U.S. Labor Market Report: April's 177,000 Job Gains And 4.2% Unemployment Rate
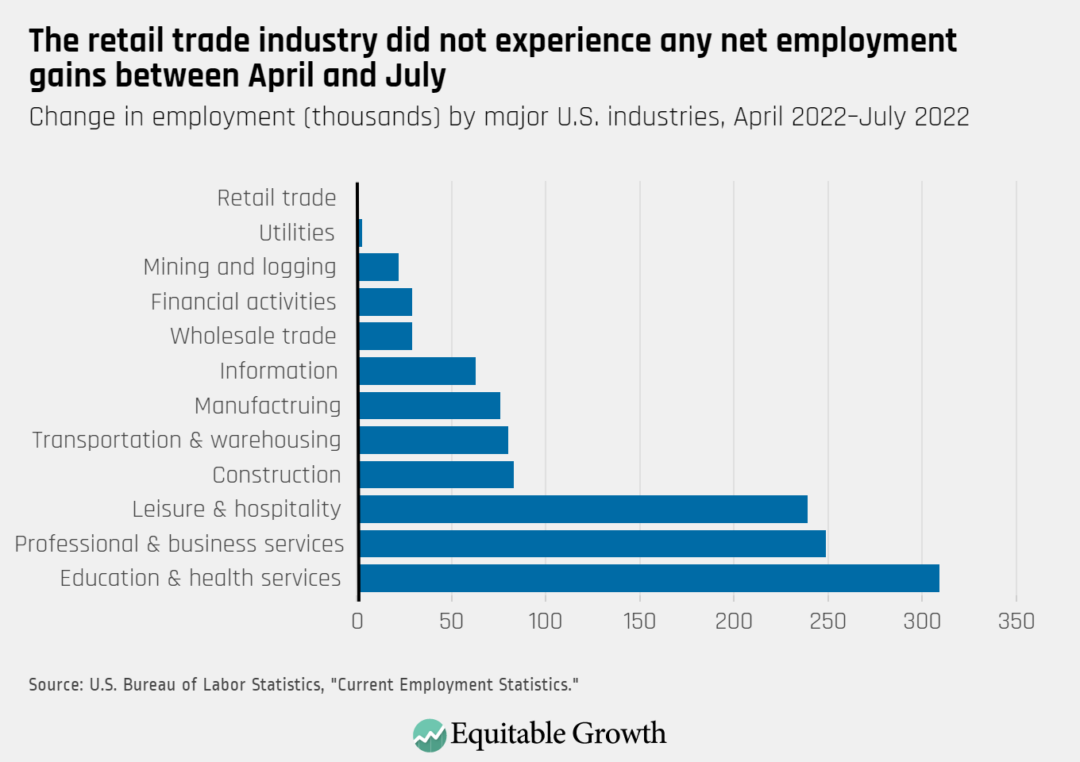
Table of Contents
Detailed Analysis of April's 177,000 Job Gains
Sector-Specific Job Growth: A Breakdown
April's job gains were spread across various sectors, reflecting a diversified economy. While the overall number was lower than in preceding months, several sectors contributed positively to the employment picture.
- Leisure and Hospitality: This sector added a significant number of jobs, continuing its recovery from pandemic-related losses. Many restaurants and hotels are experiencing increased demand, driving hiring.
- Professional and Business Services: This sector also saw robust job growth, reflecting increased business activity and demand for professional services. This includes areas such as consulting, accounting, and legal services.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing jobs showed modest growth, indicating continued strength in the production sector.
Significant Sector-Specific Trends: While most sectors showed positive growth, some experienced slower gains than anticipated. This could be attributed to various factors, including supply chain disruptions and global economic uncertainty. Further analysis is needed to fully understand these nuanced trends.
Wage Growth and Inflation
Average hourly earnings increased slightly in April, but when adjusted for inflation (real wage growth), the increase was minimal. This suggests that while wages are rising, they are not outpacing inflation, potentially impacting consumer spending.
- Average Hourly Earnings: The increase in average hourly earnings was [Insert Data Here], compared to [Insert Data Here] in the previous month and [Insert Data Here] year-over-year.
- Real Wage Growth: Considering inflation, real wage growth was [Insert Data Here], indicating that the purchasing power of wages is not significantly improving.
Implications for Federal Reserve Monetary Policy: The modest wage growth coupled with persistent inflation will likely influence the Federal Reserve's decisions on future interest rate hikes. The Fed walks a tightrope, aiming to curb inflation without triggering a recession.
Participation Rate and Labor Force Dynamics
The labor force participation rate remained relatively stable in April. This signifies that the number of people actively seeking employment is not significantly changing.
