The US Military-Industrial Complex: A Comparison With China's Rapid Growth
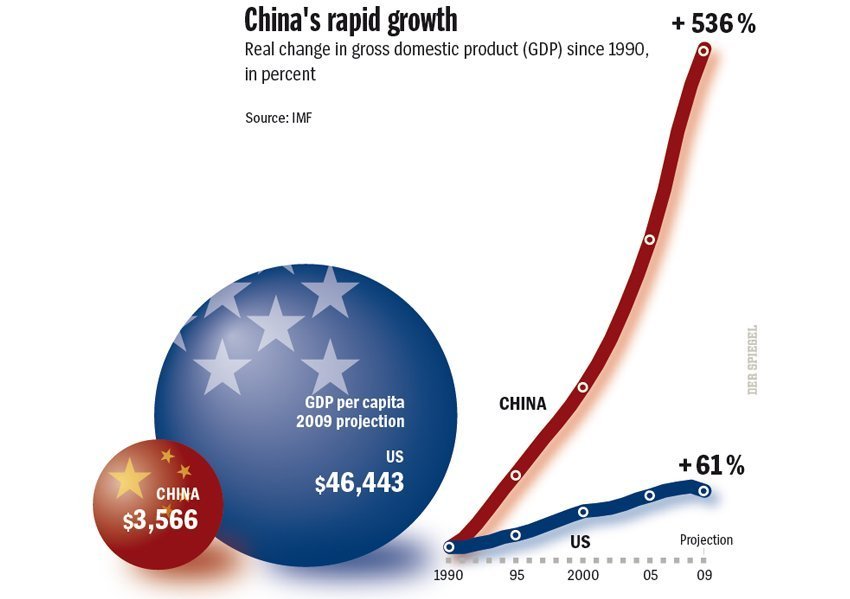
Table of Contents
China's military spending has increased by over 76% in the last decade, a stark contrast to the relatively stable—though still substantial—spending of the United States. This dramatic shift has ignited global debate about the future of military power and the evolving dynamics between the US Military-Industrial Complex (MIC) and China's rapidly modernizing armed forces. This article will delve into a comparative analysis of these two powerful forces, examining their structures, capabilities, and the implications for global security. We will explore keywords such as US Military-Industrial Complex, China military growth, military spending, and defense industry throughout our discussion.
<h2>The US Military-Industrial Complex: Structure and Influence</h2>
<h3>Historical Development of the US MIC</h3>
The US MIC’s roots trace back to World War II, accelerating during the Cold War. President Dwight D. Eisenhower famously warned against the undue influence of the military-industrial complex in his farewell address, a prescient observation that remains relevant today. The relationship between the government, the military, and private defense contractors has been a complex interplay of contracts, lobbying, and technological innovation.
- Post-WWII Expansion: The immense industrial capacity built for the war effort was repurposed and expanded for the Cold War arms race.
- Defense Procurement: A system of competitive bidding and government contracts shaped the growth of major defense companies.
- Eisenhower's Warning: His warning highlighted the potential for an unchecked MIC to exert excessive influence on national policy.
<h3>Key Players in the US MIC</h3>
The US MIC is dominated by a few powerful defense contractors. These include:
- Lockheed Martin: A leading producer of fighter jets, missiles, and other advanced weaponry.
- Boeing: A major aerospace company involved in both military and commercial aircraft production.
- Raytheon: Specializes in missile defense systems, radar technology, and cyber warfare capabilities.
These companies exert significant political influence through lobbying and campaign contributions, shaping defense budgets and procurement decisions. This influence raises concerns about potential conflicts of interest and the prioritization of profits over strategic needs. Keywords like Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Raytheon, defense lobbying, political influence, and military contracts are central to understanding this dynamic.
<h3>Strengths and Weaknesses of the US MIC</h3>
The US MIC possesses undeniable strengths:
- Technological Innovation: A long history of investment in research and development has led to cutting-edge military technology.
- Established Infrastructure: A vast industrial base and supply chain capable of producing advanced weapons systems at scale.
However, weaknesses also exist:
- Cost Overruns: Major defense projects are frequently plagued by significant cost overruns, straining the defense budget.
