School Suspensions: Harmful Effects And Effective Discipline Strategies
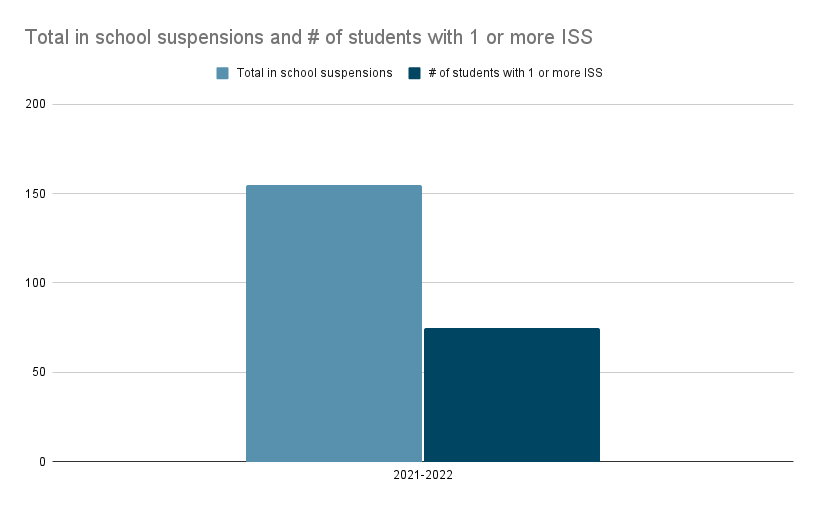
Table of Contents
The Detrimental Effects of School Suspensions
School suspensions, while seemingly a simple solution to disruptive behavior, carry significant negative consequences for students and the wider school community. The impact extends far beyond the immediate suspension period, creating a ripple effect that can hinder a student's academic, social, and emotional development.
Academic Impact
Suspensions significantly disrupt a student's learning journey. The time missed translates directly into missed classes, leading to a cascade of negative academic outcomes.
- Increased absenteeism and failing grades: Missing even a few days of school can result in falling behind on coursework, leading to lower grades and a potential decline in overall academic performance. This is particularly true for students already struggling academically.
- Difficulty catching up on missed work: The sheer volume of missed material can be overwhelming, making it challenging for students to catch up, even with extra help. This creates a sense of frustration and can lead to further disengagement from school.
- Negative impact on long-term academic success: Repeated suspensions create a cycle of academic setbacks, impacting graduation rates and future educational opportunities. The cumulative effect of missed learning can significantly hinder a student's long-term academic success.
Social and Emotional Impact
Beyond the academic consequences, school suspensions have profound social and emotional impacts on students. The isolation and stigma associated with suspension can damage a student's self-esteem and increase the risk of future behavioral problems.
- Increased feelings of alienation and isolation: Being removed from the school community can lead to feelings of isolation, loneliness, and alienation, further exacerbating existing emotional challenges.
- Damage to student-teacher relationships: Suspensions can strain the relationship between students and teachers, making it harder for students to seek help or support in the future.
- Higher likelihood of involvement in criminal activity: Research suggests a correlation between school suspension and increased involvement in criminal activity, highlighting the long-term societal consequences of this disciplinary approach.
Disproportionate Impact on Marginalized Students
A significant concern surrounding school suspensions is their disproportionate impact on marginalized students. Students of color, students with disabilities, and students from low-income families are suspended at significantly higher rates than their peers.
- Bias in disciplinary practices: Implicit bias in disciplinary practices can lead to harsher punishments for certain student populations, contributing to the disparities observed in suspension rates.
- Lack of access to support services: Students from marginalized communities often lack access to crucial support services, such as counseling and mental health support, which could help address underlying behavioral issues.
- The school-to-prison pipeline: The disproportionate suspension of marginalized students contributes to the school-to-prison pipeline, a system that funnels students from school disciplinary actions into the juvenile justice system.
Understanding the Root Causes of Misbehavior
To effectively address student misbehavior, it's crucial to understand the underlying causes. Suspensions often mask the deeper issues contributing to disruptive behavior, failing to address the root of the problem.
Identifying Underlying Issues
Misbehavior is rarely a simple matter of defiance. Often, it stems from a complex interplay of factors, including unmet needs, trauma, learning disabilities, and lack of support at home.
- Trauma-informed practices: Many students have experienced trauma, impacting their behavior and ability to regulate emotions. Trauma-informed practices are essential for creating a supportive learning environment.