- Labor Force Participation Rate: The participation rate stands at [Insert Data Here] %, representing [Insert Interpretation Here].
- Employment-Population Ratio: The employment-population ratio, which measures the proportion of the working-age population that is employed, shows [Insert Data Here] %.
Potential Implications for Future Job Growth: The stable participation rate suggests a healthy labor market, although potential future growth may be affected by factors such as demographic shifts and technological advancements.
Unemployment Rate at 4.2%: A Deeper Dive
Understanding the Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate is a key indicator of the health of the labor market. It represents the percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking employment but unable to find it.
- Unemployment Rate Calculation: The unemployment rate is calculated by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the total labor force (employed + unemployed).
- Types of Unemployment: Unemployment can be categorized as frictional (temporary unemployment between jobs), structural (mismatch between worker skills and job availability), or cyclical (due to economic downturns).
Significance of the 4.2% Figure: The 4.2% unemployment rate is relatively low compared to historical averages, suggesting a strong labor market. However, it's crucial to consider the nuances of this statistic and the types of unemployment represented.
Geographic Variations in Unemployment
Unemployment rates vary considerably across different regions of the U.S.
- High Unemployment States: [Insert Examples of States with High Unemployment and Data]. These high rates could be due to industry-specific downturns or economic factors unique to those regions.
- Low Unemployment States: [Insert Examples of States with Low Unemployment and Data]. These states might benefit from robust industry sectors or proactive economic development initiatives.
Reasons for Regional Variations: These variations often reflect differences in industry concentration, economic development strategies, and government policies.
Long-Term Unemployment Trends
The duration of unemployment is another important factor to consider. Long-term unemployment can have significant social and economic consequences.
- Long-Term Unemployment Data: [Insert data on the percentage of individuals unemployed for more than six months].
- Policy Interventions: Addressing long-term unemployment often requires targeted interventions such as job training programs, workforce development initiatives, and extended unemployment benefits.
Outlook and Implications for the U.S. Economy
Future Job Growth Projections
Experts offer varying projections for future job growth, influenced by several factors.
- Federal Reserve Projections: The Federal Reserve anticipates [Insert Fed's job growth projection and supporting details].
- Congressional Budget Office Projections: The CBO projects [Insert CBO's job growth projection and supporting details].
Potential Risks and Uncertainties: These projections are subject to uncertainties, including inflation, global economic slowdown, and geopolitical events.
Impact on Monetary Policy
The April jobs report will likely influence the Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions.
- Federal Reserve Response: The Fed will likely consider the employment data in its assessment of inflation and the overall economic situation.
- Potential Impact of Monetary Policy: Changes in interest rates can affect inflation, employment, and economic growth.
Implications for Businesses and Investors
The April report holds implications for various economic actors.
- Business Hiring Decisions: Businesses will adjust their hiring strategies based on the report's insights into sector-specific job growth and overall economic prospects.
- Investor Strategies: The data will impact investor decisions regarding stock markets and other investment assets.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways and Call to Action
The April U.S. labor market report reveals a mixed picture. While 177,000 jobs were added, the increase was less than in previous months. The unemployment rate remained at 4.2%, reflecting a generally healthy labor market but with regional disparities and challenges related to long-term unemployment. Wage growth is lagging behind inflation. Understanding these nuances is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals. Stay updated on the latest U.S. labor market data by following our future U.S. employment reports and subscribing to our newsletter for timely economic updates. Learn more about the U.S. job market and its implications for you.

Featured Posts
-
 Bradley Cooper And Will Arnett Behind The Scenes Photos From Is This Thing On Nyc Shoot
May 04, 2025
Bradley Cooper And Will Arnett Behind The Scenes Photos From Is This Thing On Nyc Shoot
May 04, 2025 -
 The Cusma Negotiations A Pivotal Meeting Between Carney And Trump
May 04, 2025
The Cusma Negotiations A Pivotal Meeting Between Carney And Trump
May 04, 2025 -
 The Bradley Cooper Gigi Hadid Leonardo Di Caprio Triangle
May 04, 2025
The Bradley Cooper Gigi Hadid Leonardo Di Caprio Triangle
May 04, 2025 -
 Ufc Des Moines Event Start Time For Tonights Fights
May 04, 2025
Ufc Des Moines Event Start Time For Tonights Fights
May 04, 2025 -
 Terence Crawfords Chances Against Canelo Alvarez An Analysis
May 04, 2025
Terence Crawfords Chances Against Canelo Alvarez An Analysis
May 04, 2025
