Negative European Electricity Prices: A Solar Revolution?
Table of Contents
The Mechanics of Negative Electricity Prices
Negative electricity prices occur when the supply of electricity dramatically surpasses demand. Understanding this requires examining both the oversupply of renewable energy and the intricacies of electricity markets.
Oversupply of Renewable Energy
A major driver of negative electricity prices is the sheer abundance of renewable energy, primarily solar and wind power.
- Peak solar generation: Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems generate the most electricity during sunny midday periods, often exceeding immediate demand.
- Increased wind energy production: Similarly, periods of high wind speeds lead to a surge in wind energy production, further adding to the oversupply.
- Low energy consumption during off-peak hours: Energy consumption typically dips overnight and during other off-peak periods, creating a mismatch between supply and demand.
The impact of weather patterns on renewable energy generation is significant. Unpredictable weather can lead to large swings in electricity production. Currently, energy storage technologies like batteries are still limited in their capacity to absorb and release this excess energy, exacerbating the problem of oversupply. This inability to effectively store and manage surplus renewable energy is a key factor contributing to negative electricity prices.
The Role of Electricity Markets
Electricity markets operate on a complex system of supply and demand. The price is often determined by the marginal cost of the most expensive power source needed to meet demand. However, when renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, flood the market, this dynamic changes dramatically.
- Wholesale electricity markets: These markets set the price for electricity traded between producers and suppliers.
- Marginal pricing: The price is typically set by the last power source brought online to meet demand – often fossil fuel plants with higher operating costs. When renewables exceed demand, this marginal price can fall, even to negative levels.
- Penalties for producers: Producers often face penalties for failing to curtail their generation when prices are negative. This incentivizes them to keep generating, even at a loss, to avoid these penalties.
This creates a scenario where electricity producers are essentially paying consumers to take their electricity, resulting in negative electricity prices. This is a unique challenge presented by the rapid integration of intermittent renewable sources.
The Growing Influence of Solar Power
The rise of negative electricity prices is intrinsically linked to the rapid expansion of solar power across Europe.
The Rapid Expansion of Solar PV
The proliferation of solar photovoltaic installations is a key contributor to the current energy market dynamics.
- Statistics on solar PV capacity increase: Europe has witnessed exponential growth in solar PV capacity in recent years, with [insert relevant statistics and sources here].
- Government incentives and subsidies: Government policies promoting renewable energy through subsidies and tax breaks have accelerated solar PV adoption.
- Falling solar panel prices: The decreasing cost of solar panels has made solar energy increasingly affordable, further fueling its expansion.
This rapid growth in solar energy capacity directly impacts electricity prices. The influx of cheap solar power during peak sun hours significantly contributes to the oversupply scenario, leading to negative pricing events.
Solar Power's Predictability Challenges
While solar power's contribution to the clean energy transition is undeniable, its inherent intermittency presents challenges for grid stability.
- Dependence on weather conditions: Solar energy production is heavily reliant on sunshine, making it inherently unpredictable.
- Need for better forecasting and grid management: Accurate forecasting of solar energy generation is crucial for effective grid management.
- The role of smart grids and energy storage solutions: Smart grids and advanced energy storage solutions are essential for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources like solar power seamlessly into the electricity grid.
Improving forecasting capabilities and investing in smart grid technologies and energy storage are crucial for mitigating the negative impacts of solar power's intermittency and for fully harnessing its potential while managing price volatility.
Other Contributing Factors
While solar power plays a dominant role, other factors also contribute to negative electricity prices in Europe.
Increased Wind Power Generation
Wind energy, another major renewable energy source, also contributes to the oversupply scenario.
- Statistics on wind power capacity growth: Similar to solar, wind power capacity has significantly increased across Europe [insert relevant statistics and sources here].
- Correlation between wind speeds and electricity production: High wind speeds translate to increased electricity generation, sometimes coinciding with peak solar generation.
- Geographical distribution of wind farms: The geographical distribution of wind farms influences the overall impact on the electricity grid.
The combined output of wind and solar energy can lead to periods of substantial oversupply, even exceeding the peak demand during periods of high wind speeds and abundant sunshine.
Reduced Energy Demand
Decreased energy consumption further exacerbates the supply-demand imbalance.
- Impact of economic downturns: Economic slowdowns can lead to lower industrial and commercial energy demand.
- Energy efficiency improvements: Increased energy efficiency in buildings and appliances reduces overall energy consumption.
- Changes in consumer behavior: Shifts in consumer behavior, such as reduced energy usage, also contribute to lower overall demand.
These factors, coupled with the increase in renewable energy generation, contribute to creating an environment where supply significantly outpaces demand, pushing electricity prices into negative territory.
