Texas Measles: New Clusters Emerge Beyond Initial Outbreak
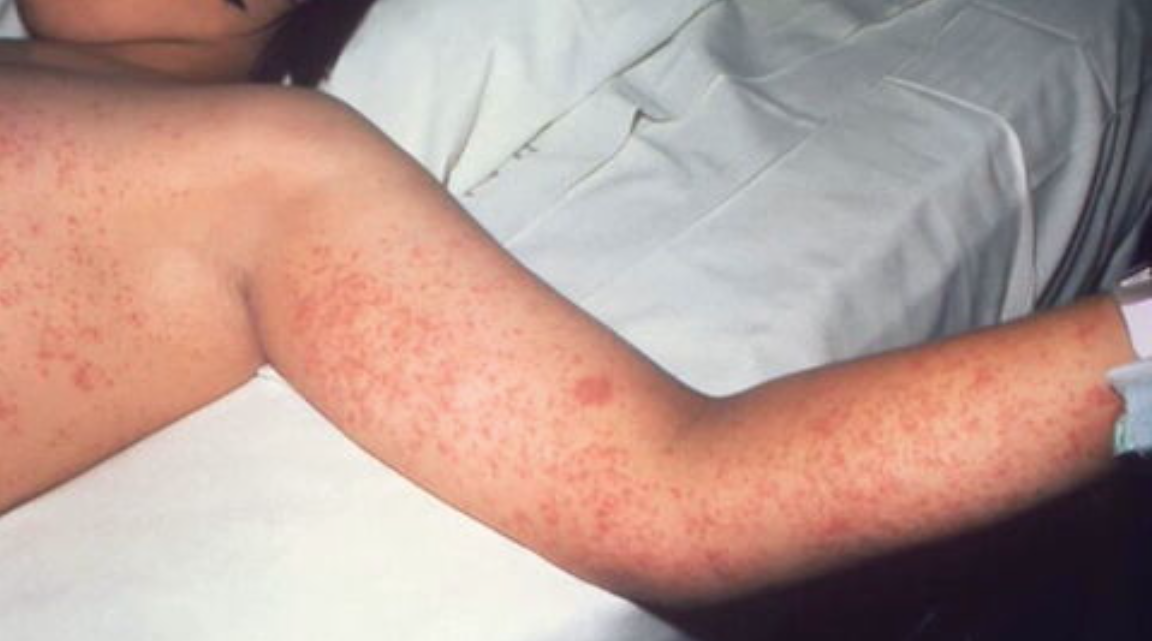
Table of Contents
Geographic Spread of the Texas Measles Outbreak
The Texas measles outbreak, initially concentrated in [mention initial affected area(s)], has unfortunately expanded its reach across the state. Understanding the geographic distribution of measles in Texas is crucial for effective containment. The emergence of new measles clusters in Texas necessitates a comprehensive approach to public health intervention. Using a Texas measles map (if available, insert map here; otherwise, describe visually the spread), we can better visualize the expanding problem.
- Specific Counties Affected: Recent increases in Texas measles cases have been reported in [List specific counties with recent increases. Example: Dallas, Tarrant, Harris counties]. This highlights the widespread nature of the outbreak.
- Correlation with Population Density and Vaccination Rates: Preliminary data suggests a correlation between higher population density areas and the spread of measles outbreak locations in Texas. Lower vaccination rates in certain communities may also be contributing factors. Further investigation is needed to confirm these correlations.
- Challenges in Containment: The geographical dispersion of the outbreak presents significant challenges in terms of contact tracing, resource allocation, and public health messaging. Rapid and coordinated action is essential to prevent further spread.
Demographic Profile of Affected Individuals
Analyzing the Texas measles demographics provides critical insights into the outbreak's vulnerability patterns. Understanding which risk groups in Texas are disproportionately affected allows for targeted public health interventions. The current data indicates a concerning trend.
- Unvaccinated Individuals: A significant percentage of those infected are unvaccinated, emphasizing the critical role of vaccination in preventing Texas measles. [Insert percentage if available]. This underscores the urgency of promoting vaccination among susceptible populations.
- Age Groups Affected: While measles can affect anyone, certain age groups appear to be more vulnerable. [Specify age groups most affected. Example: Young children and adults born before the widespread implementation of the MMR vaccine].
- Underlying Health Conditions: Individuals with weakened immune systems due to underlying health conditions may be at increased risk of severe complications from measles.
Public Health Response and Vaccination Efforts
The Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS), along with local health authorities, has implemented a multifaceted response to the Texas measles outbreak. This public health response in Texas relies heavily on vaccination campaigns and community engagement.
- Vaccination Campaigns: Increased efforts are underway to raise measles vaccination rates in Texas. This includes public awareness campaigns, vaccination clinics, and outreach to underserved communities. The focus is on ensuring access to the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine.
- Challenges in Implementation: Vaccine hesitancy and misinformation pose significant challenges. Overcoming anti-vaccine sentiments in Texas requires a strategic communication approach that builds trust and provides accurate information.
- Resources and Support: The DSHS and other public health agencies are providing resources and support, including educational materials, vaccination clinics, and contact tracing efforts to manage the Texas measles prevention strategies.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
Combating measles misinformation in Texas is paramount. The spread of false information regarding measles vaccine safety in Texas fuels vaccine hesitancy and undermines public health efforts.
- Reliable Sources of Information: It's crucial to rely on credible sources such as the CDC, WHO, and the DSHS for accurate information about measles vaccines.
- Debunking Myths: Common misconceptions surrounding vaccine safety must be addressed head-on. [Provide factual information debunking specific myths, such as the link between vaccines and autism].
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making: Promoting evidence-based decision-making is critical in combating vaccine hesitancy. Open dialogue and clear communication are essential.
Conclusion
The expansion of the Texas measles outbreak into new clusters underscores the urgent need for robust public health interventions. The demographic data highlights the vulnerability of unvaccinated individuals, particularly children and adults who missed routine childhood vaccinations. The public health response, while active, faces challenges due to vaccine hesitancy and the geographic spread of the disease. Effective communication, increased vaccination rates, and decisive action are critical to controlling this outbreak.
Call to Action: Protect yourself and your loved ones. Consult your healthcare provider to ensure your measles vaccination is up-to-date. Share accurate information about Texas measles with your community to combat misinformation and prevent further spread. Let’s work together to eliminate this preventable disease.

Featured Posts
-
 Marine Le Pen Condamnee Le Proces En Appel Hanouna En 2026 Les Declarations De Jacobelli
May 30, 2025
Marine Le Pen Condamnee Le Proces En Appel Hanouna En 2026 Les Declarations De Jacobelli
May 30, 2025 -
 Ist Der Trainerwechsel In Augsburg Die Richtige Entscheidung Eine Kritische Betrachtung
May 30, 2025
Ist Der Trainerwechsel In Augsburg Die Richtige Entscheidung Eine Kritische Betrachtung
May 30, 2025 -
 Guillermo Del Toros Sangre Del Toro Cannes Documentary Premiere Details
May 30, 2025
Guillermo Del Toros Sangre Del Toro Cannes Documentary Premiere Details
May 30, 2025 -
 Southeast Asia Solar Market How Trumps Tariffs Impacted Indian Exporters
May 30, 2025
Southeast Asia Solar Market How Trumps Tariffs Impacted Indian Exporters
May 30, 2025 -
 Ealas Upset Victory Over Keys Sends Her To Miami Open Quarterfinals
May 30, 2025
Ealas Upset Victory Over Keys Sends Her To Miami Open Quarterfinals
May 30, 2025
