Rosy Apple Aphid Threatens Apple Harvest: 10-30% Reduction Predicted
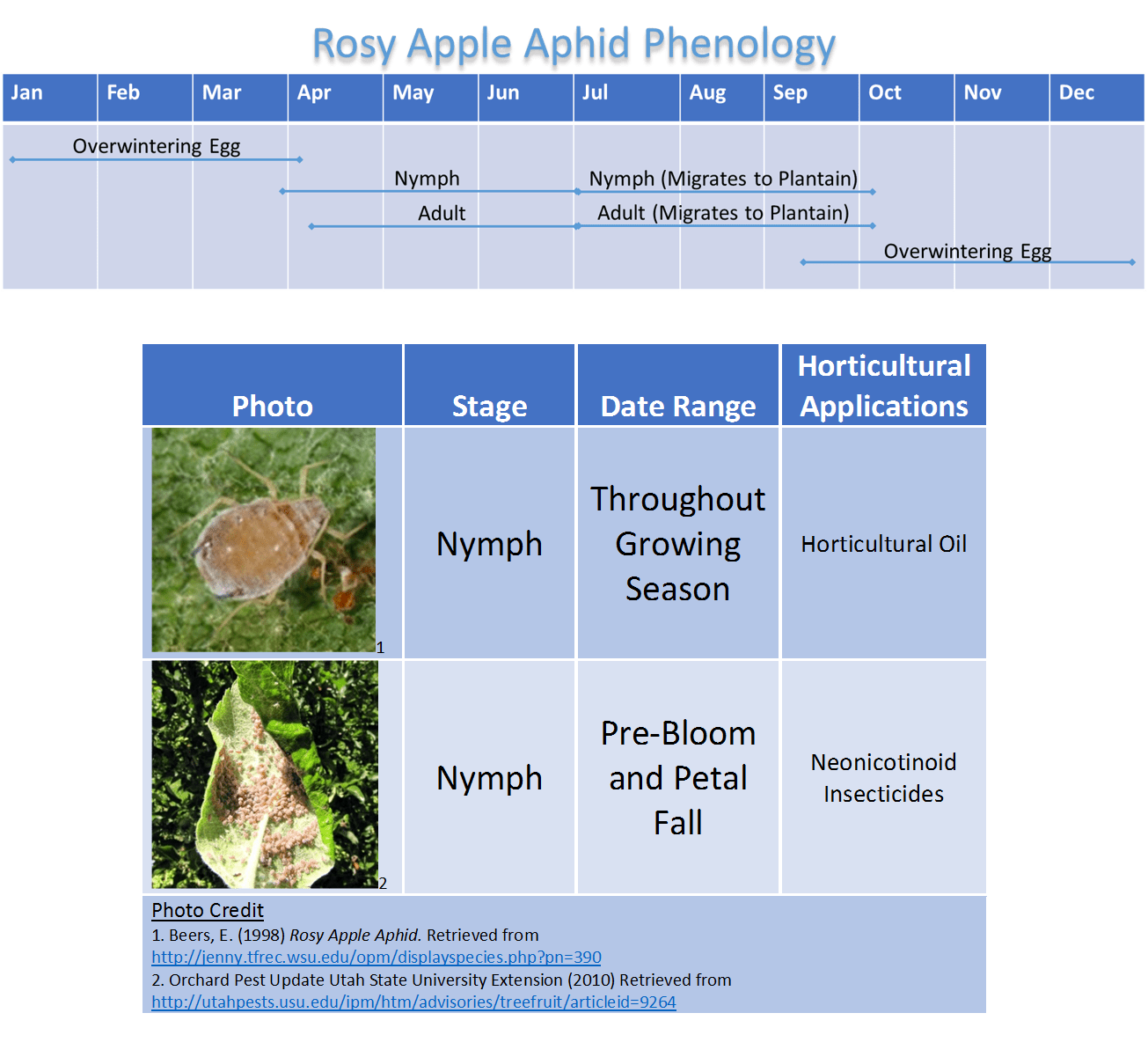
Table of Contents
Understanding the Rosy Apple Aphid Threat
Identifying Rosy Apple Aphids
The rosy apple aphid ( Dysaphis plantaginea) is easily identifiable by its distinctive pinkish-red to reddish-brown coloration, although its color can vary. Nymphs are smaller and lighter in color. They are pear-shaped, soft-bodied insects, typically measuring only a few millimeters in length. Distinguishing them from other aphids requires close observation.
- Appearance: Pinkish-red to reddish-brown body, pear-shaped, soft body.
- Lifecycle Stages: The rosy apple aphid undergoes a complete metamorphosis, including egg, nymph, and adult stages.
- Host Plants: While they primarily infest apple trees (Malus domestica), they may also occasionally feed on other plants in the Rosaceae family.
Lifecycle and Reproduction of Rosy Apple Aphids
Rosy apple aphids reproduce rapidly, both sexually and asexually. They overwinter as eggs laid on apple twigs. In spring, these eggs hatch into nymphs which feed and mature into adult aphids. These adults then reproduce asexually, producing large numbers of offspring without mating. This rapid reproduction contributes to the exponential growth of their populations.
