S&P 500 Volatility: Is Downside Insurance Right For You?
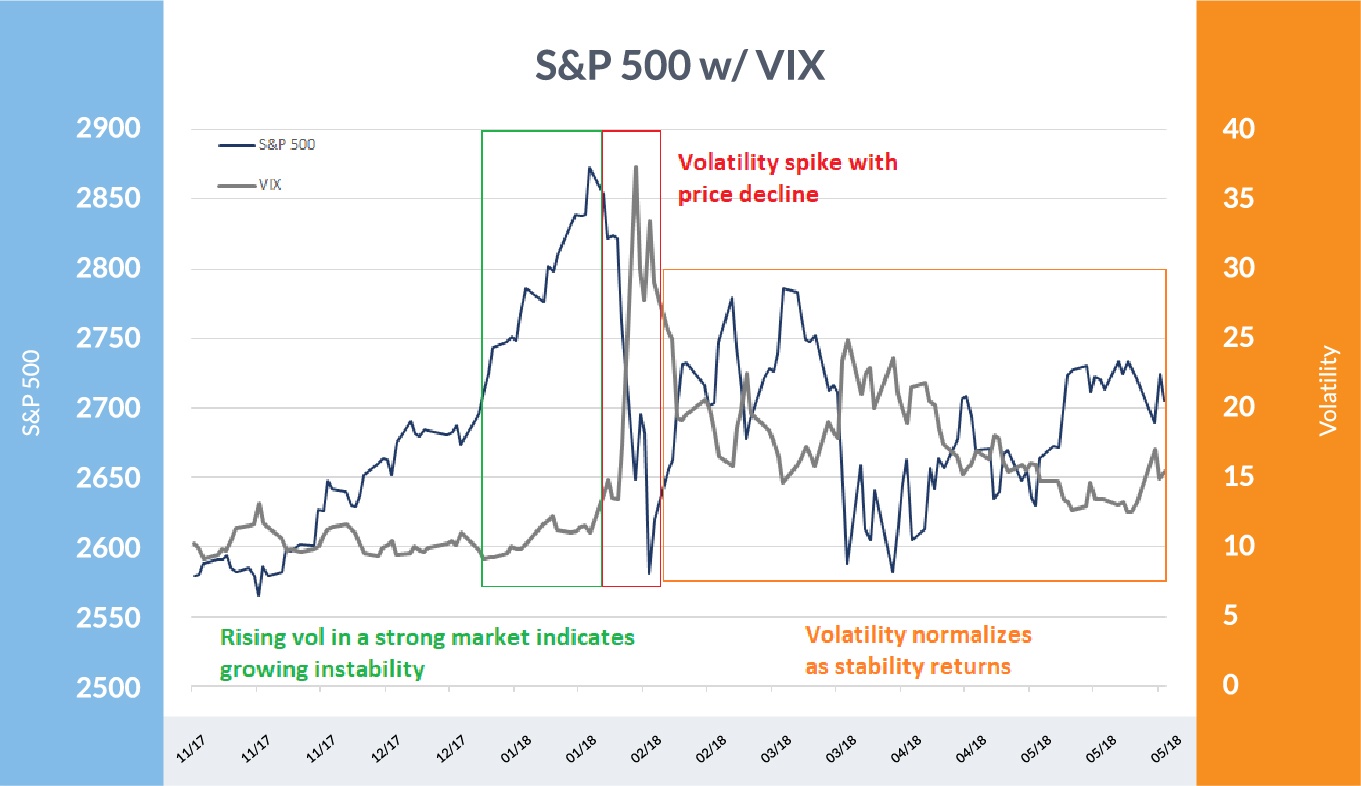
Table of Contents
Understanding S&P 500 Volatility
Historical Volatility and Market Corrections
The S&P 500's history is punctuated by periods of both exuberant growth and sharp corrections. For example, the dot-com bubble burst in 2000 and the 2008 financial crisis led to significant declines. Analyzing historical data reveals recurring patterns of volatility.
- Statistical Evidence: While long-term trends show positive growth, the standard deviation of annual returns demonstrates considerable fluctuation. This means returns can deviate significantly from the average, leading to both substantial gains and losses. Charts illustrating these fluctuations can be found readily online from reputable financial sources.
- Contributing Factors: Volatility is influenced by a myriad of factors, including:
- Economic Indicators: GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment figures all impact market sentiment and investor confidence.
- Geopolitical Events: International conflicts, political instability, and unexpected global events can trigger significant market reactions.
- Interest Rate Changes: Federal Reserve decisions on interest rates directly impact borrowing costs and investment strategies, influencing market volatility.
Measuring Volatility
Several metrics gauge S&P 500 volatility. Understanding these helps investors assess risk.
- Standard Deviation: This statistical measure quantifies the dispersion of returns around the average. A higher standard deviation indicates greater volatility.
- Beta: Beta measures the volatility of an asset relative to the overall market. A beta of 1 signifies similar volatility to the market; a beta greater than 1 indicates higher volatility.