Conclusion
The phenomenon of negative electricity prices in Europe is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. The significant contribution of solar power, coupled with increased wind energy generation and reduced energy demand, creates a scenario of substantial oversupply. While this presents challenges for grid management and electricity market stability, it also underscores the remarkable progress in the European renewable energy transition. The success of solar power in driving down electricity prices demonstrates the potential of renewable energy sources to revolutionize the energy sector. However, further investment in smart grid technologies and energy storage solutions is crucial to effectively manage the intermittency of renewable sources like solar and wind and ensure a stable and sustainable energy future. Continue to explore the implications of negative electricity prices and the ongoing solar revolution transforming the European energy landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Whats Working For Tylor Megill A Deep Dive Into His Mets Performance
Apr 29, 2025
Whats Working For Tylor Megill A Deep Dive Into His Mets Performance
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Ftc Challenges Court Ruling On Microsoft Activision Merger
Apr 29, 2025
Ftc Challenges Court Ruling On Microsoft Activision Merger
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Ray Epps Defamation Claim Against Fox News A Deep Dive Into The January 6th Narrative
Apr 29, 2025
Ray Epps Defamation Claim Against Fox News A Deep Dive Into The January 6th Narrative
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Minnesota Governor Defies Us Attorney General On Transgender Athlete Ban
Apr 29, 2025
Minnesota Governor Defies Us Attorney General On Transgender Athlete Ban
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Austin City Limits Celebrating Willie Nelson And Familys Legacy
Apr 29, 2025
Austin City Limits Celebrating Willie Nelson And Familys Legacy
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Reaching A Mature Audience You Tubes Expanding Demographics Npr
Apr 29, 2025
Reaching A Mature Audience You Tubes Expanding Demographics Npr
Apr 29, 2025 -
 How You Tube Caters To The Needs Of Older Viewers
Apr 29, 2025
How You Tube Caters To The Needs Of Older Viewers
Apr 29, 2025 -
 You Tubes Growing Senior Audience Understanding The Trend
Apr 29, 2025
You Tubes Growing Senior Audience Understanding The Trend
Apr 29, 2025 -
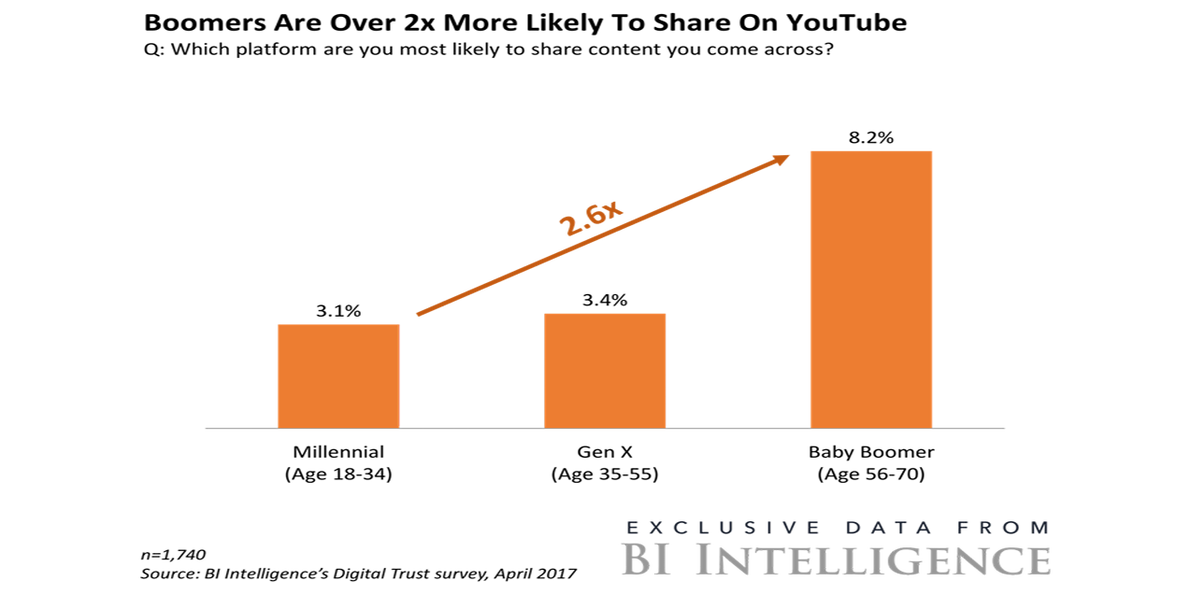 You Tubes Growing Popularity Among Older Viewers
Apr 29, 2025
You Tubes Growing Popularity Among Older Viewers
Apr 29, 2025 -
 How You Tube Is Attracting Older Viewers An Npr Analysis
Apr 29, 2025
How You Tube Is Attracting Older Viewers An Npr Analysis
Apr 29, 2025