- Egg Laying: Eggs are laid on apple tree twigs in autumn.
- Nymph Development: Nymphs go through several molts before reaching adulthood.
- Generation Times: Multiple generations can occur in a single growing season, depending on climate conditions.
- Factors Affecting Population Growth: Warmer temperatures and moderate humidity accelerate population growth.
Damage Caused by Rosy Apple Aphids
Rosy apple aphids inflict significant damage to apple trees and fruit. Their feeding activities cause leaf curling, stunted growth, and reduced fruit quality. The honeydew they excrete provides a substrate for the growth of sooty mold, further impacting the appearance and marketability of the fruit.
- Effects on Leaves: Honeydew excretion leads to sticky leaves and the growth of sooty mold, hindering photosynthesis. Leaf curling and distortion are also common.
- Effects on Fruit: Infested apples can be deformed, smaller than normal, and have reduced quality, making them unsuitable for sale.
- Impact on Overall Tree Health: Severe infestations can weaken trees, making them more susceptible to other diseases and pests.
Managing Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations
Monitoring for Rosy Apple Aphids
Early detection is critical for effective management. Regular monitoring helps identify infestations before they cause significant damage.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine apple tree leaves and twigs for the presence of aphids.
- Sticky Traps: Place sticky traps near apple trees to capture aphids and monitor their populations.
- Pheromone Traps: Pheromone traps can be used to attract and capture male aphids for monitoring purposes.
- Scouting Methods: Regularly inspect a representative sample of trees within the orchard.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a sustainable approach that emphasizes prevention and environmentally friendly control methods.
- Biological Control: Encourage the presence of natural enemies like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps, which prey on rosy apple aphids.
- Cultural Control: Proper pruning to improve air circulation, removal of infested leaves and twigs, and sanitation practices help reduce aphid populations.
- Natural Pesticides: Neem oil and insecticidal soaps can be effective in controlling rosy apple aphids, particularly in early stages of infestation.
Chemical Control (When Necessary)
Chemical control should only be used as a last resort, after other IPM methods have failed. Always follow label instructions carefully.
- Types of Insecticides: Several insecticides are effective against rosy apple aphids, but resistance can develop. Rotate insecticides to prevent resistance.
- Application Timing: Apply insecticides when aphid populations are high, targeting nymphs.
- Safety Measures: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling insecticides.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental impact of any insecticide used and select the least harmful option.
Economic Impact of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations
Impact on Apple Production and Prices
The substantial reduction in apple yields caused by rosy apple aphid infestations has significant financial repercussions for apple growers and consumers.
- Estimated Losses in Apple Production: The predicted 10-30% reduction in yield translates to substantial losses for apple farmers.
- Potential Price Increases: Reduced supply can lead to increased prices for consumers.
- Impact on Apple Industry Profits: The overall profitability of the apple industry is affected by these losses.
Long-Term Implications for the Apple Industry
Repeated rosy apple aphid infestations pose a long-term threat to the sustainability of apple production.
- Potential for Reduced Orchard Productivity: Chronic infestations can weaken trees, leading to reduced productivity over time.
- Economic Viability for Apple Farmers: Farmers may face economic hardship due to consistent crop losses.
- Need for Sustainable Management Strategies: Developing and implementing sustainable management strategies is crucial for the long-term health and profitability of the apple industry.
Conclusion:
The rosy apple aphid presents a serious threat to apple production, with potential yield reductions of 10-30%. Early detection through proactive monitoring, coupled with the implementation of integrated pest management strategies, is crucial to mitigating the damage. Failing to address this pest effectively will have long-term economic implications for the apple industry. Learn more about effective rosy apple aphid control and protection strategies. Implement proactive monitoring and management practices to protect your apple harvest from the devastating effects of the rosy apple aphid. Consult with local agricultural experts for further guidance on rosy apple aphid management in your region.

Featured Posts
-
 Anazitontas Tin Istoria I Teleti Toy Ieroy Niptiros Sta Ierosolyma
May 19, 2025
Anazitontas Tin Istoria I Teleti Toy Ieroy Niptiros Sta Ierosolyma
May 19, 2025 -
 Is This The End For A Popular Saturday Night Live Star
May 19, 2025
Is This The End For A Popular Saturday Night Live Star
May 19, 2025 -
 Mark Rylance Criticises Music Festivals Impact On London Parks
May 19, 2025
Mark Rylance Criticises Music Festivals Impact On London Parks
May 19, 2025 -
 Nqabt Almhndsyn Bghzt Ajtmaeat Mtwaslt Lwde Khtt Iemar
May 19, 2025
Nqabt Almhndsyn Bghzt Ajtmaeat Mtwaslt Lwde Khtt Iemar
May 19, 2025 -
 Ufc Vegas 106 Expert Picks Burns Vs Morales Analysis And Betting Predictions
May 19, 2025
Ufc Vegas 106 Expert Picks Burns Vs Morales Analysis And Betting Predictions
May 19, 2025