- VIX Index (Volatility Index): Often called the "fear gauge," the VIX reflects market expectations of near-term volatility. A higher VIX suggests investors anticipate increased market fluctuations. High VIX readings often precede market corrections, while low readings suggest a relatively calm market environment.
Strategies for Managing S&P 500 Volatility
Diversification
Diversification is a cornerstone of risk management. Spreading investments across different asset classes reduces overall portfolio volatility.
- Asset Allocation: A balanced portfolio might include stocks, bonds, real estate, and international equities. The optimal allocation depends on your risk tolerance and investment timeline.
- Example: A portfolio heavily weighted in S&P 500 index funds is inherently more volatile than one diversified across various asset classes. During market downturns, the diversified portfolio is likely to experience less dramatic losses.
Hedging with Options
Options contracts offer sophisticated strategies for managing risk. Protective puts are a common approach to provide downside protection.
- Protective Puts: Buying a put option gives the holder the right to sell a specific asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) before a certain date (the expiration date). This acts as insurance against losses if the market declines below the strike price.
- Costs and Benefits: Protective puts have a cost (the premium paid for the option). This cost reduces potential profits during market upturns but limits losses during downturns.
- Alternative Strategies: Covered call writing offers a different approach, generating income but limiting upside potential.
Inverse ETFs
Inverse ETFs aim to profit from market declines by providing returns inversely correlated with the underlying index. However, these instruments are inherently risky.
- Functionality: An inverse S&P 500 ETF would rise in value when the S&P 500 falls. These are best suited for short-term, speculative trading rather than long-term investing.
- Significant Risks: Inverse ETFs can amplify losses if the market moves unexpectedly in the opposite direction. These are not suitable for risk-averse investors.
Assessing Your Risk Tolerance and Investment Goals
Defining Your Investment Timeline
Your investment horizon significantly impacts your risk tolerance.
- Long-Term Investors: Those investing for retirement (20+ years) generally have a higher risk tolerance and can weather market fluctuations more easily. They may prioritize growth over immediate downside protection.
- Short-Term Investors: Those with shorter time horizons (e.g., saving for a down payment) may require more downside protection to safeguard their capital.
Determining Your Risk Profile
Understanding your risk profile is crucial for choosing suitable investment strategies.
- Risk Assessment Tools: Online questionnaires and financial advisor consultations can help determine your risk tolerance.
- Conservative Investors: Those with a low risk tolerance might benefit significantly from downside insurance strategies to protect their capital.
- Aggressive Investors: Those comfortable with higher risk might choose to forgo downside protection to maximize potential returns. The trade-off between risk and reward is fundamental in investment decisions.
Conclusion
Managing S&P 500 volatility requires a thoughtful approach. Understanding historical fluctuations, employing diversification strategies, and considering options like protective puts or inverse ETFs (with caution) are all potential components of a well-rounded strategy. However, the decision of whether or not to employ downside protection strategies for S&P 500 investments hinges on your individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and financial goals. Carefully consider your investment timeline and risk profile before making any decisions. Conduct thorough research and consult with a qualified financial advisor to determine the best approach for managing S&P 500 volatility and securing your financial future. Remember, implementing the right S&P 500 downside insurance can significantly impact your investment success.

Featured Posts
-
 Yate Explosion Live Updates From The Scene Of The Inferno
Apr 30, 2025
Yate Explosion Live Updates From The Scene Of The Inferno
Apr 30, 2025 -
 The Reasons Behind Beyonce And Jay Z Keeping Sir Carter Out Of The Public Eye
Apr 30, 2025
The Reasons Behind Beyonce And Jay Z Keeping Sir Carter Out Of The Public Eye
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Da Li Je Blu Ajvi Nova Bijonse Reakcije Na Super Bowl Nastup
Apr 30, 2025
Da Li Je Blu Ajvi Nova Bijonse Reakcije Na Super Bowl Nastup
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Shopping With Chat Gpt Open Ais Disruptive Technology
Apr 30, 2025
Shopping With Chat Gpt Open Ais Disruptive Technology
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Disneys Abc News Among Major Departments Hit By Layoffs
Apr 30, 2025
Disneys Abc News Among Major Departments Hit By Layoffs
Apr 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Johnstons Record Setting Goal Fuels Stars 6 2 Victory Over Avalanche
Apr 30, 2025
Johnstons Record Setting Goal Fuels Stars 6 2 Victory Over Avalanche
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Panthers Second Period Surge Propels Them Past Senators Tkachuk Leads The Charge
Apr 30, 2025
Panthers Second Period Surge Propels Them Past Senators Tkachuk Leads The Charge
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Obnovlenniy Prognoz N Kh L Kogda Ovechkin Prevzoydet Grettski
Apr 30, 2025
Obnovlenniy Prognoz N Kh L Kogda Ovechkin Prevzoydet Grettski
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Series Win For Yankees Judge And Goldschmidts Crucial Roles
Apr 30, 2025
Series Win For Yankees Judge And Goldschmidts Crucial Roles
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Kansas City Royals Win Thriller Garcias Blast And Witts Double Secure Victory
Apr 30, 2025
Kansas City Royals Win Thriller Garcias Blast And Witts Double Secure Victory
Apr 30, 2025
