Reducing Carbon Footprint: The Role Of Wind-Powered Trains In Sustainable Transportation

Table of Contents
The Environmental Benefits of Wind-Powered Trains
The most significant advantage of wind-powered trains lies in their potential to drastically reduce the environmental impact of railway transportation.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Switching from fossil fuel-powered trains to wind-powered alternatives leads to a considerable reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Studies suggest a potential reduction of up to 90% in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, depending on the specific implementation and wind conditions. This makes wind-powered trains a cornerstone of green transportation and a crucial step towards a sustainable railway system. The transition to clean energy trains significantly lessens our reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Improved Air Quality
Besides reducing greenhouse gas emissions, wind-powered trains also contribute to significantly improved air quality. Fossil fuel-powered locomotives release harmful pollutants like particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which negatively impact public health. By eliminating these emissions, wind-powered trains create cleaner air in and around railway lines, leading to improved respiratory health and overall well-being for communities near railway tracks. The benefits of clean energy trains extend beyond climate change mitigation to encompass immediate improvements in environmental and public health.
- Studies show a potential reduction of up to 80% in particulate matter emissions compared to diesel trains.
- Areas with significant wind power integration for railways have reported notable improvements in air quality indices.
- Reduced respiratory illnesses and other health problems linked to air pollution are observed in communities near wind-powered rail lines.
Technological Feasibility and Infrastructure
Integrating wind energy into railway systems is technologically feasible, though it requires careful planning and implementation.
Wind Turbine Integration
Several methods exist for integrating wind turbines into railway infrastructure. One approach involves installing wind turbines alongside the railway tracks, harnessing wind energy to generate electricity directly for the train network. Another involves mounting smaller wind turbines on the train carriages themselves, although this approach presents engineering challenges. Visual aids, such as diagrams illustrating these integration methods, can better demonstrate the possibilities of wind turbine technology and renewable energy integration in railway electrification.
Energy Storage and Grid Integration
The intermittent nature of wind power requires robust energy storage solutions and smart grid integration. Batteries, pumped hydro storage, and other energy storage technologies play a vital role in ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply for the trains, even when wind speeds are low. Effective energy management systems are crucial to optimize the use of wind energy and minimize reliance on the traditional power grid.
- Large-scale battery storage systems can provide backup power during periods of low wind.
- Smart grid integration allows for efficient management of energy supply and demand.
- Integrating wind energy into existing railway infrastructure necessitates careful planning and investment in upgraded grids.
Economic Considerations and Viability
While the initial investment for wind-powered train technology is significant, a cost-benefit analysis reveals compelling economic advantages.
Initial Investment Costs
Implementing wind-powered train systems requires substantial upfront investment in wind turbine installations, energy storage solutions, and grid upgrades. However, these initial costs are offset by long-term operational savings and the environmental benefits, creating a positive return on investment (ROI) over time. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is needed to accurately evaluate the economic viability of wind-powered trains compared to conventional methods.
Long-Term Operational Costs
The long-term operational costs of wind-powered trains are substantially lower than those of fossil fuel-powered trains. The reduced reliance on expensive fossil fuels results in significant savings in energy costs. Furthermore, the lifecycle cost analysis often favors wind power due to lower maintenance requirements compared to traditional diesel or electric engines. Government subsidies and incentives for sustainable infrastructure projects further enhance the economic viability.
- Reduced fuel costs represent a major factor in long-term savings.
- Lower maintenance costs compared to traditional locomotives offer economic advantages.
- Government incentives and carbon tax schemes can make wind-powered trains even more economically attractive.
Overcoming Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the promising potential, several challenges need to be addressed for widespread adoption of wind-powered trains.
Intermittency of Wind Power
The intermittent nature of wind power remains a key challenge. Hybrid systems, combining wind energy with other renewable sources or traditional power grids, help mitigate this problem. Advanced energy management systems and smart grids are essential for optimizing the utilization of wind energy and maintaining grid stability. Technological advancements are continuously improving the reliability and efficiency of wind power integration.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Public awareness and acceptance are crucial for the successful implementation of wind-powered trains. Effective public awareness campaigns and community engagement initiatives are needed to address concerns and promote the benefits of this sustainable transportation initiative. Transparency and open communication about the technology and its impact will foster public support.
- Improved forecasting models can enhance the predictability of wind energy production.
- Public education initiatives can alleviate concerns about the visual impact of wind turbines.
