Understanding AI's "Thought" Processes: A Surprisingly Simple Reality

Table of Contents
AI's Lack of Consciousness and Subjective Experience
The Absence of Sentience
AI lacks subjective experiences and feelings. It doesn't "feel" or "understand" in the human sense. This crucial distinction separates artificial intelligence from human intelligence.
- AI excels at tasks like image recognition and language translation, demonstrating impressive capabilities without requiring consciousness. These are feats of pattern recognition and data manipulation, not conscious understanding.
- It's important to differentiate between strong AI (hypothetical conscious AI) and weak AI (current AI). Current AI systems are all examples of weak AI; they are specialized tools designed for specific tasks. The notion of strong AI remains largely in the realm of science fiction.
The Role of Algorithms
AI operates based on pre-programmed algorithms and statistical models. These algorithms are sets of rules and instructions that dictate how the AI processes information and arrives at conclusions.
- Various algorithms power AI, including machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL). Machine learning allows AI to learn from data without explicit programming, while deep learning uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to analyze complex data.
- Think of it like a complex recipe: a chef (the algorithm) follows precise instructions (the code) to create a delicious meal (the AI output). While the outcome might seem impressive, it's the recipe, not consciousness, that drives the result.
Data as the Foundation of AI "Thought"
The Importance of Training Data
Massive datasets are crucial for AI's performance. The more data an AI system is trained on, the better it becomes at its assigned task.
- AI learns by identifying patterns and correlations within the data. For example, a spam filter learns to identify spam emails by analyzing millions of examples of spam and non-spam emails.
- However, biases present in the training data can significantly impact AI's outputs. If the data reflects societal biases, the AI will likely perpetuate those biases, highlighting the importance of carefully curating and evaluating training datasets.
Data Processing and Pattern Recognition
AI identifies patterns and makes predictions based on the analyzed data. This process involves complex statistical computations and the application of learned algorithms.
- Spam filtering is a perfect example: The AI analyzes the text, sender information, and other features of an email to determine the probability of it being spam.
- Medical diagnosis is another area where AI excels. By analyzing medical images and patient data, AI can assist doctors in identifying patterns indicative of diseases, thereby improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. This relies on statistical probability and pattern recognition within vast medical datasets.
Deconstructing the "Thinking" Process in AI
Probabilistic Reasoning
AI uses probabilities to make decisions, not human-like logic. It doesn't "think" through problems in the same way humans do.
- Bayesian inference is a common method used by AI. It involves updating probabilities based on new evidence, allowing the AI to refine its predictions over time.
- Many AI applications rely on probabilistic reasoning, from self-driving cars estimating the likelihood of an accident to recommendation systems predicting your preferences.
The Illusion of Intelligence
The complexity of AI outputs can create a false impression of genuine intelligence. However, beneath the surface, these systems often operate on surprisingly simple rules.
- An AI might appear "smart" by playing chess at a grandmaster level, yet its "thinking" is based on evaluating a vast number of possible moves and choosing the one with the highest probability of success. It doesn't possess strategic understanding in the human sense.
- Emergent behavior, where complex patterns arise from the interaction of simple rules, is a key characteristic of many AI systems. This complexity can sometimes be mistaken for genuine intelligence.
Conclusion
In summary, AI's thought processes are not based on human-like consciousness or understanding. Instead, they rely on sophisticated algorithms, data analysis, and statistical probability. While the capabilities of modern AI are impressive, it's crucial to understand the surprising simplicity underlying their functionality. The sophistication lies in the algorithms and the scale of the data processing, not in a replication of human thought. Continue exploring the fascinating world of AI's thought processes and gain a clearer understanding of this rapidly evolving technology. Learn more about the algorithms driving AI and demystify the complexities of artificial intelligence.

