Rising Rainfall Amounts In Western Massachusetts Due To Climate Change
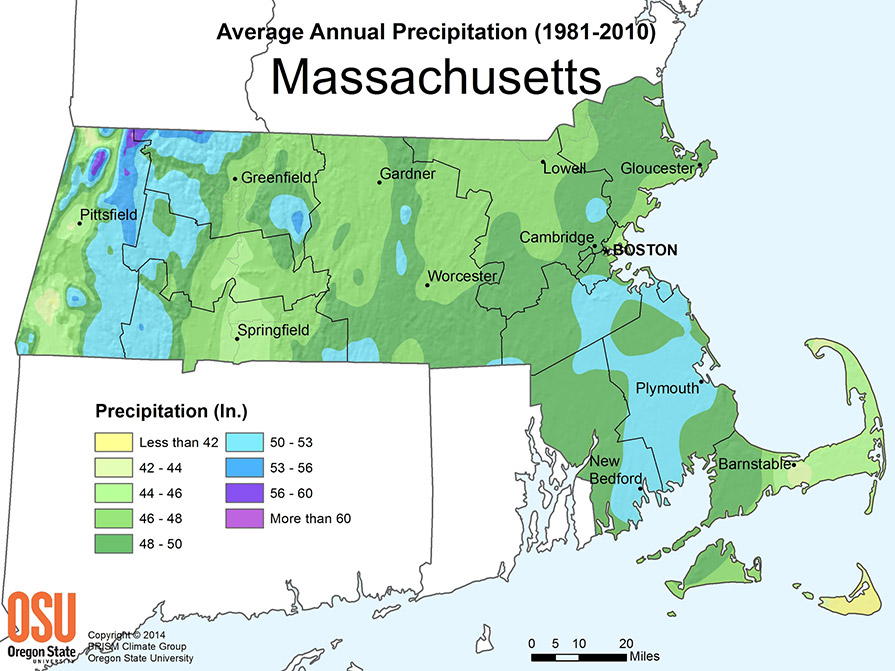
Table of Contents
Increased Precipitation: Evidence and Trends
Data from the past several decades paints a clear picture: Western Massachusetts is experiencing significantly higher rainfall amounts. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the United States Geological Survey (USGS) have collected extensive data showcasing this trend. For example, analysis of weather stations in cities like Pittsfield and Northampton reveals a consistent increase in average annual rainfall.
(Insert graph/chart here showing average annual rainfall increase in Western MA over the past 30-50 years)
Specific areas within Western Massachusetts, particularly those in the Berkshires, have witnessed the most dramatic increases. This is evidenced by:
- Average annual rainfall increase: A documented increase of X% over the past Y years (cite specific NOAA/USGS data).
- Number of extreme rainfall events: A rise in the number of days exceeding Z inches of rainfall per year (cite specific NOAA/USGS data).
- Changes in rainfall intensity: A noticeable increase in the intensity of downpours, leading to more rapid runoff and increased flooding risk.
Climate Change as the Driving Force
The scientific consensus firmly links the observed increase in precipitation in Western Massachusetts to climate change. Warmer temperatures, a direct consequence of increased greenhouse gas emissions, lead to a greater capacity of the atmosphere to hold water vapor. This heightened capacity translates into more intense and frequent rainfall events.
Furthermore, shifts in atmospheric circulation patterns, including alterations to the jet stream, are influencing weather systems affecting Western Massachusetts. These changes contribute to more persistent and wetter weather patterns in the region.
- The Greenhouse Effect: The accumulation of greenhouse gases traps heat, warming the planet and increasing atmospheric moisture.
- Climate Model Predictions: Numerous climate models predict a continued increase in precipitation for Western Massachusetts in the coming decades (cite specific climate model studies and their projections).
- Changes in Snowfall: The shift towards less snowfall and more rain, even in winter months, contributes to a greater overall annual water volume.
Impacts of Increased Rainfall on Western Massachusetts
The consequences of these rising rainfall amounts are far-reaching and impact various aspects of life in Western Massachusetts.
- Infrastructure Damage: Heavier rainfall leads to increased erosion, road damage, and potential failures in aging infrastructure like bridges and culverts.
- Agricultural Impacts: Intense rainfall can damage crops, lead to soil erosion, and affect yields, impacting the regional economy.
- Ecological Disruption: Changes in water flow regimes can alter habitats, affecting sensitive ecosystems and wildlife populations.
- Increased Flooding: More frequent and severe flooding events result in property damage, displacement, and economic losses. (Include examples of recent flooding events and their associated costs).
- Water Quality: Increased runoff can lead to pollution of water sources, impacting both drinking water quality and aquatic life.
- Tourism and Recreation: Severe weather events can disrupt tourism and recreational activities, impacting the local economy.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Addressing the challenge of rising rainfall amounts in Western Massachusetts requires a two-pronged approach: mitigation and adaptation.
Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation are crucial steps.
Adaptation: Implementing strategies to manage and adapt to the increased rainfall is equally important. This includes:
- Improved Drainage Systems: Upgrading existing drainage infrastructure to handle increased water volumes.
- Flood Control Measures: Investing in flood control measures such as levees, retention ponds, and improved flood warning systems.
- Community Planning: Developing comprehensive land-use plans that account for increased flood risks.
- Individual Actions: Reducing individual carbon footprints through sustainable practices.
The roles of local, state, and federal governments are vital in coordinating and implementing these mitigation and adaptation strategies. Community-based initiatives play a crucial role in raising awareness, promoting preparedness, and fostering collaboration.
Conclusion: Addressing Rising Rainfall Amounts in Western Massachusetts
The evidence is clear: rising rainfall amounts in Western Massachusetts are a significant concern directly linked to climate change. The impacts are substantial, affecting infrastructure, agriculture, ecosystems, and the overall well-being of the community. Addressing this challenge requires urgent action on both mitigation and adaptation fronts. We must reduce greenhouse gas emissions to curb climate change's effects while simultaneously investing in infrastructure improvements and community preparedness to adapt to the increased rainfall we are already experiencing. Learn more about climate change in Western Massachusetts, support local initiatives focused on climate adaptation and mitigation, and engage in informed discussions about the future of our region. Let's work together to address increased rainfall in Western Massachusetts and build a more resilient future.

Featured Posts
-
 Mondays Metro Detroit Weather Chilly Start Clear And Sunny Afternoon
May 31, 2025
Mondays Metro Detroit Weather Chilly Start Clear And Sunny Afternoon
May 31, 2025 -
 Un Jour En Mer Experiences Et Conseils Pour Naviguer
May 31, 2025
Un Jour En Mer Experiences Et Conseils Pour Naviguer
May 31, 2025 -
 Life Changing Impact Duncan Bannatynes Philanthropy In Morocco
May 31, 2025
Life Changing Impact Duncan Bannatynes Philanthropy In Morocco
May 31, 2025 -
 Chainalysis And Alterya Merge Strengthening Blockchain Ai Capabilities
May 31, 2025
Chainalysis And Alterya Merge Strengthening Blockchain Ai Capabilities
May 31, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Leadership A Critical Analysis
May 31, 2025
Elon Musks Leadership A Critical Analysis
May 31, 2025
