The Impact Of Climate Change On The Spread Of Internal Fungal Infections
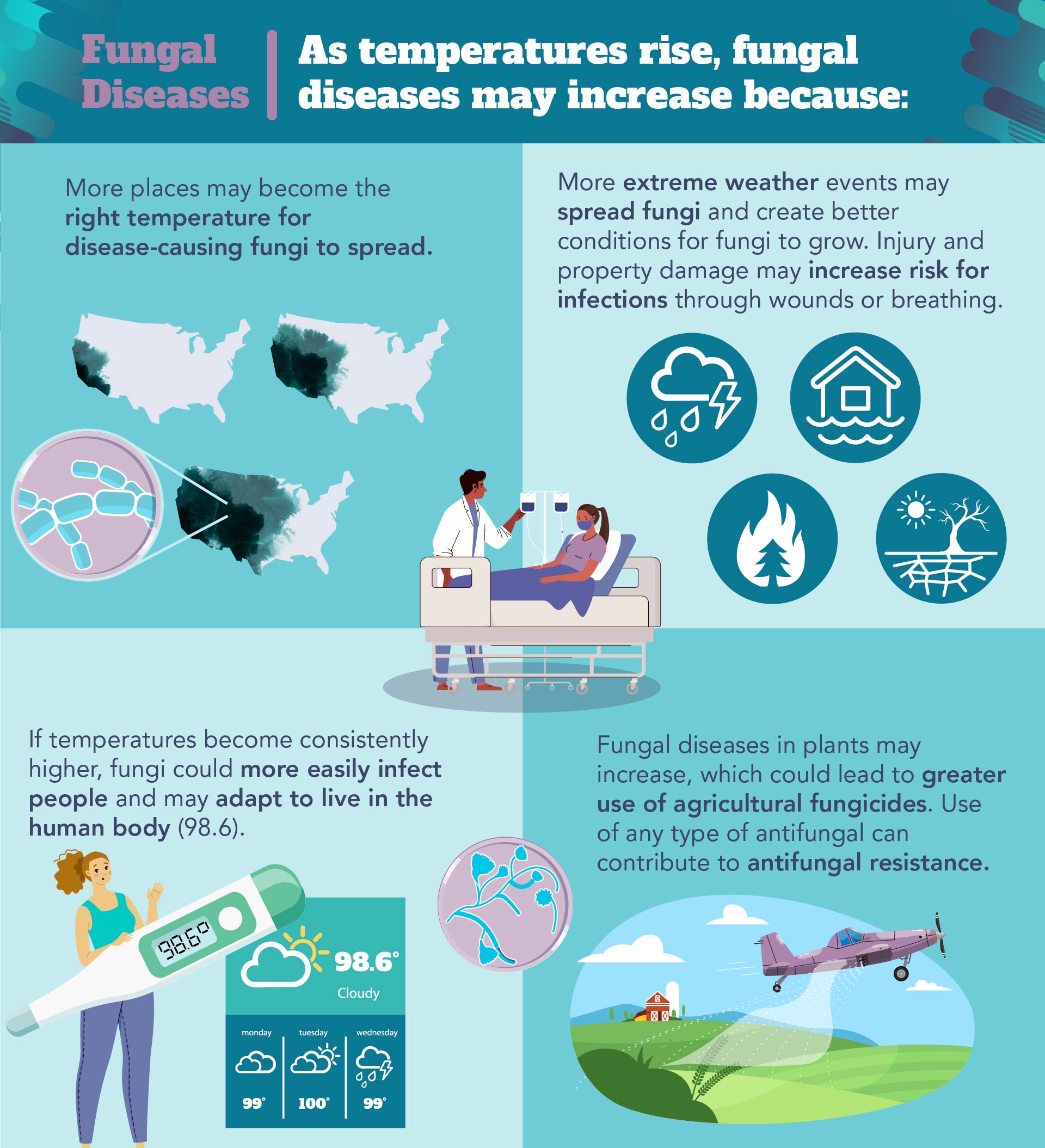
Table of Contents
Warmer Temperatures and Fungal Growth
Increased temperatures create ideal environments for fungal growth and reproduction, directly impacting the prevalence of internal fungal infections. This heightened proliferation is a significant factor contributing to the increasing incidence of these often-deadly diseases.
Optimal Conditions for Pathogen Proliferation
- Examples of thriving fungi: Warmer climates provide optimal conditions for the growth of various fungal pathogens, including Aspergillus fumigatus, a leading cause of invasive aspergillosis, and Candida albicans, responsible for candidiasis. These fungi thrive in warmer, more humid environments.
