The Canadian Economy Under Trump's Trade War: 8 Indicators To Watch

Table of Contents
The Trump administration's trade policies cast a long shadow over the global economy, and Canada, a significant trading partner of the United States, felt the impact acutely. The uncertainty and volatility created by these protectionist measures significantly affected various sectors of the Canadian economy. This article analyzes eight key economic indicators to understand the lingering effects of this period of trade conflict on the Canadian economy under Trump's trade war, offering insights into its resilience and future trajectory.
<h2>Impact on the Canadian Manufacturing Sector</h2>
The Canadian manufacturing sector, heavily reliant on exports to the US, experienced significant challenges during the trade war.
<h3>Decline in Exports to the US</h3>
- Affected Sectors: The lumber, automotive parts, and dairy industries faced substantial export declines due to tariffs and trade restrictions. The imposition of tariffs on Canadian softwood lumber, for example, severely impacted producers.
- Data Points: Statistics Canada data revealed a sharp drop in manufacturing exports to the US during the peak of the trade war, with specific percentages showing declines across various sectors. (Note: Insert actual data and sources here for SEO optimization and credibility).
- Job Losses: The decline in exports led to job losses, particularly concentrated in regions heavily reliant on manufacturing, impacting communities across the country.
<h3>Increased Input Costs</h3>
- Tariffs on Imported Goods: Tariffs on imported raw materials and intermediate goods used in Canadian manufacturing increased production costs.
- Price Competitiveness: This made Canadian-made goods less price-competitive in both domestic and international markets. Businesses faced difficult choices: absorb the higher costs, raise prices and risk losing market share, or reduce production and potentially lay off workers.
- Affected Materials: Specific examples include steel, aluminum, and various chemicals used extensively in manufacturing processes.
<h2>Fluctuations in the Canadian Dollar (CAD)</h2>
The Canadian dollar's value is intrinsically linked to the health of the Canadian economy and its trade relations.
<h3>CAD Volatility and Trade Wars</h3>
- Correlation with Trade Tensions: Trade tensions and uncertainty generally weaken a nation's currency. The Canadian dollar experienced significant volatility during the trade war, reflecting investor concerns about the economic outlook.
- Impact on Imports and Exports: A weaker CAD made Canadian exports cheaper for US buyers, potentially offsetting some of the negative impacts of tariffs. However, it also made imports more expensive, fueling inflation.
- CAD Performance Data: (Insert data and sources on CAD performance during the period of trade conflict. Show highs and lows and compare to pre-trade war performance).
<h2>Changes in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)</h2>
Trade uncertainty significantly impacts investor confidence.
<h3>Impact on Investor Confidence</h3>
- Uncertainty and Investment Decisions: The trade war created uncertainty, making foreign investors hesitant to commit capital to Canada.
- Trends in FDI Inflow: (Insert data and sources on FDI inflow to Canada during and after the trade war, highlighting any shifts in investment sources—away from the US, for instance).
- Diversification of Investment Sources: Canada actively sought to diversify its investment sources, reducing reliance on the US market.
<h2>Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Inflation</h2>
Tariffs directly impact consumer prices.
<h3>Tariffs and Inflationary Pressure</h3>
- Increased Prices for Consumers: Tariffs on imported goods increased prices for consumers, reducing their purchasing power.
- CPI and Inflation Rates: (Include data points on CPI and inflation rate changes during the trade war period, showing the impact of tariffs on consumer costs).
- Impact on Consumer Spending: Higher prices led to decreased consumer spending, potentially slowing overall economic growth.
<h2>Employment Rates and Job Creation</h2>
The trade war had a direct impact on employment across various sectors.
<h3>Sector-Specific Employment Impacts</h3>
- Job Losses: Manufacturing and related industries experienced job losses.
- Unemployment Rate Changes: (Include data on unemployment rate changes during and after the trade conflict. Highlight any regional variations).
- Government Responses: The Canadian government implemented programs to support workers affected by job losses, offering retraining and support services.
<h2>Growth in the Canadian Services Sector</h2>
While manufacturing struggled, the Canadian services sector demonstrated relative resilience.
<h3>Diversification and Resilience</h3>
- Services Sector Performance: The services sector, encompassing diverse industries like finance, technology, and tourism, showed more stability than the manufacturing sector.
- Growth Opportunities: Specific service sectors, such as technology and professional services, experienced growth opportunities.
- Economic Composition Shifts: The trade war accelerated the ongoing shift in the Canadian economy towards a more services-based model.
<h2>Canada-US Trade Relations Beyond the Trade War</h2>
The lingering effects of the trade war continue to shape Canada-US trade relations.
<h3>Repairing and Strengthening Ties</h3>
- Post-Trump Administration Efforts: The new US administration focused on repairing relations with Canada.
- Long-Term Impact: The trade war left a lasting mark on bilateral relations, necessitating ongoing efforts to rebuild trust and strengthen cooperation.
- New Trade Agreements: New trade agreements and improved communication are crucial for fostering a positive trade environment.
<h2>Government Response and Economic Policies</h2>
The Canadian government took steps to mitigate the negative economic consequences of the trade war.
<h3>Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies</h3>
- Government Policies: The government implemented various programs aimed at supporting affected industries and workers.
- Policy Effectiveness: (Analyze the effectiveness of these policies in mitigating the negative impacts of the trade war).
- Long-Term Strategies: Long-term strategies focused on economic diversification and resilience are crucial for navigating future trade uncertainties.
