Tracking The Measles Outbreak: Where Cases Are Rising In The United States
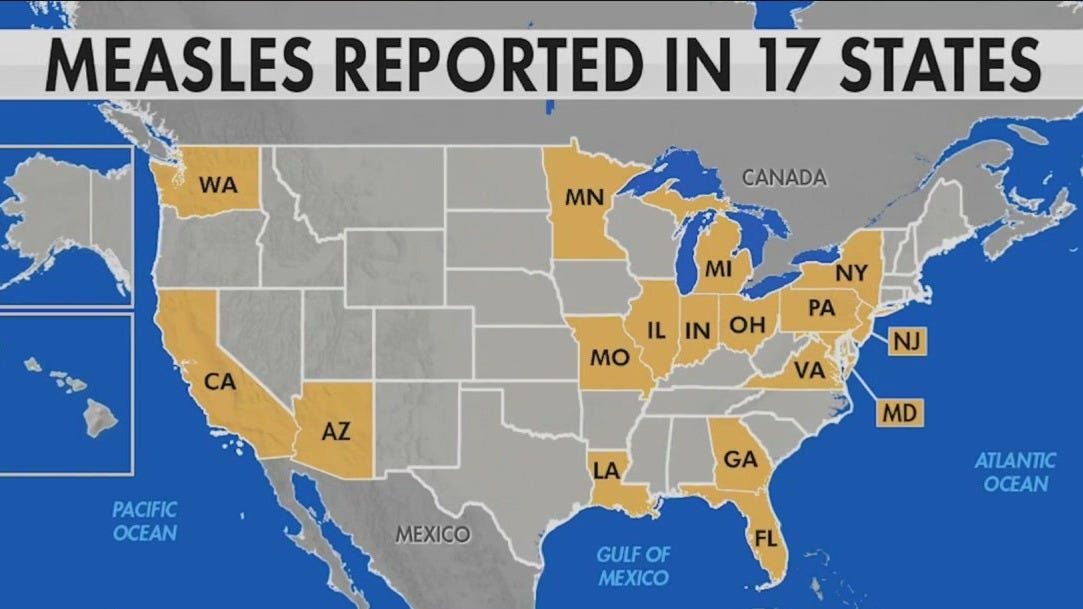
Table of Contents
Geographic Distribution of Measles Cases
Understanding the geographic spread of measles is paramount to containing the outbreak. Analyzing the distribution helps public health officials allocate resources effectively and target prevention efforts where they are most needed.
States with the Highest Case Counts
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides up-to-date data on measles cases. While specific numbers fluctuate, consistently monitoring the CDC website is crucial. [Insert link to CDC measles data here]. Generally, states with lower vaccination rates tend to report higher case counts.
- Top States (Example Data – Replace with Current Data from CDC): While the specific ranking changes, consistently affected states often include Ohio, New York, and Texas. These states may experience higher case numbers due to factors like population density and variations in vaccination rates across different counties.
- Reasons for Higher Case Counts: Several factors contribute to regional variations in measles cases. These include:
- Lower vaccination rates in certain communities.
- Higher population density, facilitating faster disease transmission.
- Increased international travel bringing the virus into the country.
- Outbreaks concentrated within specific religious or cultural groups with lower vaccination rates.
Tracking the Spread Across Regions
The measles outbreak doesn't remain static; its spread evolves over time. Monitoring the progression helps identify areas needing immediate attention and informs targeted public health responses.
- Counties and Cities: Outbreaks often cluster in specific counties or cities within states. For example, (insert example of a city or county experiencing an outbreak with a link to a reliable news source if possible). This highlights the need for localized interventions.
- Demographic Correlations: Measles disproportionately affects unvaccinated children and individuals in communities with lower vaccination coverage. Specific demographic groups, such as those adhering to religious beliefs that discourage vaccination, might also experience higher rates. This emphasizes the importance of community engagement and targeted educational campaigns.
Factors Contributing to the Measles Resurgence
The resurgence of measles isn't accidental; several interconnected factors have contributed to its comeback. Addressing these root causes is vital for long-term prevention.