- Early intervention and support services: Early identification and intervention are crucial for addressing underlying issues before they escalate into more serious behavioral problems. Providing access to support services, such as counseling and tutoring, can make a significant difference.
- Addressing learning disabilities and providing appropriate accommodations: Learning disabilities can significantly impact a student's ability to succeed academically, leading to frustration and behavioral issues. Providing appropriate accommodations and support can help students thrive.
The Role of the School Environment
The school environment itself plays a significant role in shaping student behavior. A negative or unsupportive school climate can contribute to disruptive behavior, while a positive and inclusive environment fosters positive behaviors.
- Creating a positive and inclusive school culture: A school culture that values respect, inclusivity, and empathy can create a safer and more supportive learning environment for all students.
- Improving teacher-student relationships: Strong teacher-student relationships are crucial for creating a positive learning environment and addressing behavioral issues proactively.
- Providing opportunities for student voice and participation: Giving students a voice and involving them in decision-making processes can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility, reducing disruptive behaviors.
Effective Alternative Discipline Strategies
Moving beyond punitive measures like suspensions requires embracing effective alternative discipline strategies that address the root causes of misbehavior and promote positive behavior change.
Restorative Justice Practices
Restorative justice focuses on repairing harm and building relationships. Instead of punishing students, it emphasizes accountability, reconciliation, and community involvement.
- Circle meetings and conflict resolution: Circle meetings provide a safe space for students to discuss conflicts, understand different perspectives, and find solutions together.
- Repairing harm caused by misbehavior: Restorative justice focuses on helping students understand the impact of their actions and making amends for any harm caused.
- Focus on accountability and reconciliation: It emphasizes accountability without resorting to punitive measures, focusing instead on helping students understand the consequences of their actions and make amends.
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS)
PBIS is a proactive approach to discipline that focuses on preventing misbehavior and teaching positive behaviors. It utilizes clear expectations, consistent consequences, and positive reinforcement.
- Clear expectations and consistent consequences: Establishing clear expectations and consistently applying consequences helps students understand what is expected of them and the repercussions of inappropriate behavior.
- Positive reinforcement and rewards: Positive reinforcement and rewards motivate students to exhibit positive behaviors and reinforce desired actions.
- Data-driven decision-making: Data-driven decision-making ensures that interventions are effective and tailored to the specific needs of students and the school community.
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Social-emotional learning (SEL) equips students with the skills they need to manage their emotions, build relationships, and make responsible decisions.
- Mindfulness and emotional regulation techniques: Teaching mindfulness and emotional regulation techniques helps students develop self-awareness and manage their emotions effectively.
- Conflict resolution and communication skills: Developing conflict resolution and communication skills empowers students to navigate disagreements peacefully and constructively.
- Empathy and perspective-taking: Encouraging empathy and perspective-taking helps students understand the viewpoints of others and build stronger relationships.
Conclusion
School suspensions, while seemingly a quick fix for disruptive behavior, ultimately inflict significant harm on students' academic progress, social-emotional development, and future prospects. Their disproportionate impact on marginalized groups further underscores the need for a paradigm shift in school discipline. By understanding the root causes of misbehavior and implementing evidence-based alternative strategies like restorative justice, PBIS, and SEL, we can create safer, more supportive, and more equitable learning environments for all students. Let's move beyond the harmful effects of school suspensions and embrace innovative, evidence-based approaches to discipline. Learn more about restorative justice, PBIS, and SEL to create safer and more supportive learning environments for all students. Let's work together to build schools where every child can thrive.

Featured Posts
-
 Xrp Ripple Price Under 3 A Critical Evaluation For Potential Investors
May 02, 2025
Xrp Ripple Price Under 3 A Critical Evaluation For Potential Investors
May 02, 2025 -
 Lara Crofts Fortnite Return New Leak Details
May 02, 2025
Lara Crofts Fortnite Return New Leak Details
May 02, 2025 -
 Review Of Splice Cay Fest On Film
May 02, 2025
Review Of Splice Cay Fest On Film
May 02, 2025 -
 Analyzing Ripples Xrp Explosive Growth A Path To Financial Freedom
May 02, 2025
Analyzing Ripples Xrp Explosive Growth A Path To Financial Freedom
May 02, 2025 -
 How Tonga Outplayed Si A Match Analysis And Highlights
May 02, 2025
How Tonga Outplayed Si A Match Analysis And Highlights
May 02, 2025
