDP on defense, there has been a notable increase in overall NATO defense spending. This upward trend reflects a growing recognition of the need for robust collective defense capabilities in a more volatile global security environment.
- Significant Increases: Several key members, including the United States, the United Kingdom, and Poland, have significantly increased their defense budgets, demonstrating a commitment to strengthening their military capabilities.
- Aggregate Growth: Data from NATO reports show a substantial aggregate increase in defense spending across the alliance since 2014. While exact figures vary depending on the reporting methodology and currency conversions, the overall trend is clear. (Source: [Insert relevant NATO report link here]).
- Ukraine War Impact: The 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine served as a stark reminder of the importance of adequate defense spending. The war has undoubtedly accelerated the increase in defense budgets for many NATO members, bolstering their commitment to collective security and deterring further aggression.
Investment in Modernization and Capabilities
Increased NATO defense spending has also fueled significant investments in modernization and the enhancement of military capabilities. This includes the acquisition of advanced technologies and equipment crucial for maintaining a strong military posture.
- Next-Generation Fighter Jets: Many NATO members are investing in advanced fighter jets like the F-35, improving air superiority and interoperability.
- Cyber Defense Systems: Increased spending is dedicated to building robust cyber defense systems to counter emerging threats in the digital realm. This reflects the growing understanding of the importance of cybersecurity in national security.
- Intelligence Gathering: Investments are improving intelligence gathering capabilities through advanced surveillance technologies and improved data analysis techniques. This enhances situational awareness and allows for proactive defense strategies.
- Collective Defense Benefits: These modernization efforts significantly enhance the alliance's collective defense capabilities, improving interoperability, and ensuring NATO's ability to respond effectively to a wide range of threats.
Challenges to Achieving the 2% GDP Target
Despite the progress made, significant challenges hinder the achievement of the 2% GDP target for defense spending. These challenges are multifaceted and stem from a range of economic, political, and strategic factors.
Budgetary Constraints and Domestic Priorities
For many NATO members, budgetary constraints represent a major obstacle to increasing defense spending. Competing demands on national budgets often limit the resources available for defense.
- Economic Limitations: Some countries, particularly those facing economic difficulties, struggle to allocate sufficient funds to defense while addressing other vital domestic priorities such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
- Competing Demands: The allocation of resources is a complex process involving political trade-offs. Decisions on defense spending are inevitably influenced by the relative importance placed on various sectors by the government.
- Economic Models and Fiscal Policies: The different economic models and fiscal policies adopted by NATO members impact their capacity and willingness to increase defense spending.
Geopolitical Factors and National Security Strategies
Differing geopolitical situations and national security assessments influence how NATO members prioritize defense spending.
- Unique Security Challenges: Countries facing unique security challenges – such as those bordering regions of instability – may prioritize different aspects of defense, impacting their spending patterns.
- Regional Threats and Alliances: Regional threats and existing alliances outside NATO can also influence defense spending decisions, potentially diverting resources away from NATO commitments.
- Differing Perspectives on Threats: Differing perceptions of threats and their severity can lead to varied approaches to defense spending among NATO members, even with a common goal of collective security.
Transparency and Accountability
Ensuring transparency and accountability in defense budgeting is vital for maintaining public trust and optimizing resource allocation.
- NATO Transparency Initiatives: NATO has implemented initiatives aimed at improving transparency in defense budgeting, but challenges remain in ensuring consistent and accurate reporting across all member states.
- Reporting Discrepancies: Variations in accounting practices and reporting standards can make it difficult to accurately assess the actual level of defense spending by individual members.
- Independent Audits and Oversight: Regular independent audits and robust oversight mechanisms are essential for ensuring accountability for the allocated funds and minimizing the potential for mismanagement or corruption.
Future Prospects for NATO Defense Spending
Sustaining Momentum
Sustaining the momentum in increasing NATO defense spending requires a multifaceted approach. The continued growth will depend on several crucial factors.
- Economic Forecasts and Geopolitical Stability: Continued economic growth and a stable geopolitical environment will be crucial in allowing member states to maintain their increased defense spending levels.
- NATO Initiatives: Ongoing NATO initiatives aimed at improving coordination and streamlining defense spending can contribute to sustaining momentum.
- Strategic Planning: Effective strategic planning is essential to justify and prioritize increased defense budgets to national legislatures and the public.
Addressing the Challenges
Addressing the challenges that hinder the 2% GDP target requires a concerted effort from all NATO members.
- Improved Coordination: Increased coordination among member states in defense planning and resource allocation can help optimize spending and avoid duplication of efforts.
- Addressing Budgetary Constraints: NATO can explore mechanisms to support members facing budgetary constraints, possibly through joint procurement initiatives or other forms of financial assistance.
- NATO Framework Reforms: Reforms within the NATO framework might be necessary to address the unique challenges faced by specific member states while ensuring collective security.
Conclusion
NATO defense spending has shown progress since 2014, but significant challenges persist in achieving the 2% GDP target. Budgetary constraints, geopolitical factors, and the need for enhanced transparency continue to impact member states' ability to fully meet their commitments. Sustaining the momentum requires a coordinated effort to address these hurdles, focusing on improved resource allocation, strategic planning, and fostering greater transparency and accountability. The future of collective security hinges on a robust and equitable approach to NATO defense spending. Continued efforts to increase and sustain NATO defense spending are essential for maintaining the alliance's credibility and effectiveness in addressing emerging threats. The commitment to strengthening NATO defense spending must remain a priority for all members to ensure the long-term security of the alliance and its partners.

Featured Posts
-
 Cristiano Ronaldo Marka Degeri Ve Gelecegi
May 28, 2025
Cristiano Ronaldo Marka Degeri Ve Gelecegi
May 28, 2025 -
 Kanyes Wife Bianca Censori Spotted Rollerblading In Italy Latest Stunt Details
May 28, 2025
Kanyes Wife Bianca Censori Spotted Rollerblading In Italy Latest Stunt Details
May 28, 2025 -
 Tuerk Taraftarin Ronaldo Ya Fenerbahce Teklifi Danimarka Dan Seslendi
May 28, 2025
Tuerk Taraftarin Ronaldo Ya Fenerbahce Teklifi Danimarka Dan Seslendi
May 28, 2025 -
 Rotterdam Thriller Psv Defeat Feyenoord Closing In On Ajax
May 28, 2025
Rotterdam Thriller Psv Defeat Feyenoord Closing In On Ajax
May 28, 2025 -
 Ipswich Towns Managerial Decisions Tuanzebe Phillips Chaplin And Murics Injury
May 28, 2025
Ipswich Towns Managerial Decisions Tuanzebe Phillips Chaplin And Murics Injury
May 28, 2025
