The 31% Reduction In BP's Chief Executive's Pay: What It Means

Table of Contents
The Context of the 31% BP CEO Pay Reduction
BP's Financial Performance in 2022-2023
Understanding the 31% BP CEO pay cut requires examining BP's financial performance in 2022 and 2023. BP's financial results during this period were marked by a complex interplay of factors influencing profitability and shareholder returns. Keywords like "BP financial results," "BP profit margin," and "BP shareholder return" are crucial here. Analyzing these metrics is key to understanding the context of the CEO's pay reduction.
- Quantifiable Data: While specific figures require access to official BP reports, we can generally say that the company experienced fluctuations in its profit margin due to volatile energy prices. Geopolitical events significantly impacted global energy markets, creating both opportunities and challenges.
- Significant Events: The war in Ukraine, for example, led to significant energy price increases, boosting BP's profits in the short term. However, these increases were also accompanied by increased scrutiny of energy companies' profits and a focus on their social responsibility. This contributed to the pressure on executive compensation.
- Connection to Pay Reduction: The connection between BP's financial performance and the CEO's pay reduction lies in the increased shareholder pressure for responsible and performance-linked executive compensation. High profits during periods of global uncertainty sparked criticism, leading to demands for greater accountability and a more equitable distribution of rewards.
Shareholder Activism and Pressure on Executive Compensation
The Role of Institutional Investors
The 31% BP CEO pay cut is strongly linked to increasing shareholder activism and pressure regarding executive compensation. Keywords like "Shareholder activism," "ESG investing," and "Executive pay transparency" are central to this discussion. Large institutional investors, wielding significant voting power, are increasingly vocal about their expectations for executive pay.
- Shareholder Resolutions: Many institutional investors have filed shareholder resolutions focusing on executive pay transparency, linking CEO compensation more closely to long-term performance, and incorporating ESG factors into compensation decisions. The increase in such resolutions puts significant pressure on company boards.
- Performance-Linked Compensation: There's a growing trend towards aligning executive pay more closely with company performance metrics, moving away from fixed salaries and focusing on long-term value creation. The BP CEO pay cut aligns with this trend.
- ESG Factors: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are playing an increasingly important role in influencing investor decisions and executive compensation. Concerns about climate change and social responsibility influence investor attitudes towards executive pay, pushing for responsible business practices.
Implications of the 31% Pay Cut for BP and the Broader Energy Sector
Setting a Precedent for Other Energy Companies
The 31% BP CEO pay cut could potentially set a precedent for other energy companies. Keywords such as "Energy sector executive pay," "Corporate governance best practices," and "Executive compensation trends" become highly relevant here. This move has significant implications for the broader energy sector's approach to executive compensation.
- Future Negotiations: This decision may influence future executive compensation negotiations in the energy sector, potentially leading to greater moderation and a stronger emphasis on linking pay to long-term performance and sustainability goals.
- Message to Other CEOs and Boards: The pay cut sends a clear message to other CEOs and boards of directors that excessive executive compensation in times of uncertainty and social concern is no longer acceptable.
- Corporate Governance: The decision reflects a shift towards improved corporate governance and more responsible business practices, demonstrating a willingness to align executive incentives with broader societal expectations.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes in BP's Executive Compensation Strategy
Long-Term Effects on CEO Incentive and Motivation
The 31% BP CEO pay cut has significant implications for the CEO's incentives and motivation, affecting their long-term commitment to the company. Keywords such as "Executive compensation structure," "CEO performance," and "Long-term incentives" are critical for understanding the long-term effects.
- Changes in Compensation Plans: BP might adjust its future executive compensation plans to further emphasize long-term performance, sustainability targets, and other key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with shareholder and societal expectations.
- Impact on Long-Term Commitment: While a pay cut might not immediately impact short-term performance, the long-term implications for the CEO's commitment and motivation require careful consideration. The company might need to implement strategies to mitigate any potential negative effects.
- Adjustments to Incentive Programs: To maintain CEO motivation and retain talent, BP may explore adjustments to its incentive programs, potentially focusing on longer-term performance-based bonuses and equity-based compensation.
Conclusion
The 31% BP CEO pay cut represents a significant development in executive compensation, highlighting the growing influence of shareholder activism, ESG considerations, and a shift towards greater accountability within the energy sector. This decision sets a potential precedent for other energy companies and underscores the evolving expectations surrounding corporate governance and responsible business practices. The long-term implications for CEO motivation and BP's compensation strategy require ongoing monitoring.
Stay updated on the evolving landscape of executive compensation in the energy sector by following reputable financial news outlets and industry analyses for further insights on the BP CEO pay cut and similar developments. Continue researching keywords like "BP CEO pay cut," "BP executive compensation," and "energy sector executive pay" to stay informed.

