School Desegregation Order Terminated: A New Era For Education?

Table of Contents
The History and Impact of the Terminated Desegregation Order
The Indianapolis desegregation order, implemented in the wake of Brown v. Board of Education (1954), aimed to dismantle legally mandated segregation in the city's schools. It mandated specific measures like busing and school redistricting to achieve racial balance and provide equal educational opportunities for all students, regardless of race.
- Key Dates and Milestones: The order's implementation faced significant resistance, leading to numerous legal challenges and ongoing monitoring by the courts. Key dates include the initial ruling (1970s), periods of significant progress and setbacks, and the final ruling in 2023 that terminated the order.
- Initial Successes and Challenges: While the order initially achieved some degree of racial integration, challenges persisted. These included resistance from some communities, difficulties in maintaining racial balance amidst shifting demographics, and ongoing disparities in school resources and academic achievement.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects are complex and multifaceted. While the order undeniably contributed to increased opportunities for some minority students, significant racial and socioeconomic achievement gaps remain. Data comparing student demographics and academic achievement before and after the order's implementation would paint a clearer picture of its overall long-term impact, although such data is often contested and interpreted differently.
Potential Consequences of Termination
The termination of the desegregation order raises serious concerns about the potential for increased school segregation.
-
Increased Segregation Concerns: The lifting of the order may lead to a resurgence of racial and socioeconomic segregation in Indianapolis schools. This is particularly concerning given the existing patterns of residential segregation and the resulting concentration of disadvantaged students in specific schools.
- Analysis of Potential Demographic Shifts: Future demographic analysis is crucial to monitor school populations and identify potential trends toward re-segregation. Data on student enrollment by race and socioeconomic status will be closely watched.
- Impact on Access to Resources: Increased segregation could exacerbate existing inequalities in access to high-quality teachers, advanced courses, and other educational resources. Minority students in predominantly minority schools might face disproportionately limited opportunities.
- Exacerbation of Achievement Gaps: The potential for re-segregation poses a significant threat to closing the persistent achievement gap between white and minority students. Segregated schools often lack the resources and support needed to effectively address the unique challenges faced by disadvantaged students.
- Role of Housing Segregation: The role of broader societal factors, such as housing segregation and socioeconomic disparities, cannot be ignored. Addressing these underlying issues is vital to preventing school re-segregation.
-
Opportunities for Educational Reform: Conversely, the termination could, in theory, offer opportunities for educational reform. Local control could empower individual schools and communities to develop innovative programs that address their specific needs.
- Innovative Educational Programs: This could lead to the development of tailored programs that promote diversity and inclusion, fostering a more equitable learning environment for all students.
- Community Engagement: Increased local control could facilitate greater community engagement and parental involvement in shaping school policies, leading to a more responsive and accountable educational system.
- Addressing Specific Needs: Schools could focus more effectively on addressing the unique academic, social, and emotional needs of diverse student populations.
The Role of the Courts and Future Legal Challenges
The legal basis for the termination of the Indianapolis desegregation order is likely to face scrutiny. The decision itself may be challenged in court.
- Legal Ramifications of Termination: The legal arguments surrounding the termination will likely revolve around the interpretation of existing Supreme Court precedents on school desegregation.
- Arguments for and Against: Supporters of the termination might argue that the order has outlived its usefulness and that local control is necessary for effective educational reform. Opponents will likely argue that the termination threatens to reverse decades of progress towards racial integration and educational equity.
- Potential Future Lawsuits: Further legal actions are likely, potentially involving challenges to the constitutionality of the termination or claims of discriminatory practices in the re-allocation of resources.
- Role of the Supreme Court: The Supreme Court's future role in shaping the legal landscape of school desegregation will be closely watched.
Moving Forward: Ensuring Educational Equity
Despite the termination of the desegregation order, the pursuit of educational equity must continue. Proactive strategies are needed to ensure all students have equal opportunities.
- Strategies for Promoting Inclusive Education: A multi-pronged approach is required, including robust diversity and inclusion programs, equitable resource allocation, and high-quality teacher training.
- Effective Diversity and Inclusion Programs: Schools need to implement programs that actively promote intercultural understanding, respect, and equity, ensuring all students feel valued and included.
- Equitable Funding and Resource Allocation: Addressing systemic inequalities in school funding is crucial. Resources must be allocated fairly to ensure all schools, regardless of their student demographics, have the resources they need to provide a high-quality education.
- Equitable Access to High-Quality Education: This requires investment in infrastructure, technology, and high-quality teachers in all schools, particularly those serving disadvantaged communities.
- Teacher Training: Teacher training and professional development programs must prioritize cultural competency, inclusive pedagogy, and strategies for addressing the diverse learning needs of all students.
