The Hypocrisy Of Western Sanctions: Examining Britain And Australia's Approach To Myanmar
Table of Contents
The Inconsistent Application of Sanctions by Britain and Australia
The application of sanctions by Britain and Australia against the Myanmar military junta has been far from uniform, creating loopholes and undermining their intended effect. This inconsistency casts doubt on the commitment of these nations to truly holding the junta accountable for its human rights violations.
Selective Targeting and Loopholes
Despite the imposed Myanmar sanctions, several businesses continue to operate within the country, exploiting loopholes in enforcement. This selective targeting renders the sanctions largely ineffective.
- Specific companies: While naming specific companies requires careful consideration of potential legal ramifications, reports indicate that certain businesses in the extractive industries and other sectors have continued operations with minimal disruption, suggesting weaknesses in the sanctions' scope and enforcement.
- Sectors benefiting from weak enforcement: Areas such as timber, gemstones, and potentially even certain aspects of the tourism industry have reportedly continued to operate with limited interference, highlighting a lack of comprehensive targeting within the sanctions regime.
- Types of sanctions circumvented: The circumvention of sanctions often involves complex financial transactions, utilizing shell companies and offshore accounts to obscure the flow of funds to the junta and its affiliated businesses.
The impact of this selective enforcement is a significant erosion of the overall sanction strategy's credibility and effectiveness. It allows the junta to maintain crucial revenue streams, hindering its true isolation from the global economy.
Lack of Transparency and Accountability
A significant criticism of the UK and Australian Myanmar sanctions is the lack of transparency surrounding their implementation and enforcement. This opacity undermines public trust and accountability.
- Examples of missing data: Precise figures regarding the number of sanctioned individuals and entities, the value of frozen assets, and the specific measures taken to enforce the sanctions are often unavailable to the public.
- Lack of reporting mechanisms: Clear and accessible reporting mechanisms to track the effectiveness of the sanctions and address instances of non-compliance are generally lacking.
- Difficulties in monitoring sanctions: The complexity of international finance and the inherent challenges in monitoring transactions across multiple jurisdictions contribute to difficulties in effectively monitoring and enforcing the sanctions.
This lack of transparency creates an environment conducive to circumvention and undermines the legitimacy of the sanctions regime.
The Role of Business Interests
The potential influence of business interests with ties to both Western nations and the Myanmar junta further complicates the situation and raises concerns about conflicts of interest.
- Specific examples of business lobbying: While concrete examples require careful investigation to avoid unsubstantiated claims, anecdotal evidence suggests lobbying efforts by businesses with interests in Myanmar may have influenced the scope and enforcement of the sanctions.
- Political donations: The possibility of political donations from companies with business ties to Myanmar to political parties in the UK and Australia warrants further scrutiny to ensure transparency and prevent undue influence on policy.
- Influence on sanction policy: The potential interplay between business interests and the shaping of sanction policy requires careful examination to ensure sanctions are driven by ethical concerns and not compromised by economic pressures.
These business interests may undermine the effectiveness and integrity of the sanctions by influencing policy decisions and creating obstacles to effective enforcement.
The Limited Impact of Sanctions on the Myanmar Military Junta
Despite the intentions behind the Myanmar sanctions, their impact on the military junta has been limited, failing to significantly alter its behavior or financial standing.
Financial Resilience of the Junta
The Myanmar military junta has demonstrated a surprising resilience to the imposed sanctions, maintaining its financial stability through various means.
- Alternative revenue streams: The junta continues to benefit from revenue generated through natural resources, including jade and timber, as well as through various state-owned enterprises.
- Internal financial mechanisms: Sophisticated internal financial networks and mechanisms allow the junta to manage its finances and circumvent international banking systems.
- Support from other countries: The junta likely receives support from various countries, mitigating the impact of Western sanctions.
This financial resilience indicates a need for a more comprehensive and targeted approach to crippling the junta's access to funds.
Human Rights Violations Continue Unabated
Despite the sanctions imposed, human rights abuses in Myanmar continue unabated. This highlights the sanctions' failure to effectively deter the junta's actions.
