The Dark Side Of AI Therapy: Surveillance And State Control

Table of Contents
Data Privacy and Security Risks in AI Therapy
AI therapy platforms collect extensive data, raising serious concerns about data privacy and security. This data forms the foundation of the AI's ability to understand and respond to users, but its collection and use must be carefully examined.
Data Collection and Storage
AI therapy apps collect a wide range of personal data, including:
- Personal Identifiers: Name, address, contact information.
- Mental Health History: Diagnoses, symptoms, treatment plans, medication details.
- Session Transcripts: Detailed records of therapy sessions, including voice recordings and text-based communications.
- Biometric Data: Heart rate, sleep patterns (if integrated with wearables).
The lack of transparency regarding data usage and storage practices is alarming. Many platforms fail to clearly explain how data is stored, protected, and potentially shared with third parties. This opacity increases the risk of data breaches, which could expose highly sensitive personal information to malicious actors, leading to identity theft, blackmail, and further harm to already vulnerable individuals seeking mental healthcare.
Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination
AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the algorithm will perpetuate and even amplify them. In AI therapy, this means biases based on race, gender, socioeconomic status, or sexual orientation could lead to:
- Inaccurate diagnoses: The AI might misinterpret symptoms or behaviors based on pre-existing biases in the training data.
- Inappropriate treatment recommendations: The algorithm might suggest treatments less effective or even harmful for certain demographic groups.
- Exacerbated inequalities: Algorithmic bias could worsen existing disparities in access to quality mental healthcare.
Addressing algorithmic bias requires careful attention to the data used to train AI models, ensuring diverse and representative datasets and rigorous testing for bias.
Surveillance and Monitoring through AI Therapy
The potential for surveillance and monitoring through AI therapy platforms poses significant threats to individual privacy and freedom.
Potential for State Surveillance
Governments could potentially access the vast amounts of personal and sensitive data collected by AI therapy platforms. This raises troubling scenarios:
- Political profiling: Data on individuals' mental health could be used to target dissidents or political opponents.
- Social control: Information gleaned from therapy sessions could be misused to monitor and control individuals deemed "at risk."
- Violation of patient confidentiality: The very foundation of trust in the therapeutic relationship is undermined by the potential for state surveillance.
Current legal frameworks may not adequately protect user data in the face of such powerful state actors. Stronger safeguards and legislation are crucial.
Lack of Transparency and User Consent
Many AI therapy users are unaware of the extent to which their data is being collected, stored, and potentially shared. Obtaining truly informed consent is challenging:
- Complex technical details: The intricacies of data collection and processing can be difficult for non-technical users to understand.
- Vulnerable populations: Individuals seeking mental health support may be particularly vulnerable to exploitative data practices, as they are often in a state of emotional distress and may not be able to critically assess the terms and conditions of AI therapy apps.
Clear, concise, and easily understandable information about data practices is vital, alongside mechanisms for users to effectively control their data.
The Chilling Effect on Self-Expression
The fear of surveillance can significantly inhibit open and honest self-expression during AI therapy sessions. Users might:
- Self-censor: Avoid discussing sensitive topics for fear of repercussions.
- Provide inaccurate information: To protect themselves from potential consequences.
This can severely hinder the effectiveness of the therapy, undermining the therapeutic relationship and potentially harming the user's mental well-being. Trust and confidentiality are paramount in mental healthcare, and the potential for surveillance directly threatens these foundational elements.
The Ethical Implications of AI Therapy and State Control
The development and deployment of AI therapy necessitates a careful balancing act between technological innovation and ethical considerations.
Balancing Innovation and Ethical Concerns
Regulatory bodies must play a vital role in developing and enforcing robust ethical guidelines for AI therapy. This includes:
- Data protection regulations: Stringent laws are needed to protect user data from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Algorithmic accountability: Mechanisms for identifying and mitigating algorithmic bias are essential.
- Transparency requirements: AI therapy platforms must be transparent about their data practices and provide users with meaningful control over their data.
Ethical guidelines for developers and providers are equally important, emphasizing user privacy, data security, and responsible use of AI in mental healthcare.
The Future of AI Therapy and its Regulation
The future of AI therapy hinges on the development of robust regulations and ethical frameworks that prioritize user rights and prevent state control. This requires:
- Interdisciplinary collaboration: Collaboration between ethicists, technologists, policymakers, and mental health professionals is crucial to navigate the complex ethical challenges.
- Proactive policymaking: Regulations should anticipate and address emerging risks associated with AI therapy.
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation: Ongoing evaluation of the impact of AI therapy on users and society is essential to ensure responsible innovation.
Conclusion
The potential benefits of AI therapy are undeniable, but the dark side – encompassing surveillance and potential state control – cannot be ignored. The key concerns revolve around data privacy risks, algorithmic bias, the chilling effect on self-expression, and the ethical implications of leveraging this technology in mental healthcare. Demand transparency and informed consent from AI therapy providers, and help shape a future where AI supports mental well-being without sacrificing our fundamental rights. Let's ensure the benefits of AI therapy outweigh its potential dark side, creating a future where this powerful technology truly serves the needs of individuals seeking mental health support responsibly and ethically.

Featured Posts
-
 Military Discharge Of Transgender Sergeant Sparks Outrage
May 15, 2025
Military Discharge Of Transgender Sergeant Sparks Outrage
May 15, 2025 -
 Fan Codes Multi Year Partnership With La Liga A New Era For Football Fans
May 15, 2025
Fan Codes Multi Year Partnership With La Liga A New Era For Football Fans
May 15, 2025 -
 Creatine Supplements Everything You Need To Know
May 15, 2025
Creatine Supplements Everything You Need To Know
May 15, 2025 -
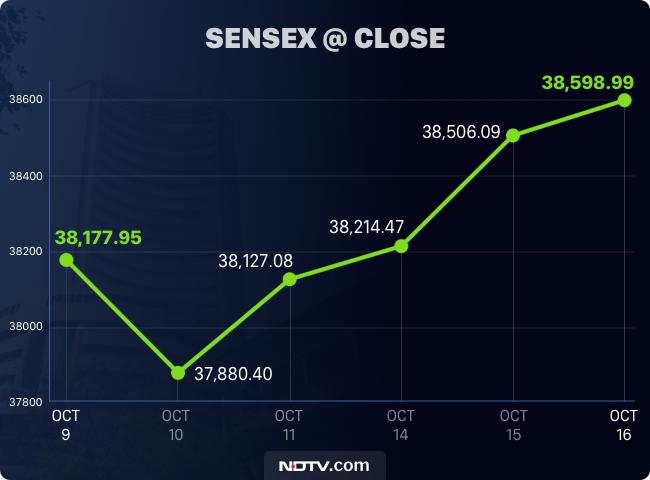 10 Gains On Bse Sensex Rally Lifts These Stocks
May 15, 2025
10 Gains On Bse Sensex Rally Lifts These Stocks
May 15, 2025 -
 High Bids For Kid Cudis Personal Effects At Recent Auction
May 15, 2025
High Bids For Kid Cudis Personal Effects At Recent Auction
May 15, 2025
