Trump's Tariffs And The Small Business Struggle: A Case Study
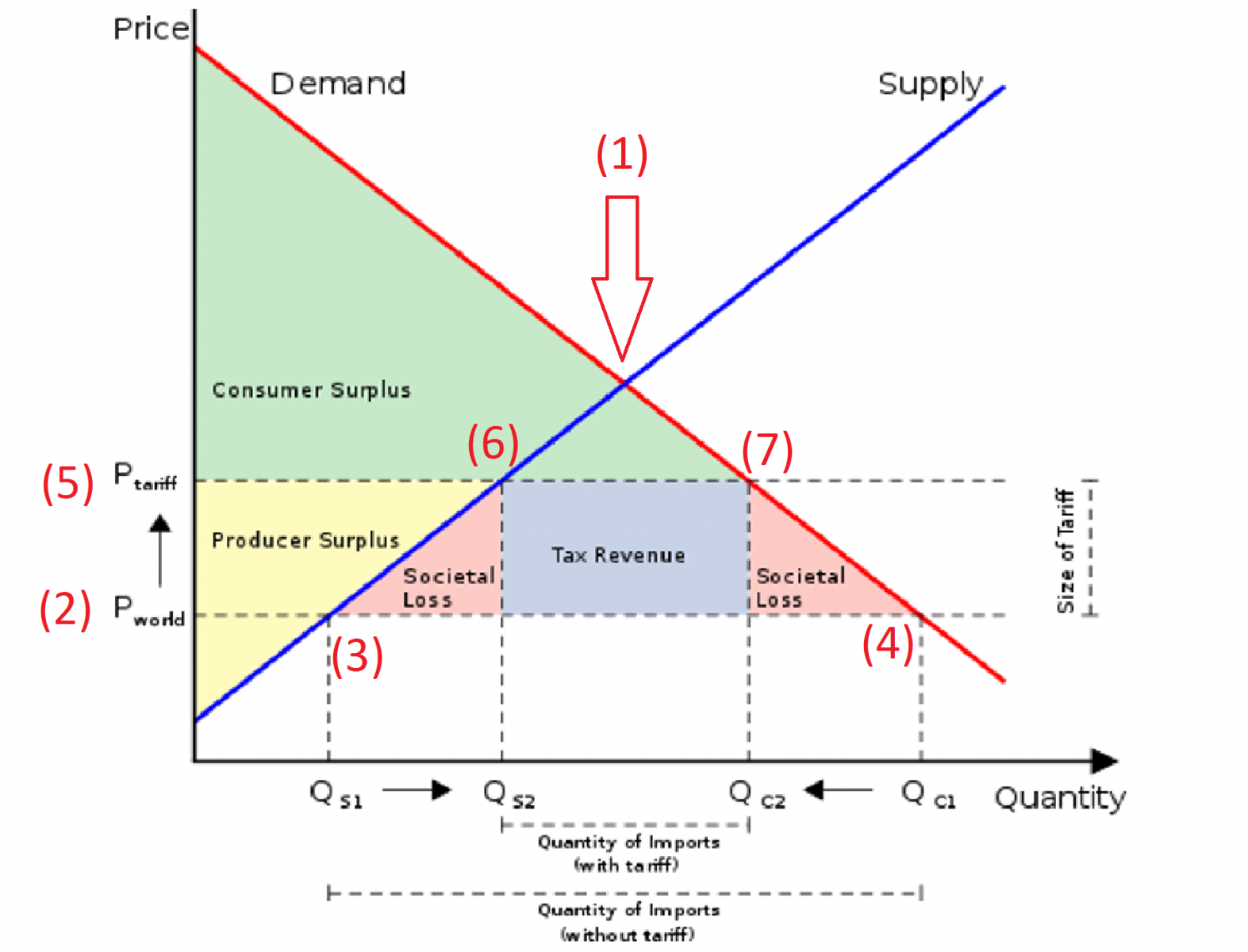
Table of Contents
The closure of over 100,000 small businesses in 2018—a year marked by escalating trade tensions—serves as a stark reminder of the economic fragility faced by many small businesses. This article focuses on Trump's tariffs and the small business struggle, examining how the administration's protectionist trade policies, intended to bolster American industry, inadvertently inflicted significant hardship on small business owners across various sectors. While the tariffs aimed to protect American industries through increased import costs, we will explore the unintended consequences and analyze specific case studies illustrating the significant challenges faced by small businesses. This analysis will demonstrate the detrimental effects of these tariffs on small business profitability, operations, and access to capital.
H2: Increased Input Costs and Reduced Profit Margins
The imposition of tariffs under the Trump administration led to a substantial increase in the cost of imported goods, significantly impacting small businesses reliant on global supply chains.
H3: Rising Prices of Imported Goods:
Tariffs dramatically increased the price of raw materials, components, and finished goods imported from targeted countries, squeezing profit margins for many small businesses.
- Manufacturing: A 25% tariff on steel, for example, increased the cost of production for countless manufacturers, from furniture makers to appliance producers. The ripple effect impacted downstream businesses using these steel products.