- Specific instances of violence: Ongoing reports document widespread violence, including extrajudicial killings, arbitrary arrests, and the use of excessive force against civilians.
- Oppression and human rights violations: Systematic oppression of ethnic minorities, restrictions on freedom of speech and assembly, and the persecution of political opponents persist.
The continued human rights violations demonstrate the inadequacy of the current sanctions regime in protecting the Myanmar population.
Impact on the Civilian Population
The sanctions, while intended to target the military junta, have had unintended and devastating consequences for the civilian population of Myanmar.
- Economic hardship: The sanctions have contributed to widespread economic hardship, leading to increased poverty and unemployment.
- Lack of access to essential goods and services: Restrictions on trade and financial transactions have severely impacted access to essential goods and services, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis.
- Humanitarian crises: The cumulative effects of the coup, conflict, and sanctions have created a dire humanitarian situation, requiring substantial international aid.
This disproportionate impact on civilians raises significant ethical concerns about the current sanction strategy and its unintended consequences.
Alternative Approaches to Addressing the Myanmar Crisis
The ineffectiveness of the current sanctions regime necessitates a reassessment and the adoption of alternative strategies.
Strengthening International Cooperation
Closer collaboration between nations is crucial for improving sanction enforcement and maximizing their impact.
- Sharing intelligence: Enhanced intelligence sharing among countries could help identify and disrupt networks involved in circumventing sanctions.
- Coordinating actions: A coordinated and unified international approach would make it significantly more difficult for the junta to evade sanctions.
- Multilateral pressure: Increased multilateral pressure through international organizations like the UN could exert significant influence on the junta.
A more unified international response would strengthen the effectiveness of the sanctions and exert greater pressure on the junta.
Targeted Sanctions and Asset Freezing
A more focused strategy targeting key individuals and entities within the junta is essential.
- Specific examples of individuals and entities to target: Focusing on the key leaders responsible for human rights abuses and those directly involved in financial transactions would be more effective.
- Mechanisms for asset freezing: Robust mechanisms for freezing assets held by sanctioned individuals and entities in foreign jurisdictions are essential.
This more surgical approach would minimize the unintended consequences on the civilian population while maximizing the impact on the junta.
Supporting Civil Society and Human Rights Organizations
Providing greater support to pro-democracy groups and human rights organizations is crucial for promoting democratic change in Myanmar.
- Financial aid: Providing financial assistance allows these organizations to continue their critical work promoting human rights and democracy.
- Logistical support: Offering logistical support, including secure communication and technology, is essential for their safety and effectiveness.
- International advocacy: Amplifying the voices of these organizations on the international stage is crucial in raising awareness and pressuring the junta.
Supporting civil society is vital for fostering a democratic transition and ensuring a more just and equitable future for Myanmar.
Conclusion
The inconsistent application and limited impact of Britain and Australia's sanctions on Myanmar raise serious questions about the effectiveness and ethical implications of this approach. While the intention behind imposing Myanmar sanctions—to pressure the Myanmar military junta and uphold human rights—is laudable, the current strategy demonstrably falls short. A more transparent, accountable, and strategically targeted approach, coupled with robust international cooperation and support for civil society, is crucial for achieving tangible progress in addressing the ongoing crisis in Myanmar. We must move beyond the perceived hypocrisy of current Myanmar sanctions and develop more effective strategies that genuinely promote human rights and democratic transition in the country. Let’s demand a more ethical and effective response to the situation in Myanmar. It’s time for a reassessment of Myanmar sanctions and a commitment to more impactful action.