- Impact of humidity and rainfall: Increased humidity and altered rainfall patterns create favorable conditions for fungal spore dispersal and germination. Higher humidity levels extend the survival time of fungal spores in the environment, increasing the likelihood of infection.
- Scientific studies: Numerous studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between rising temperatures and increased rates of fungal infections. For example, research published in The Lancet has linked increased temperatures to a higher incidence of aspergillosis in regions experiencing prolonged heatwaves.
Changing Weather Patterns and Geographic Expansion
Altered weather patterns, intensified by climate change, facilitate the geographic expansion of fungal pathogens, leading to a wider spread of internal fungal infections in previously unaffected regions.
Increased Range of Fungal Vectors
- Role of vectors: Insects and rodents, acting as vectors, play a crucial role in dispersing fungal spores over longer distances. Changes in their habitats due to climate change can lead to the expansion of fungal ranges.
- Examples of expanding diseases: Certain fungal diseases are expanding their geographic reach due to climate change. For instance, the range of Coccidioides, a fungus causing valley fever, is expanding due to altered rainfall patterns and warmer temperatures.
- Geographic expansion illustration: Maps demonstrating the expanding geographic range of various fungal diseases, particularly in regions experiencing significant climate shifts, visually highlight the impact of climate change on disease spread.
Weakened Immune Systems and Increased Susceptibility
Climate change indirectly contributes to the increased susceptibility to internal fungal infections by weakening human immune systems through various mechanisms.
Climate Change-Induced Stress on Human Health
- Impact of extreme weather events: Extreme weather events, such as heat waves and floods, can cause stress, malnutrition, and displacement, all of which compromise immune function, making individuals more vulnerable to fungal infections.
- Air pollution and respiratory immunity: Increased air pollution associated with climate change can further impair respiratory immunity, increasing the susceptibility to airborne fungal infections like aspergillosis.
- Research on climate-related health issues: Studies show a clear link between climate change-related health issues and a higher incidence of internal fungal infections, especially among vulnerable populations. The synergistic effect of weakened immunity and increased environmental fungal burden significantly increases the risk.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment of Internal Fungal Infections
The increasing prevalence of internal fungal infections, coupled with the challenges in diagnosis and treatment, is further exacerbated by climate change's indirect influence.
Emergence of Antifungal Resistance
- Overuse of antifungals: The widespread use of antifungals in agriculture and medicine contributes to the development and spread of antifungal resistance, making treatment more difficult and increasing mortality rates.
- Diagnostic difficulties: Diagnosing invasive fungal infections can be challenging, often requiring specialized tests and expertise. Delays in diagnosis can lead to worse outcomes.
- Development of new antifungals: Research into the development of novel antifungal drugs and strategies to combat resistance is crucial to address the growing threat of antifungal-resistant fungal infections.
Conclusion
Climate change significantly influences the spread and severity of internal fungal infections. Warmer temperatures promote fungal growth, altered weather patterns expand their geographic range, and climate change-induced health problems weaken human immune systems, increasing susceptibility. The emergence of antifungal resistance further complicates treatment. Understanding the impact of climate change on internal fungal infections is crucial. Further research and collaborative efforts are essential to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies to combat this growing global health threat. Addressing climate change and improving public health infrastructure are paramount to mitigating the spread of internal fungal infections and protecting vulnerable populations worldwide.

Featured Posts
-
 Pavel I I Trillery Fedor Lavrov O Psikhologicheskikh Aspektakh Schekotaniya Nervov
May 25, 2025
Pavel I I Trillery Fedor Lavrov O Psikhologicheskikh Aspektakh Schekotaniya Nervov
May 25, 2025 -
 Skolko Let Geroyam Filma O Bednom Gusare Zamolvite Slovo
May 25, 2025
Skolko Let Geroyam Filma O Bednom Gusare Zamolvite Slovo
May 25, 2025 -
 Gryozy Lyubvi Ili Ilicha Gazeta Trud Kratkoe Soderzhanie I Analiz
May 25, 2025
Gryozy Lyubvi Ili Ilicha Gazeta Trud Kratkoe Soderzhanie I Analiz
May 25, 2025 -
 Cohere Faces Copyright Infringement Lawsuit Court Case Details
May 25, 2025
Cohere Faces Copyright Infringement Lawsuit Court Case Details
May 25, 2025 -
 Serious M56 Motorway Collision Car Overturn And Casualty Treatment
May 25, 2025
Serious M56 Motorway Collision Car Overturn And Casualty Treatment
May 25, 2025
