The Congo Cobalt Crisis: Assessing The Export Ban And Its Effects On The Global Market
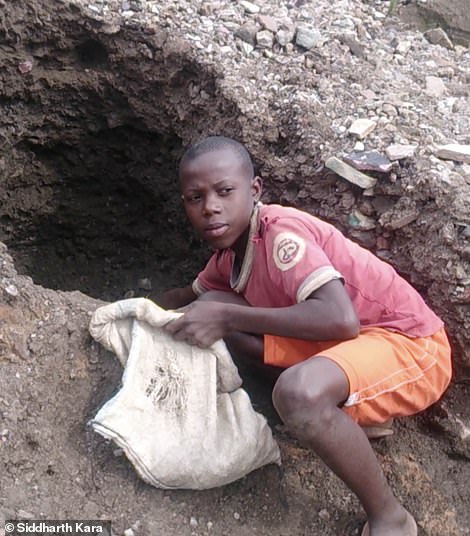

Table of Contents
The DRC's Cobalt Dependence and Economic Realities
The DRC's economy is heavily reliant on cobalt mining, making it particularly vulnerable to fluctuations in global demand and price. This dependence creates a precarious situation, intertwining economic stability with the ethical concerns surrounding cobalt extraction.
Economic Reliance on Cobalt Exports
- Cobalt revenue contributes significantly to government budgets and employment: A substantial portion of the DRC's government revenue comes directly from cobalt exports, funding essential public services and infrastructure projects. Employment in the cobalt sector, both formal and informal, supports a significant portion of the population.
- A drop in cobalt exports could severely cripple the DRC's economy and social programs: Any disruption to cobalt exports, including an export ban, would have devastating consequences for the DRC's economy. This could lead to reduced government revenue, impacting crucial social programs like healthcare and education.
- The potential for economic instability fuels political instability and conflict: The DRC has a history of political instability and conflict, often linked to resource control. Economic instability caused by cobalt market volatility can exacerbate these issues, leading to further unrest and violence.
Informal Mining and Human Rights Concerns
Much of the DRC's cobalt is extracted through informal mining practices, raising significant human rights concerns. This unregulated sector is characterized by dangerous conditions and exploitative labor practices.
- Child labor is a widespread problem in artisanal cobalt mining: Children as young as five years old are often forced to work in dangerous conditions, risking their health and education for meager wages. This is a major human rights violation and a significant ethical concern for consumers of cobalt-based products.
- Unsafe working conditions lead to numerous injuries and fatalities: Informal cobalt mines lack basic safety measures, resulting in a high number of injuries and fatalities among miners. Exposure to hazardous materials and unstable mine shafts pose constant threats.
- Lack of environmental regulations causes severe environmental damage: Informal mining operations often disregard environmental regulations, resulting in deforestation, water pollution, and soil degradation. This environmental damage has long-term consequences for the communities and ecosystems surrounding the mines.
Potential Impacts of a Cobalt Export Ban
A cobalt export ban from the DRC would have far-reaching and potentially catastrophic consequences for the global economy and the DRC itself. The ripple effects would be felt across various sectors and industries.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions
An export ban would severely disrupt global supply chains, particularly for the electric vehicle (EV) industry, which relies heavily on cobalt for battery production.
- Manufacturers would face cobalt shortages, leading to increased prices and production delays: A sudden lack of cobalt supply would cause significant price increases, impacting the profitability of EV manufacturers and potentially slowing down the transition to electric vehicles.
- This could hinder the growth of the electric vehicle market and the transition to renewable energy: The disruption to cobalt supply could hamper the growth of the EV market, delaying the shift towards cleaner energy sources and potentially hindering global efforts to combat climate change.
- Alternative sourcing strategies would need to be implemented quickly but might not be sufficient in the short term: While countries might explore alternative sources of cobalt, finding sufficient quantities to meet global demand in the short term would be challenging, leading to continued supply shortages and price volatility.
Price Volatility and Market Speculation
An export ban would create significant price volatility in the cobalt market, leading to market speculation and potentially harming smaller companies.
- Speculation and hoarding could further exacerbate price increases: Market players might engage in speculative trading and hoarding of cobalt, further driving up prices and making it difficult for companies to secure reliable supplies.