Low Vaccination Rates
One of the most significant contributors to the measles resurgence is the decline in vaccination rates. This directly impacts herd immunity, a crucial concept in preventing the spread of infectious diseases.
- Herd Immunity: Herd immunity protects even those who cannot be vaccinated (due to medical reasons). When a high percentage of the population is vaccinated, it's less likely the virus will spread widely.
- Misinformation and Vaccine Hesitancy: Misinformation about vaccine safety has fueled vaccine hesitancy, leading many parents to delay or forgo vaccinating their children. This is exacerbated by the spread of false claims and conspiracy theories through social media and unreliable online sources. Studies consistently demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the MMR vaccine. [Insert links to reputable studies].
International Travel and Importation of Cases
International travel plays a significant role in introducing measles into communities with high vaccination coverage. Travelers can unknowingly carry the virus and spread it upon their return.
- Outbreaks Linked to Travel: Several measles outbreaks have been directly traced back to international travelers. (Insert examples of specific outbreaks linked to travel if possible, with appropriate citations).
- Global Travel Patterns: Increased global travel and interconnectedness make it easier for infectious diseases like measles to spread rapidly across geographical boundaries. This emphasizes the need for robust global surveillance and coordination in public health responses.
Public Health Response and Prevention Strategies
Combating the measles resurgence requires a multi-pronged approach involving both national and local initiatives.
CDC Recommendations and Guidelines
The CDC provides clear guidelines to prevent and control measles outbreaks. Adherence to these recommendations is vital.
- MMR Vaccination: The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is highly effective and safe, providing crucial protection against measles. CDC recommendations advocate for timely vaccination of children.
- Quarantine and Contact Tracing: In the event of a confirmed measles case, quarantine and contact tracing are essential to limit further spread. Identifying and isolating individuals who have been in contact with an infected person can significantly curb transmission.
Community-Level Interventions
Effective measles prevention also hinges on community-level interventions that address vaccination hesitancy and promote health literacy.
- Public Health Campaigns: Public health campaigns play a critical role in promoting vaccination and dispelling misinformation. These campaigns must use clear, evidence-based messaging to counter vaccine hesitancy.
- Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy: Community-based educational programs can address concerns regarding vaccine safety, offering accurate information from trusted sources and allowing community members to ask questions in a safe space.
Conclusion
The resurgence of measles in the United States underscores the importance of consistent vaccination efforts and proactive public health strategies. The geographic distribution of cases highlights the need for targeted interventions in areas with lower vaccination rates and higher rates of international travel. Addressing vaccine hesitancy through education and community engagement is vital to achieving and maintaining herd immunity. The factors contributing to the outbreak – low vaccination rates and the ease of international travel – necessitate a comprehensive approach that includes both national guidelines from the CDC and local community-level initiatives.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the ongoing measles outbreak by regularly checking the CDC website and your local health department for updates. Get vaccinated against measles, and encourage your family and friends to do the same. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns regarding measles vaccination. Understanding and addressing the spread of the measles outbreak is vital for collective action to protect our communities. Learn more about measles prevention and vaccination to safeguard yourself and your loved ones.

Featured Posts
-
 Dara O Briain A Voice Of Reason In Modern Comedy
May 30, 2025
Dara O Briain A Voice Of Reason In Modern Comedy
May 30, 2025 -
 Aeroport De Bordeaux Manifestation Contre Le Maintien De La Piste Secondaire
May 30, 2025
Aeroport De Bordeaux Manifestation Contre Le Maintien De La Piste Secondaire
May 30, 2025 -
 Gouweleeuw Bij Fc Augsburg Een Nieuwe Era Onder Nieuwe Leiding
May 30, 2025
Gouweleeuw Bij Fc Augsburg Een Nieuwe Era Onder Nieuwe Leiding
May 30, 2025 -
 Dara O Briains Voice Of Reason Analyzing His Stand Up And Broadcasting
May 30, 2025
Dara O Briains Voice Of Reason Analyzing His Stand Up And Broadcasting
May 30, 2025 -
 Iowa High School Track And Field State Meet Results May 22 25
May 30, 2025
Iowa High School Track And Field State Meet Results May 22 25
May 30, 2025