- Bureaucratic Inefficiencies: Complex procurement processes and bureaucratic hurdles can slow down development and deployment.
- Potential for Corruption: The immense sums of money involved create opportunities for corruption and unethical practices.
<h2>China's Military Modernization: A Rapid Ascent</h2>
<h3>The Pace of China's Military Growth</h3>
China's military spending has seen dramatic growth in recent decades, though the exact figures remain subject to debate. This growth fuels its military modernization across multiple domains:
- Hypersonic Weapons: China is making rapid progress in developing hypersonic missiles, capable of exceeding five times the speed of sound.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Integration of AI into various military systems, such as surveillance, targeting, and autonomous weapons.
- Cyber Warfare: Significant investment in cyber capabilities for both offensive and defensive purposes.
<h3>State-Owned Enterprises and the Chinese Military</h3>
The Chinese military-industrial sector is heavily reliant on state-owned enterprises (SOEs). These SOEs play a crucial role in:
- Military-Civil Fusion: A policy that integrates military and civilian technologies, accelerating technological development in both sectors.
- Technological Integration: Facilitates the rapid transfer of technologies from civilian applications to military use.
<h3>Challenges and Limitations of China's Military Growth</h3>
Despite rapid progress, challenges remain for China's military modernization:
- Technological Dependence: Reliance on foreign technologies for certain critical components creates vulnerabilities.
- Innovation Gap: While catching up rapidly, a persistent gap remains in core technological capabilities compared to the US.
- Supply Chains: Maintaining robust and secure supply chains for critical military components is crucial.
<h2>Comparison: US MIC vs. China's Military Growth</h2>
<h3>A Comparative Analysis of Spending and Capabilities</h3>
Direct comparison of US and Chinese military spending reveals significant differences in scale and approach. While the US maintains a larger overall defense budget, China's growth rate is far higher. A key point of comparison lies in their technological capabilities. The US retains an edge in certain areas, but China's rapid progress is closing the gap, particularly in hypersonic weapons and certain aspects of AI.
<h3>Strategic Implications of the Shifting Global Balance</h3>
China's rising military power has profound geopolitical implications:
- Global Security: The shift in the balance of power increases the potential for miscalculation and conflict.
- Strategic Competition: Both nations are actively engaged in strategic competition, aiming to maintain or enhance their respective advantages.
- Arms Race: Concerns exist that the ongoing military expansion could trigger a new arms race, potentially destabilizing the international order.
<h2>Conclusion: Understanding the Future of the US Military-Industrial Complex and China's Rise</h2>
The US Military-Industrial Complex and China's burgeoning military represent two distinct, yet interconnected, forces shaping global security. While the US MIC benefits from established infrastructure and technological innovation, it faces challenges related to cost and efficiency. China's rapid military modernization, driven by state-owned enterprises and a focus on military-civil fusion, poses a significant challenge to US dominance. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both systems is crucial for navigating the complexities of great power competition. Further research and informed public discourse are essential for comprehending the implications of this evolving strategic landscape. We encourage you to delve deeper into the intricacies of the US Military-Industrial Complex and explore the ongoing developments in China's military capabilities. This understanding is vital for responsible engagement with this crucial aspect of international relations.

Featured Posts
-
 High Fentanyl Levels Confirmed In Princes Autopsy March 26th 2016
May 31, 2025
High Fentanyl Levels Confirmed In Princes Autopsy March 26th 2016
May 31, 2025 -
 Exploring Bernard Keriks Family Wife Hala Matli And Children
May 31, 2025
Exploring Bernard Keriks Family Wife Hala Matli And Children
May 31, 2025 -
 The Growing Problem Of Drug Addicted Rats In Houston
May 31, 2025
The Growing Problem Of Drug Addicted Rats In Houston
May 31, 2025 -
 Evolusi Gaya Busana Miley Cyrus Dari Disney Hingga Kini
May 31, 2025
Evolusi Gaya Busana Miley Cyrus Dari Disney Hingga Kini
May 31, 2025 -
 Duncan Bannatynes Philanthropy A Moroccan Childrens Charity Benefits
May 31, 2025
Duncan Bannatynes Philanthropy A Moroccan Childrens Charity Benefits
May 31, 2025