Featured Posts
-
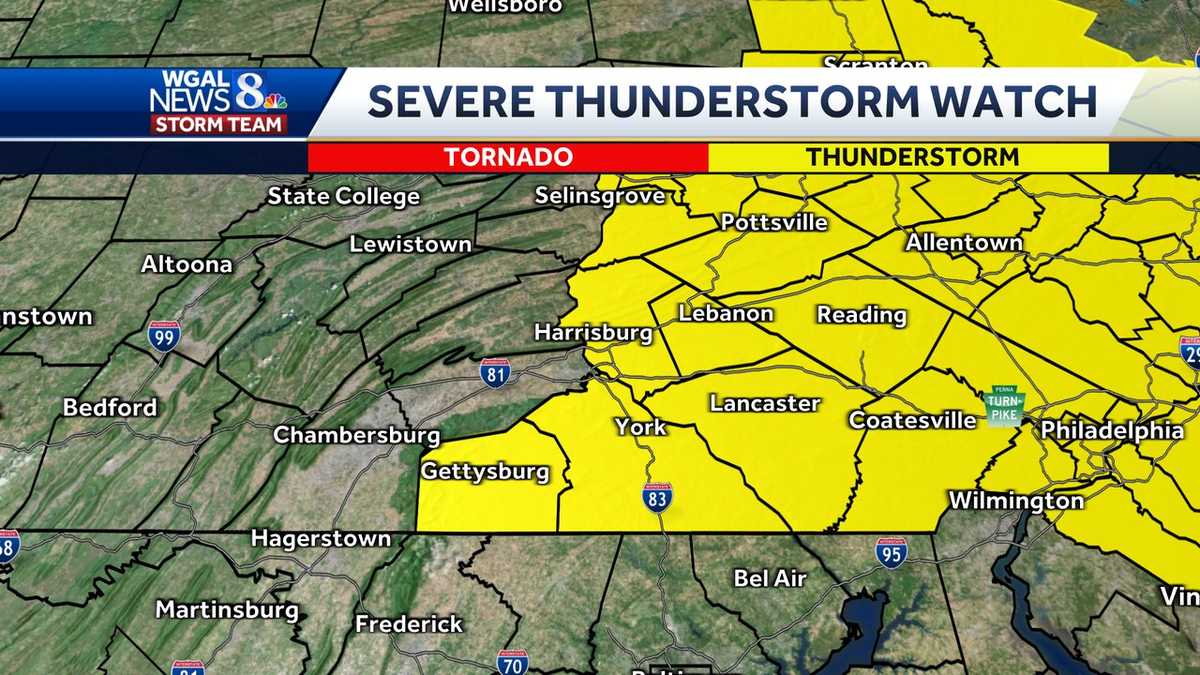 South Central Pennsylvania Under Severe Thunderstorm Watch
May 22, 2025
South Central Pennsylvania Under Severe Thunderstorm Watch
May 22, 2025 -
 Altshkylt Aljdydt Lmntkhb Amryka 3 Njwm Yndmwn Lawl Mrt
May 22, 2025
Altshkylt Aljdydt Lmntkhb Amryka 3 Njwm Yndmwn Lawl Mrt
May 22, 2025 -
 Ai Mode The Future Of Google Search
May 22, 2025
Ai Mode The Future Of Google Search
May 22, 2025 -
 Making The Team Jesse James Relives His Draft Day
May 22, 2025
Making The Team Jesse James Relives His Draft Day
May 22, 2025 -
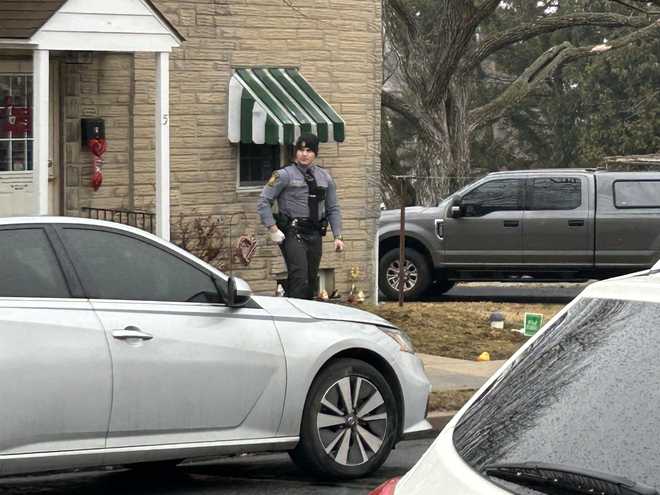 Fbi Search Warrant Executed In Lebanon County Pa
May 22, 2025
Fbi Search Warrant Executed In Lebanon County Pa
May 22, 2025