- Smaller companies may be squeezed out of the market: Smaller companies with less financial flexibility could struggle to compete in a market with rapidly fluctuating prices and limited supply, potentially leading to business closures.
- Consumers may ultimately bear the increased costs: The increased cost of cobalt would eventually be passed on to consumers through higher prices for electronic devices and electric vehicles.
Geopolitical Ramifications
The DRC's cobalt crisis has significant geopolitical implications, impacting relationships between the DRC, its trading partners, and other stakeholders.
- Increased competition for cobalt resources from other countries: An export ban would intensify competition for cobalt resources from other producing countries, potentially leading to diplomatic tensions and resource conflicts.
- Potential for diplomatic tensions and resource conflicts: Countries vying for cobalt supplies may engage in diplomatic maneuvering or even direct conflict to secure access to this crucial resource.
- Increased pressure on international organizations to address the crisis: The crisis will likely put increased pressure on international organizations like the UN and the World Bank to intervene and assist the DRC in developing sustainable and ethical cobalt mining practices.
Strategies for Sustainable Cobalt Production in the DRC
Addressing the Congo cobalt crisis requires a multifaceted approach involving sustainable mining practices and international collaboration. Focusing on ethical sourcing and responsible mining is crucial for long-term solutions.
Promoting Responsible Mining Practices
Investing in sustainable and ethical cobalt mining practices is paramount to addressing the human rights and environmental concerns surrounding the industry.
- Support for formalization of artisanal mining operations: Formalizing artisanal mining operations would bring them under regulatory frameworks, improving working conditions, ensuring fair wages, and promoting environmental protection.
- Implementation of stricter environmental and labor regulations: Enforcing stricter regulations on environmental protection and labor standards would significantly improve working conditions and mitigate environmental damage.
- Improved traceability and transparency in the cobalt supply chain: Improving traceability and transparency would allow consumers and businesses to verify the ethical sourcing of cobalt, promoting responsible purchasing decisions.
International Collaboration and Development Aid
International cooperation and development aid are essential for supporting the DRC in its efforts to reform its cobalt mining sector.
- Financial aid for infrastructure development and capacity building: Financial assistance from international organizations and developed countries is crucial for improving infrastructure, providing training, and supporting the development of local expertise.
- Technical assistance for improving mining practices and environmental protection: Technical assistance from experts in mining engineering, environmental protection, and labor rights can help the DRC implement best practices.
- Strengthening governance and anti-corruption measures: Strengthening governance and combating corruption are essential for ensuring that the benefits of cobalt mining reach the DRC's population and are not diverted by corrupt officials.
Conclusion
The Congo cobalt crisis is a complex issue with far-reaching implications for the global economy, human rights, and geopolitical stability. A potential export ban would significantly disrupt the global supply chain, leading to price volatility and exacerbating ethical concerns. Addressing this crisis requires a multi-faceted approach involving sustainable mining practices, international collaboration, and responsible sourcing initiatives. We must move beyond merely reacting to the crisis and proactively implement solutions to ensure a more ethical and sustainable future for cobalt production in the DRC. To learn more about ongoing efforts to mitigate the effects of the Congo Cobalt Crisis, explore further resources and engage in the conversation.

Featured Posts
-
 Padres Create Mlb History Breaking An 1889 Record
May 15, 2025
Padres Create Mlb History Breaking An 1889 Record
May 15, 2025 -
 Car Industry Renews Opposition To Electric Vehicle Regulations
May 15, 2025
Car Industry Renews Opposition To Electric Vehicle Regulations
May 15, 2025 -
 Dijital Veri Tabani Isguecue Piyasasi Rehberi Ledra Palace Ta Tanitim
May 15, 2025
Dijital Veri Tabani Isguecue Piyasasi Rehberi Ledra Palace Ta Tanitim
May 15, 2025 -
 Joopiter Auction Features Kid Cudis Exclusive Collection
May 15, 2025
Joopiter Auction Features Kid Cudis Exclusive Collection
May 15, 2025 -
 Ufc Gordon Ramsay Comments On Chandlers Training And Loss To Pimblett
May 15, 2025
Ufc Gordon Ramsay Comments On Chandlers Training And Loss To Pimblett
May 15, 2025