<h2>Conclusion: Understanding the Long-Term Effects of the Canadian Economy Under Trump's Trade War</h2>
The Trump administration's trade policies significantly impacted the Canadian economy, affecting various key indicators like manufacturing exports, the Canadian dollar, FDI, CPI, and employment. While the manufacturing sector experienced challenges, the services sector demonstrated resilience, and the Canadian government implemented mitigation strategies. Monitoring these eight key indicators continues to be essential for understanding the lasting effects of this period of trade conflict. The Canadian economy's adaptability and diversification efforts will determine its long-term success in navigating future trade complexities. Stay informed about these crucial economic indicators and their influence on the Canadian economy under Trump's trade war and its future trajectory. For further in-depth analysis, consult resources from Statistics Canada and the Bank of Canada.

Featured Posts
-
 Mobilite Durable Le Renforcement De La Cooperation Entre La France Et Le Vietnam
May 30, 2025
Mobilite Durable Le Renforcement De La Cooperation Entre La France Et Le Vietnam
May 30, 2025 -
 From Marvel To Sinner Should You Watch The Post Credits Scenes
May 30, 2025
From Marvel To Sinner Should You Watch The Post Credits Scenes
May 30, 2025 -
 Preparate Para El Concierto Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm Juntos
May 30, 2025
Preparate Para El Concierto Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm Juntos
May 30, 2025 -
 Preoccupations Des Parents D Eleves De Bouton D Or Remplacements Et Problemes De Rats A Florange
May 30, 2025
Preoccupations Des Parents D Eleves De Bouton D Or Remplacements Et Problemes De Rats A Florange
May 30, 2025 -
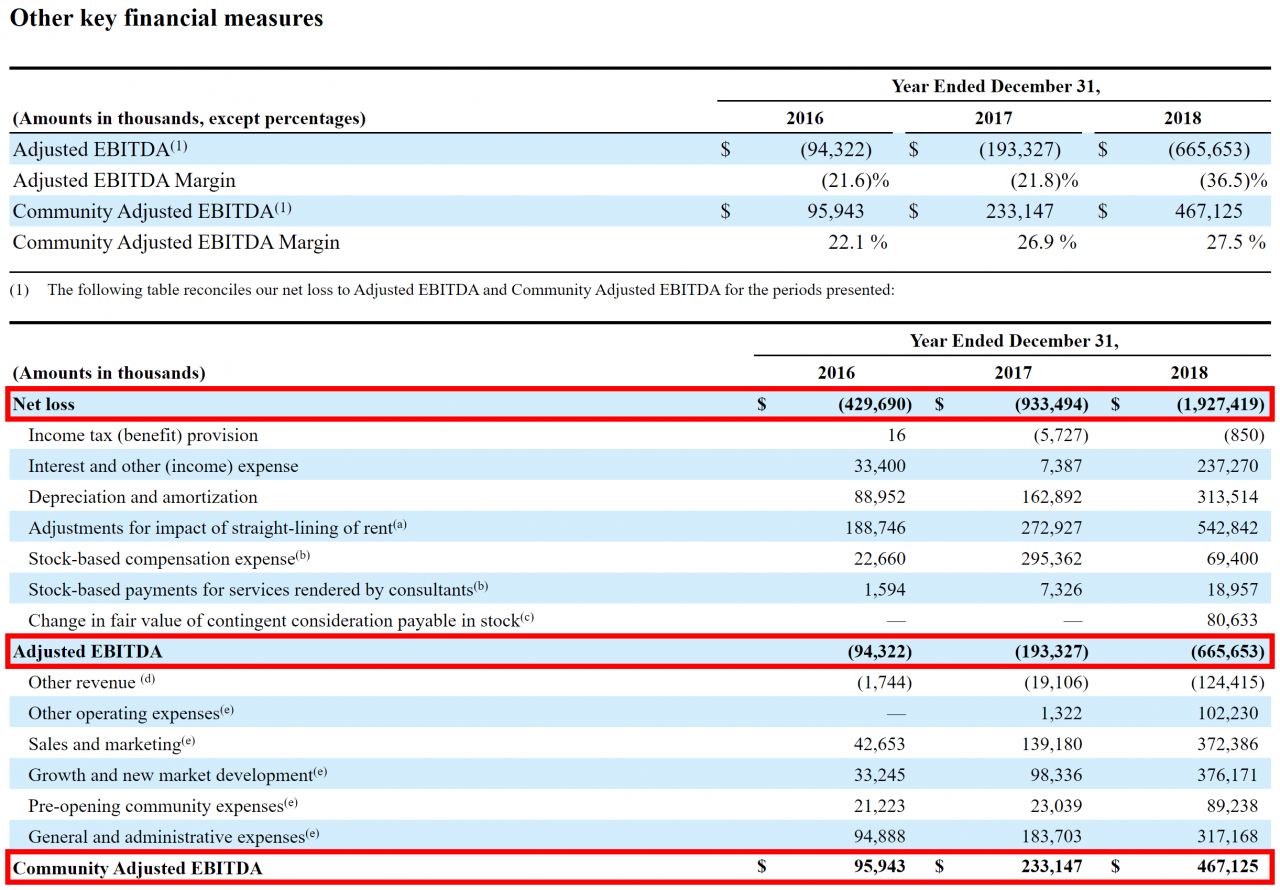 Eventim Q1 Financial Report Climbing Revenue And Adjusted Ebitda
May 30, 2025
Eventim Q1 Financial Report Climbing Revenue And Adjusted Ebitda
May 30, 2025