- Collaborative efforts between governments, industries and communities are needed to ensure acceptance.
Conclusion
Wind-powered trains offer a compelling solution for reducing the carbon footprint of the railway sector. Their environmental benefits, including significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality, are undeniable. While initial investments are needed, long-term operational cost savings and the potential for government incentives make this a financially viable option. By addressing the challenges related to wind power intermittency and public perception, we can pave the way for widespread adoption of wind-powered rail transport and eco-friendly railway solutions. We urge readers to learn more about sustainable transportation options and support initiatives aimed at developing and implementing wind-powered trains as a crucial step towards a greener future. Let's embrace sustainable train technology and build a more sustainable tomorrow.

Featured Posts
-
 Paramount Leaders Considered 20 Million Trump Lawsuit Settlement Exclusive Details
May 03, 2025
Paramount Leaders Considered 20 Million Trump Lawsuit Settlement Exclusive Details
May 03, 2025 -
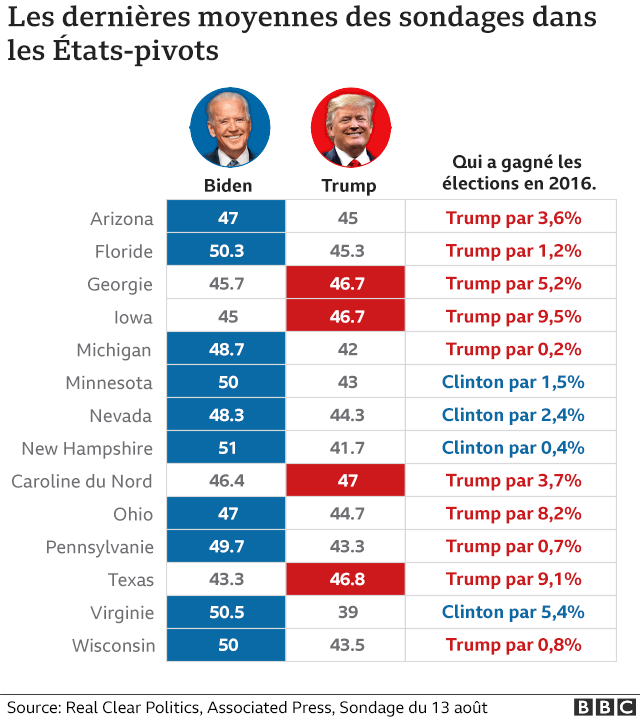 Rumeurs D Ingerence Macron Et L Election Du Prochain Pape
May 03, 2025
Rumeurs D Ingerence Macron Et L Election Du Prochain Pape
May 03, 2025 -
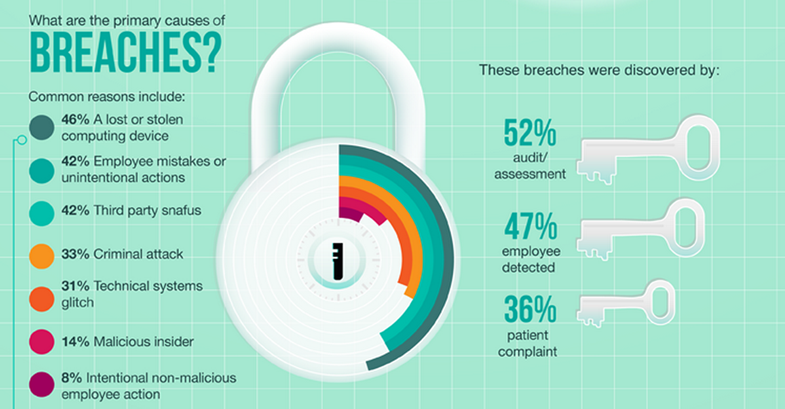 Data Breaches Cost T Mobile 16 Million A Three Year Security Breakdown
May 03, 2025
Data Breaches Cost T Mobile 16 Million A Three Year Security Breakdown
May 03, 2025 -
 Chaos On Bbcs Celebrity Traitors Last Minute Sibling Withdrawals
May 03, 2025
Chaos On Bbcs Celebrity Traitors Last Minute Sibling Withdrawals
May 03, 2025 -
 Farages Nat West Debanking Case Resolved Settlement Reached
May 03, 2025
Farages Nat West Debanking Case Resolved Settlement Reached
May 03, 2025