- Agriculture: Tariffs on agricultural inputs, such as fertilizers and machinery, raised production costs for farmers, impacting their profitability and potentially leading to farm closures.
- Retail: Retailers faced increased prices for imported goods, forcing them to either absorb the higher costs, reducing profit margins, or pass them on to consumers, potentially impacting sales.
These increased costs made it difficult for small businesses to compete effectively, especially against larger corporations with greater financial resilience. Many struggled to maintain their profit margins, leading to reduced profitability and, in some cases, business failure.
H3: Difficulty Passing on Increased Costs to Consumers:
Small businesses often faced significant challenges in passing increased costs onto consumers. Increased prices could lead to decreased consumer demand and lost market share.
- Reduced consumer demand: Higher prices on everyday goods, directly affected by tariffs, led to consumers cutting back on spending.
- Lost market share: Small businesses with less brand recognition often struggled to compete against larger companies that could absorb some of the tariff-related costs without raising prices.
- Decreased sales: The combination of reduced consumer demand and increased competition led to decreased sales for many small businesses.
To mitigate losses, some small businesses resorted to cost-cutting measures, such as reducing staff or delaying investments in upgrades, further hampering their long-term growth.
H2: Supply Chain Disruptions and Delays
Many small businesses rely heavily on global supply chains, and Trump’s tariffs severely disrupted these established networks.
H3: Dependence on Global Supply Chains:
Tariffs created significant bottlenecks in supply chains, leading to delays in receiving materials and increased shipping costs.
- Supply chain bottlenecks: The imposition of tariffs created significant delays in receiving essential materials from affected countries, resulting in production halts and unmet customer orders.
- Delays in receiving materials: Businesses faced extended lead times, impacting production schedules and potentially leading to late deliveries and dissatisfied customers.
- Increased shipping costs: Businesses were forced to explore more expensive shipping routes or alternative suppliers, further increasing costs.
H3: Search for Alternative Suppliers:
Finding and vetting new suppliers proved challenging and costly for small businesses, often resulting in higher costs and longer lead times.
- Establishing new relationships: Building trust and reliable relationships with new suppliers requires time and resources, which small businesses often lack.
- Quality control issues: Shifting to new suppliers could result in quality control issues and product inconsistencies, impacting customer satisfaction and potentially leading to returns.
- Increased administrative burdens: Managing multiple suppliers, negotiating contracts, and navigating new regulations added significant administrative burden for already-overwhelmed business owners.
H2: Impact on Small Business Lending and Investment
The uncertainty created by the Trump administration's tariffs negatively affected small businesses' access to capital and investment.
H3: Reduced Access to Capital:
Lenders became more cautious in providing loans, fearing the increased economic uncertainty.
- Lenders’ concerns about risk: The economic uncertainty caused by tariffs increased the perceived risk for lenders, making them more reluctant to approve loan applications for small businesses.
- Reduced willingness to provide financing: Banks and other financial institutions tightened lending criteria, making it harder for small businesses to secure necessary funding.
H3: Decreased Investor Confidence:
The uncertainty surrounding trade policy discouraged investment in small businesses.
- Decreased venture capital funding: Venture capitalists and angel investors became hesitant to invest in small businesses facing potential disruptions due to tariffs.
- Reduced angel investor participation: The perceived increased risk associated with tariffs discouraged many angel investors from participating in small business funding rounds.
Conclusion:
Trump's tariffs had a demonstrably negative impact on small businesses, leading to increased input costs, reduced profit margins, supply chain disruptions, and decreased access to capital. The case studies presented illustrate the significant challenges faced by these businesses, many of whom were forced to make difficult decisions, including downsizing, delaying expansion plans, or ultimately closing their doors. The key takeaway is that protectionist trade policies, while potentially benefiting certain large industries, can inadvertently cause significant harm to the small business sector, undermining economic growth and jeopardizing countless jobs. Understanding the effects of trade policies on small businesses is crucial for policymakers and investors alike. We must advocate for policies that mitigate the impact of future tariffs on small businesses and support small businesses in navigating the complexities of global trade. Let's work together to build a more resilient and supportive environment for small businesses facing trade challenges.

Featured Posts
-
 Crazy Rich Asians The Upcoming Television Series Everything You Need To Know
May 12, 2025
Crazy Rich Asians The Upcoming Television Series Everything You Need To Know
May 12, 2025 -
 The China Factor Assessing The Difficulties Faced By Bmw Porsche And Competitors
May 12, 2025
The China Factor Assessing The Difficulties Faced By Bmw Porsche And Competitors
May 12, 2025 -
 Harnessing Ai To Create A Podcast From Repetitive Scatological Documents
May 12, 2025
Harnessing Ai To Create A Podcast From Repetitive Scatological Documents
May 12, 2025 -
 Jon M Chus Crazy Rich Asians Tv Show Coming To Max
May 12, 2025
Jon M Chus Crazy Rich Asians Tv Show Coming To Max
May 12, 2025 -
 James Gunn On Henry Cavills Dc Departure Was He Wronged
May 12, 2025
James Gunn On Henry Cavills Dc Departure Was He Wronged
May 12, 2025
