New COVID-19 Variant: Surge In Cases Explained

Table of Contents
Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant
Understanding the properties of the new COVID-19 variant is critical to managing the current surge. Key characteristics include its transmission rate, severity of illness, and the effectiveness of existing vaccines and treatments.
Transmission Rate
The new variant's transmissibility is a major concern. While precise R0 (basic reproduction number) data may vary depending on the specific variant and location, initial observations suggest it might be even more contagious than previous variants.
- Higher transmission rate than previous variants? Early evidence points towards a significantly higher transmission rate, leading to rapid community spread.
- Evidence of increased community spread? Reports of increased case numbers in various regions strongly suggest widespread community transmission.
- Factors contributing to increased spread: This rapid spread could be attributed to several factors, including waning immunity from previous infections or vaccinations, reduced mask usage in many communities, and increased indoor gatherings during colder months.
Severity of Illness
Determining the severity of illness caused by this new variant is crucial. While early data is still emerging, it's vital to monitor hospitalization and death rates.
- Higher risk of severe illness in certain populations? While initial data may suggest milder symptoms in generally healthy individuals, vulnerable populations like the unvaccinated and immunocompromised remain at higher risk of severe illness.
- Increased likelihood of long COVID? The potential for long COVID, with its lingering symptoms, remains a concern and requires ongoing monitoring and research.
- Symptoms different from previous variants? Though many symptoms overlap with previous variants, subtle differences in symptom presentation might be observed and require further study.
Effectiveness of Vaccines and Treatments
The effectiveness of existing vaccines and treatments against the new variant is under continuous evaluation.
- Reduced vaccine effectiveness? While vaccines still offer significant protection against severe illness and hospitalization, some reduction in effectiveness against infection may be observed.
- Are booster shots recommended? Public health authorities generally recommend booster shots to enhance protection against newer variants, particularly for vulnerable individuals.
- Do current antiviral treatments remain effective? Current antiviral treatments may still be effective, but their efficacy against specific mutations in the new variant needs ongoing assessment. Clinical trials and real-world data are crucial for determining the effectiveness of these treatments against the new variant.
Factors Contributing to the Surge in Cases
Several factors contribute to the current surge in COVID-19 cases beyond the characteristics of the new variant itself.
Seasonality and Weather Patterns
Seasonal changes can significantly influence viral transmission.
- Increased indoor gatherings during colder months? As temperatures drop, people tend to spend more time indoors, facilitating closer contact and increasing the risk of transmission.
- Impact of humidity and temperature on viral survival: Lower humidity and colder temperatures may favor the survival and spread of the virus.
Reduced Public Health Measures
A relaxation of public health interventions plays a significant role in increased transmission.
- Correlation between relaxed restrictions and case increases? Data analysis often reveals a correlation between the easing of restrictions and a subsequent increase in COVID-19 cases.
- Impact of reduced testing and reporting: Decreased testing and reporting can lead to an underestimation of the actual number of cases, hindering effective public health response.
Immune Evasion
The ability of the new variant to evade the immune system contributes to the surge.
- Mutations affecting antibody binding? Mutations in the virus's spike protein can affect the binding of antibodies, reducing the effectiveness of both natural immunity and vaccine-induced immunity.
- Impact on immune memory? The virus's ability to evade immune memory can lead to reinfections, even in individuals who have previously been infected or vaccinated.
- Studies showing immune evasion capabilities: Ongoing research is crucial to understand the extent of immune evasion and its impact on the pandemic's trajectory.
Public Health Response and Recommendations
A robust public health response is essential to mitigate the impact of the new COVID-19 variant surge.
Testing and Surveillance
Enhanced testing and genomic surveillance are critical for monitoring the spread of the variant.
- Increased availability of testing? Ensuring readily available testing, including rapid antigen tests, is vital for early detection and isolation of infected individuals.
- Importance of rapid antigen tests? Rapid antigen tests enable quick results, aiding in prompt isolation and contact tracing.
- Genomic sequencing to track mutations: Genomic sequencing allows for the precise identification of mutations, helping scientists understand the variant's characteristics and potential threat.
Vaccination and Boosters
Vaccination and booster shots remain crucial for protection against severe illness.
- Recommendations for booster shots? Public health authorities often recommend booster shots, especially for vulnerable populations, to enhance protection against the new variant.
- Effectiveness of different vaccine types against the new variant? Studies continuously assess the effectiveness of various vaccines against emerging variants.
- Vaccination rates and their impact: High vaccination rates significantly reduce the severity of the pandemic's impact, including hospitalization and death rates.
Preventive Measures
Simple yet effective preventive measures remain crucial.
- Importance of handwashing and sanitizing: Frequent handwashing and the use of hand sanitizers remain essential for reducing the spread of the virus.
- Effectiveness of different mask types: Wearing well-fitting masks, especially in crowded indoor settings, can significantly reduce transmission.
- Benefits of social distancing and ventilation: Maintaining social distancing and ensuring proper ventilation in indoor spaces can help limit the spread of the virus.
Conclusion
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant, alongside contributing factors such as reduced public health measures and immune evasion, has resulted in a surge in cases. Understanding the variant's characteristics and implementing a robust public health response, including vaccination, boosters, testing, and preventive measures, remains crucial to mitigating its impact. Stay informed about the latest developments from reliable sources like the World Health Organization (WHO) and your local public health authorities. Protect yourself and your community by getting vaccinated and boosted, practicing good hygiene, and following public health guidelines. Staying informed about the latest information regarding this new COVID-19 variant is vital for protecting yourself and your loved ones from future surges.

Featured Posts
-
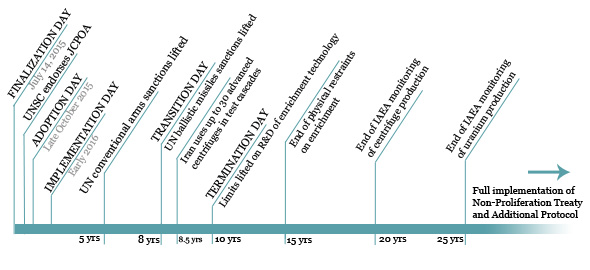 Iran Nuclear Deal Implications For Israels Regional Security
May 31, 2025
Iran Nuclear Deal Implications For Israels Regional Security
May 31, 2025 -
 Ryujinx Emulator Project Abandoned After Nintendo Intervention
May 31, 2025
Ryujinx Emulator Project Abandoned After Nintendo Intervention
May 31, 2025 -
 Rolan Garos 2024 Grigor Dimitrov Se Zavrscha
May 31, 2025
Rolan Garos 2024 Grigor Dimitrov Se Zavrscha
May 31, 2025 -
 Le Combat Environnemental Selon Isabelle Autissier L Importance De L Unite
May 31, 2025
Le Combat Environnemental Selon Isabelle Autissier L Importance De L Unite
May 31, 2025 -
 Giro D Italia 2025 Vatican City To Host Final Stage In Papal Tribute
May 31, 2025
Giro D Italia 2025 Vatican City To Host Final Stage In Papal Tribute
May 31, 2025