Featured Posts
-
 Market Rally S And P 500 Up Over 3 Following Trade Deal Progress
May 13, 2025
Market Rally S And P 500 Up Over 3 Following Trade Deal Progress
May 13, 2025 -
 Experience Japans Cherry Blossoms A Springwatch Guide
May 13, 2025
Experience Japans Cherry Blossoms A Springwatch Guide
May 13, 2025 -
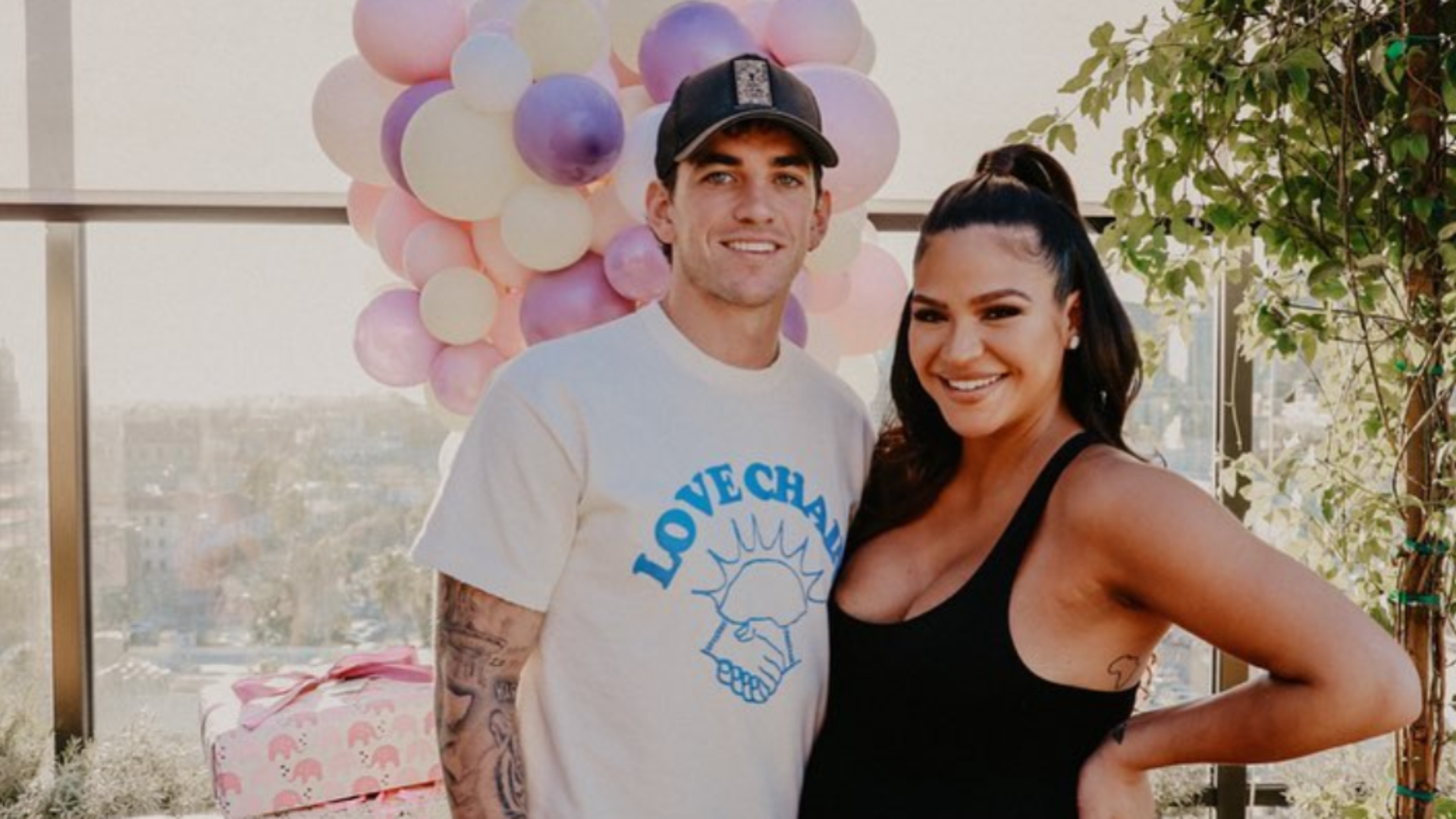 Pregnant Cassie Third Baby Gender Reveal On Alex Fines Birthday