Conclusion
The termination of the Indianapolis school desegregation order presents a complex and multifaceted challenge. While it offers the potential for increased local control and tailored educational approaches, it also raises significant concerns about the potential for increased segregation and the exacerbation of existing achievement gaps. The central question – does this signal a new era for education? – remains open to interpretation, depending on how the community, schools, and policymakers respond to this pivotal moment. The potential for both regression and progress exists. The path forward necessitates a renewed commitment to equitable resource allocation, the implementation of robust diversity and inclusion programs, and a sustained focus on closing achievement gaps. Let's work together to ensure that the termination of this school desegregation order doesn't lead to a regression but instead inspires further progress towards true educational equity and school integration. Contact organizations like the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund for further information and ways to advocate for educational equality.

Featured Posts
-
 Aljbht Alwtnyt Tfasyl Wrqt Syasat Alastthmar Alaqtsadyt Aljdydt
May 03, 2025
Aljbht Alwtnyt Tfasyl Wrqt Syasat Alastthmar Alaqtsadyt Aljdydt
May 03, 2025 -
 Fortnite Servers Offline Planned Maintenance For Update 34 40
May 03, 2025
Fortnite Servers Offline Planned Maintenance For Update 34 40
May 03, 2025 -
 Chloe Kelly Returns To England Squad For Nations League
May 03, 2025
Chloe Kelly Returns To England Squad For Nations League
May 03, 2025 -
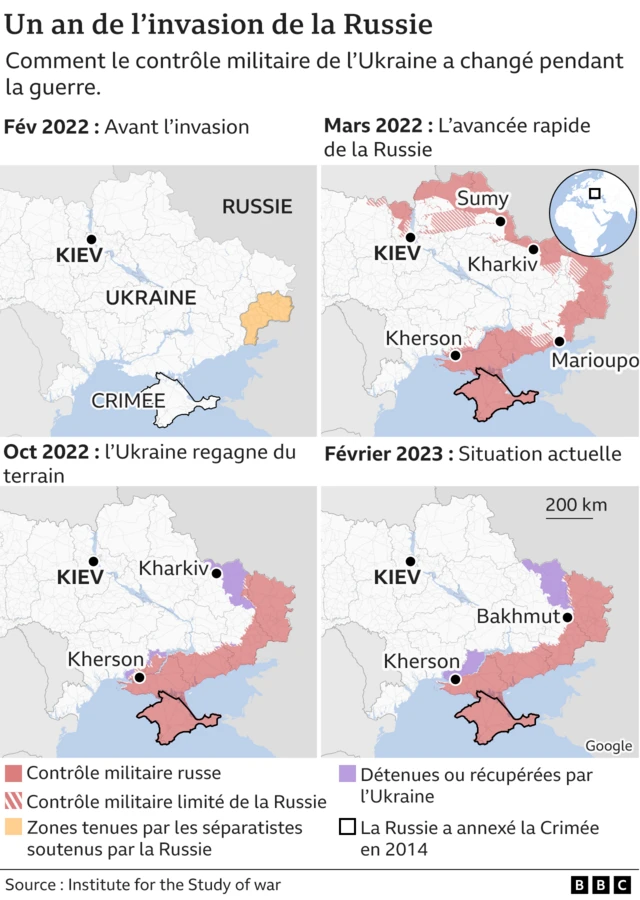 Pression Sur La Russie Macron Annonce De Nouvelles Mesures
May 03, 2025
Pression Sur La Russie Macron Annonce De Nouvelles Mesures
May 03, 2025 -
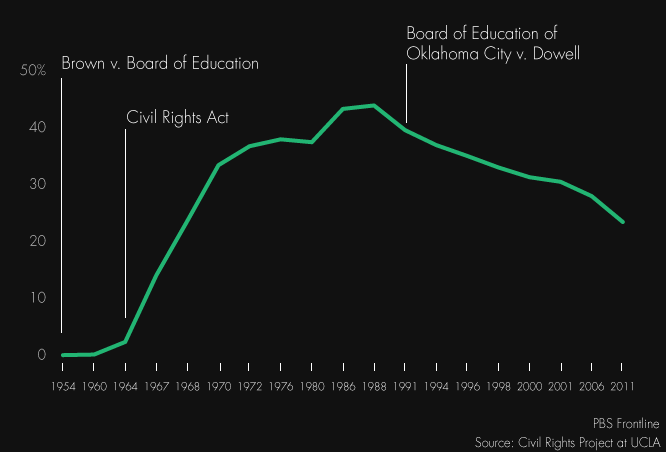 End Of School Desegregation Order Implications For Other Districts
May 03, 2025
End Of School Desegregation Order Implications For Other Districts
May 03, 2025
