Offshore Wind Farm Development: A Costly Undertaking
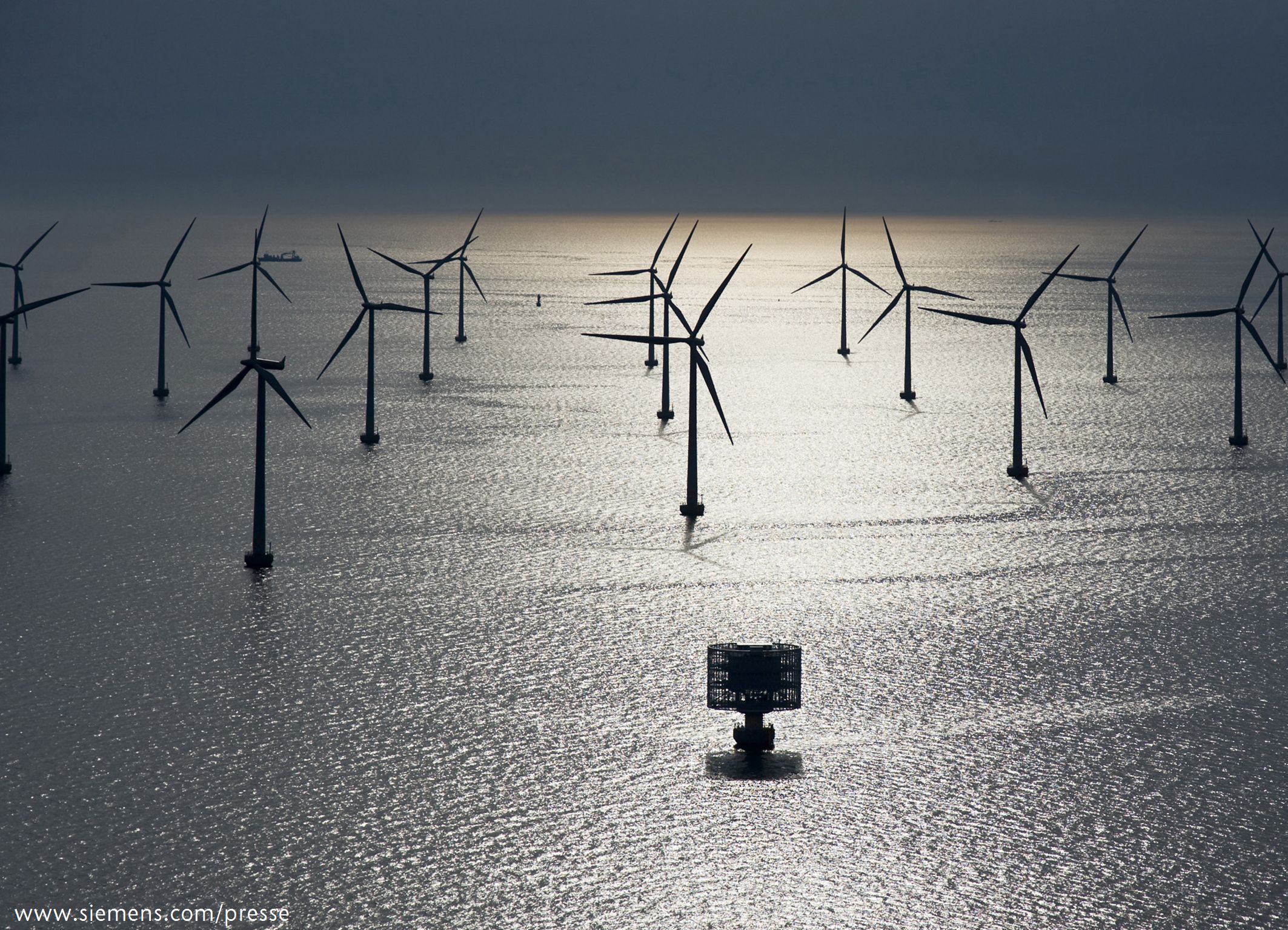

Table of Contents
High Initial Capital Expenditure (CAPEX)
Developing an offshore wind farm requires a substantial upfront investment. The cost of offshore wind projects is significantly impacted by several key factors during the initial phases:
Site Assessment and Planning
Before a single turbine can be installed, extensive planning and assessment are necessary. This stage includes:
- Detailed seabed surveys: Identifying suitable locations requires thorough seabed surveys to assess depth, soil conditions, and potential hazards. This is crucial for foundation design and stability.
- Environmental impact assessments (EIAs): Rigorous EIAs are mandated to evaluate the potential impact on marine ecosystems, including bird and marine mammal populations. Mitigation strategies must be developed and incorporated into the project plan, adding to the cost.
- Grid connection studies and agreements: Securing grid connection is crucial. Negotiating agreements with transmission system operators (TSOs) and planning for the necessary upgrades to the electricity grid can be a lengthy and costly process. This includes the cost of subsea cables connecting the wind farm to the onshore grid.