May 13, 2025
Pregnant Cassie Third Baby Gender Reveal On Alex Fines Birthday
May 13, 2025 -
 Remembering Lost Loved Ones Recent Local Obituaries
May 13, 2025
Remembering Lost Loved Ones Recent Local Obituaries
May 13, 2025 -
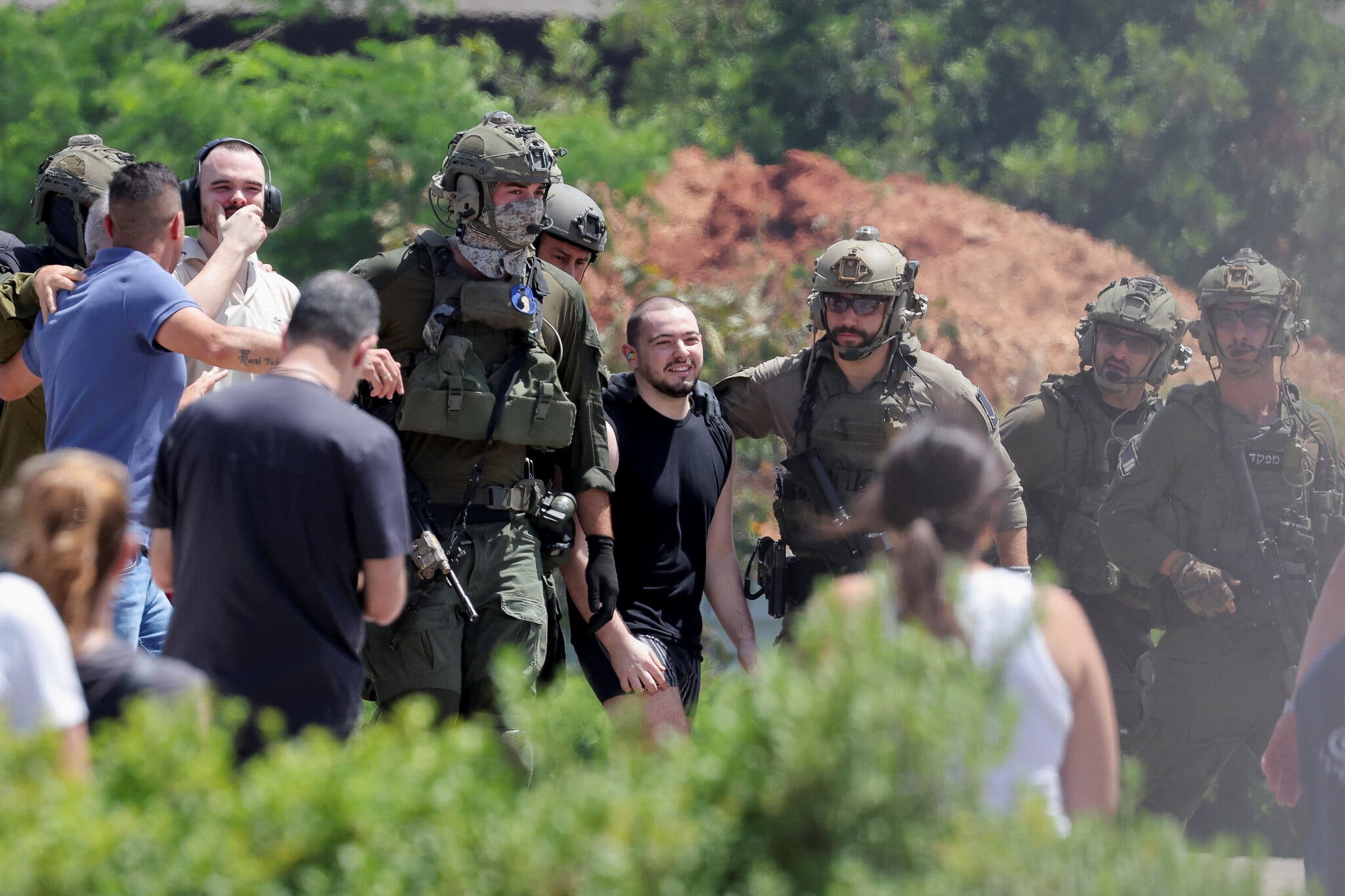 Gaza Hostage Crisis The Families Ongoing Struggle
May 13, 2025
Gaza Hostage Crisis The Families Ongoing Struggle
May 13, 2025
