The US Fiscal Situation And Its Effect On Stock Prices
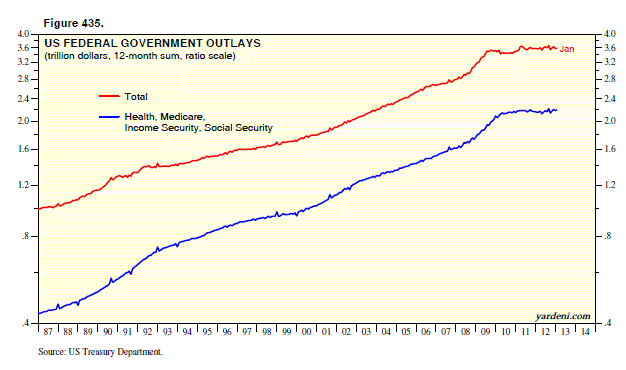
Table of Contents
Government Spending and its Impact on Stock Prices
Government spending, a cornerstone of fiscal policy, significantly influences stock prices. Understanding its impact requires examining both short-term boosts and long-term consequences.
Stimulus Packages and Market Reactions
Past stimulus packages have demonstrated a mixed bag of effects on the stock market. While some provide immediate boosts, others raise concerns about long-term inflation.
-
Short-term boosts vs. long-term inflation concerns: The immediate injection of capital into the economy through stimulus often leads to a short-term surge in stock prices as businesses and consumers benefit. However, excessive spending can fuel inflation, potentially eroding those gains over time. The 2008-2009 stimulus package, for example, initially boosted the market but also contributed to long-term inflationary pressures.
-
Sector-specific impacts: Stimulus packages often target specific sectors. Infrastructure spending, for instance, directly benefits construction and related companies, leading to increased stock prices in those sectors. Conversely, sectors unrelated to the stimulus might see little to no impact.
-
Examples of specific stimulus bills and their market consequences: The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, while initially positive for the market, faced criticism for its long-term inflationary potential. Analyzing such historical examples helps understand the nuanced effects of government spending on various stock sectors.
Government Debt and Investor Sentiment
Increasing national debt significantly influences investor confidence and risk appetite. High debt levels can trigger concerns about the government's ability to repay its obligations.
-
The role of credit rating agencies: Credit rating agencies like Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch play a vital role in assessing the creditworthiness of the US government. Downgrades can negatively impact investor sentiment, leading to higher borrowing costs for the government and potentially impacting stock prices.
-
Impact on interest rates: Higher debt levels can lead to increased interest rates, making borrowing more expensive for businesses and potentially slowing economic growth. This can negatively affect corporate profits and, consequently, stock valuations.
-
Flight to safety: During periods of fiscal uncertainty, investors often move their capital to safer assets like government bonds, leading to a decline in stock prices as money flows out of the equity market. This "flight to safety" phenomenon highlights the sensitivity of stock markets to changes in the US fiscal situation.
Fiscal Policy Changes and Market Volatility
Changes in fiscal policy, such as tax cuts and budget adjustments, introduce considerable volatility into the stock market.
Tax Cuts and their Effect on Stock Markets
Tax cuts can stimulate economic activity by boosting corporate profits and consumer spending. However, their impact on stock markets is complex and depends on various factors.
-
Examples of past tax cuts and their market effects: The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, for example, led to a short-term boost in corporate profits and stock prices, but its long-term effects are still being debated.
-
The role of investor expectations: The market's reaction to tax cuts largely depends on investor expectations. If a tax cut is perceived as beneficial for the economy, it can boost stock prices. Conversely, if it's seen as unsustainable or inflationary, it can have the opposite effect.
-
Potential for increased economic activity: Tax cuts can stimulate investment and hiring, leading to economic growth that benefits stock prices. However, the extent of this positive effect depends on the economy's overall health and how effectively the tax cuts are implemented.