Turbine and Infrastructure Procurement
The procurement of essential components represents a massive portion of the initial investment:
- High manufacturing costs for specialized offshore wind turbines: Offshore turbines are larger and more robust than their onshore counterparts, requiring specialized materials and manufacturing processes.
- Significant transportation and installation challenges: Transporting massive turbine components and foundations to offshore locations presents logistical challenges, requiring specialized vessels and potentially increasing the cost of offshore wind significantly.
- Price volatility in raw materials: Fluctuations in the prices of steel, concrete, and other essential raw materials impact the overall project budget and can lead to unexpected cost overruns. The choice of foundation (monopiles, jackets, or floating structures) also significantly affects costs.
Installation and Commissioning
Installation and commissioning represent another significant cost driver:
- High cost of specialized installation vessels and equipment: Specialized heavy-lift vessels, cranes, and other equipment are required for the installation of turbines and foundations, adding substantially to the overall cost.
- Need for experienced and highly trained personnel: Offshore wind farm installation requires skilled technicians, engineers, and other professionals, driving up labor costs.
- Potential for delays and cost overruns: Weather conditions and unforeseen technical issues can cause delays, leading to cost overruns and impacting the project's profitability.
Ongoing Operational Expenditure (OPEX)
Even after commissioning, significant costs are associated with maintaining and operating an offshore wind farm.
Maintenance and Repair
The remote location and harsh marine environment necessitate regular maintenance:
- Regular inspections and maintenance of wind turbines: Routine inspections and maintenance are essential to prevent malfunctions and ensure optimal performance. This requires specialized vessels and skilled technicians for offshore access.
- Repair and replacement of damaged components: Components can be damaged due to storms, corrosion, or other factors, requiring expensive repairs or replacements.
- Specialized vessels and equipment for offshore maintenance: Dedicated maintenance vessels and specialized equipment are required for efficient and safe offshore maintenance operations.
Insurance and Financing
Securing insurance and financing adds to the ongoing expense:
- High insurance costs: The inherent risks associated with offshore operations, such as storms and equipment damage, lead to high insurance premiums.
- Competitive financing landscape: Securing financing for these large-scale projects can be challenging, with varying interest rates and loan terms impacting the overall cost.
Grid Connection and Transmission
Maintaining grid connection and transmission remains a crucial ongoing cost:
- Potential need for significant grid upgrades: Integrating large amounts of renewable energy from offshore wind farms may require significant upgrades to the onshore grid infrastructure.
- Costs associated with laying and maintaining subsea cables: Subsea cables are susceptible to damage, requiring regular monitoring and maintenance, adding to the operational expenditure.
Environmental and Regulatory Factors
Environmental considerations and regulatory processes also influence the cost of offshore wind.
Environmental Impact Assessments and Mitigation
Environmental protection plays a crucial role:
- Studies assessing impact on marine life and bird populations: Detailed studies are necessary to assess the potential impact on marine life and bird populations, often leading to the implementation of mitigation measures.
- Implementation of measures to minimize environmental impact: Measures such as bird deterrent systems and careful cable routing add to the project costs.
Permitting and Licensing
Navigating the regulatory landscape is complex and time-consuming:
- Extensive permitting process involving various regulatory bodies: Obtaining necessary permits and approvals from various regulatory bodies can be a lengthy and costly process.
- Potential for delays and appeals: Appeals and legal challenges can further delay projects and increase costs.
Conclusion
Offshore wind farm development is undoubtedly a costly undertaking, involving high CAPEX and significant OPEX. Specialized equipment, challenging installation conditions, and complex regulatory processes all contribute to the high price tag. However, the long-term benefits of clean energy production, reduced carbon emissions, and potential economic opportunities associated with offshore wind farm development are substantial. Investing in efficient project management, technological advancements (such as improved turbine designs and floating platforms), and streamlined regulatory processes are crucial to mitigate costs and accelerate the growth of this vital sector in the energy transition. To further explore ways to reduce the costs associated with offshore wind farm development, continued research into innovative technologies and best practices is essential. Let's work together to make offshore wind energy a more cost-effective and widely adopted renewable energy source.

Featured Posts
-
 Ufc Espn 67 Sandhagen Vs Figueiredo Fight Night Results And Analysis
May 04, 2025
Ufc Espn 67 Sandhagen Vs Figueiredo Fight Night Results And Analysis
May 04, 2025 -
 New Parent Max Verstappen Ready For Miami Gp After Babys Arrival
May 04, 2025
New Parent Max Verstappen Ready For Miami Gp After Babys Arrival
May 04, 2025 -
 Final Destination Franchise Box Office Success Ranking All Films Including Bloodline
May 04, 2025
Final Destination Franchise Box Office Success Ranking All Films Including Bloodline
May 04, 2025 -
 Transparency Concerns Rise Over French Defense Policy Decisions Under Current Pm
May 04, 2025
Transparency Concerns Rise Over French Defense Policy Decisions Under Current Pm
May 04, 2025 -
 Bra Smuggling Case Featured In Thursdays Court Roundup
May 04, 2025
Bra Smuggling Case Featured In Thursdays Court Roundup
May 04, 2025