Budget Deficits and Market Uncertainty
Large budget deficits can create market uncertainty and volatility, leading to increased risk aversion among investors.
-
Increased inflation risks: Persistent large deficits can lead to increased money supply, potentially triggering inflation. Inflation erodes the value of investments, impacting stock valuations.
-
Potential for currency devaluation: Large deficits can weaken a nation's currency, making imports more expensive and potentially hurting corporate profitability. This currency devaluation can negatively impact stock prices of companies with significant international operations.
-
Impact on foreign investment: Large budget deficits can signal fiscal instability, deterring foreign investment and impacting stock markets reliant on foreign capital inflows.
The Federal Reserve's Role in Managing the Fiscal Situation and its Influence on Stock Prices
The Federal Reserve (the Fed) plays a crucial role in managing the US fiscal situation and its influence on stock prices. Its actions, particularly interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing, have far-reaching effects.
Interest Rate Hikes and their Impact
Interest rate hikes by the Fed aim to curb inflation but can have complex effects on stock valuations.
-
The relationship between interest rates and bond yields: Higher interest rates make bonds more attractive, potentially drawing investment away from stocks. This can lead to a decline in stock prices, especially for growth stocks that rely heavily on future earnings.
-
Impact on corporate borrowing costs: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for businesses, potentially reducing investment and slowing economic growth. This can negatively impact corporate profits and, consequently, stock valuations.
-
Effects on different stock sectors: The impact of interest rate hikes varies across different sectors. Sectors sensitive to interest rates, such as real estate and utilities, might be more negatively affected than others.
Quantitative Easing and its Effects on Stock Prices
Quantitative easing (QE), a monetary policy tool used by the Fed, involves injecting liquidity into the market by purchasing assets.
-
Inflationary pressures: QE can lead to inflationary pressures if it increases the money supply too rapidly. This can erode the value of stocks and other assets.
-
Potential for asset bubbles: QE can inflate asset prices, potentially creating bubbles in certain markets. These bubbles are unsustainable and can lead to sharp corrections when they burst.
-
The long-term consequences of QE: The long-term effects of QE are still being debated. Some argue it’s essential for economic stability, while others point to potential risks like inflation and asset bubbles.
Conclusion
The US fiscal situation and stock prices are inextricably linked. Government spending, debt levels, fiscal policy changes, and the Federal Reserve's actions all play significant roles in shaping investor sentiment and market performance. Understanding this intricate relationship requires monitoring various economic indicators and carefully assessing the potential impact of government policies. The interplay between short-term gains and long-term risks necessitates a comprehensive approach to investment strategies.
Call to Action: Stay updated on the US fiscal situation and its potential impact on your investment strategies. Monitor key economic indicators affecting stock prices, and understand the relationship between US fiscal policy and your investment portfolio. By staying informed about the interplay between the US fiscal situation and stock prices, you can make more informed investment decisions and navigate market volatility more effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 6 000 For Cannes Access Investigating The Pure Auteur Fuel Black Market
May 23, 2025
6 000 For Cannes Access Investigating The Pure Auteur Fuel Black Market
May 23, 2025 -
 Swiss Respond To Landslide Threat Livestock Evacuated Via Helicopter And Trail
May 23, 2025
Swiss Respond To Landslide Threat Livestock Evacuated Via Helicopter And Trail
May 23, 2025 -
 100 Test Wickets Blessing Muzarabanis Ambitious Goal
May 23, 2025
100 Test Wickets Blessing Muzarabanis Ambitious Goal
May 23, 2025 -
 Englands Dan Lawrence A Look At His Opening Prospects And Career Aspirations
May 23, 2025
Englands Dan Lawrence A Look At His Opening Prospects And Career Aspirations
May 23, 2025 -
 Hospital Update Dylan Dreyers Sons Surgery
May 23, 2025
Hospital Update Dylan Dreyers Sons Surgery
May 23, 2025