Featured Posts
-
 Adidas Anthony Edwards 2 Release Date Specs And Where To Buy
Apr 29, 2025
Adidas Anthony Edwards 2 Release Date Specs And Where To Buy
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Australias Lynas Seeks Us Government Support For Texas Rare Earths Plant
Apr 29, 2025
Australias Lynas Seeks Us Government Support For Texas Rare Earths Plant
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Us Researcher Exodus How Funding Cuts Fuel Global Talent Acquisition
Apr 29, 2025
Us Researcher Exodus How Funding Cuts Fuel Global Talent Acquisition
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Understanding Chicagos Zombie Office Buildings And Their Implications
Apr 29, 2025
Understanding Chicagos Zombie Office Buildings And Their Implications
Apr 29, 2025 -
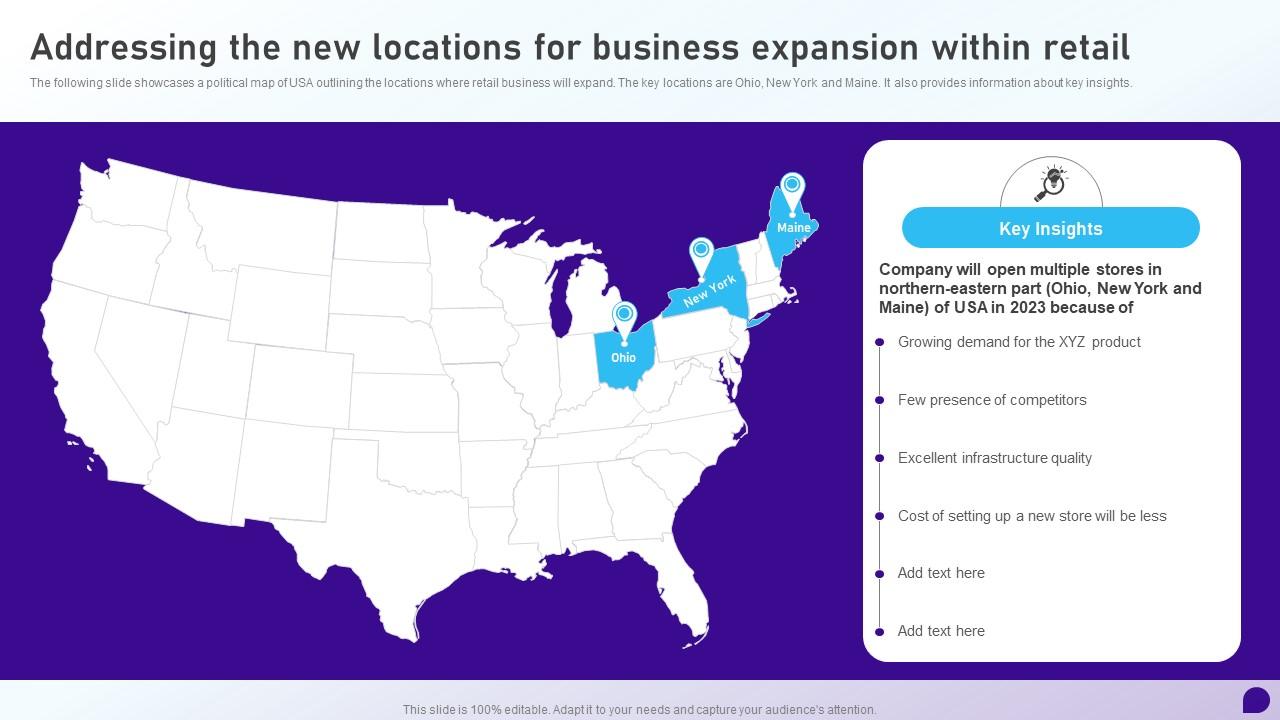 Mapping The Countrys Hottest New Business Locations
Apr 29, 2025
Mapping The Countrys Hottest New Business Locations
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Willie Nelsons Wife Responds To False Media Report
Apr 29, 2025
Willie Nelsons Wife Responds To False Media Report
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Resistance Grows Car Dealerships Renew Fight Against Electric Vehicle Regulations
Apr 29, 2025
Resistance Grows Car Dealerships Renew Fight Against Electric Vehicle Regulations
Apr 29, 2025 -
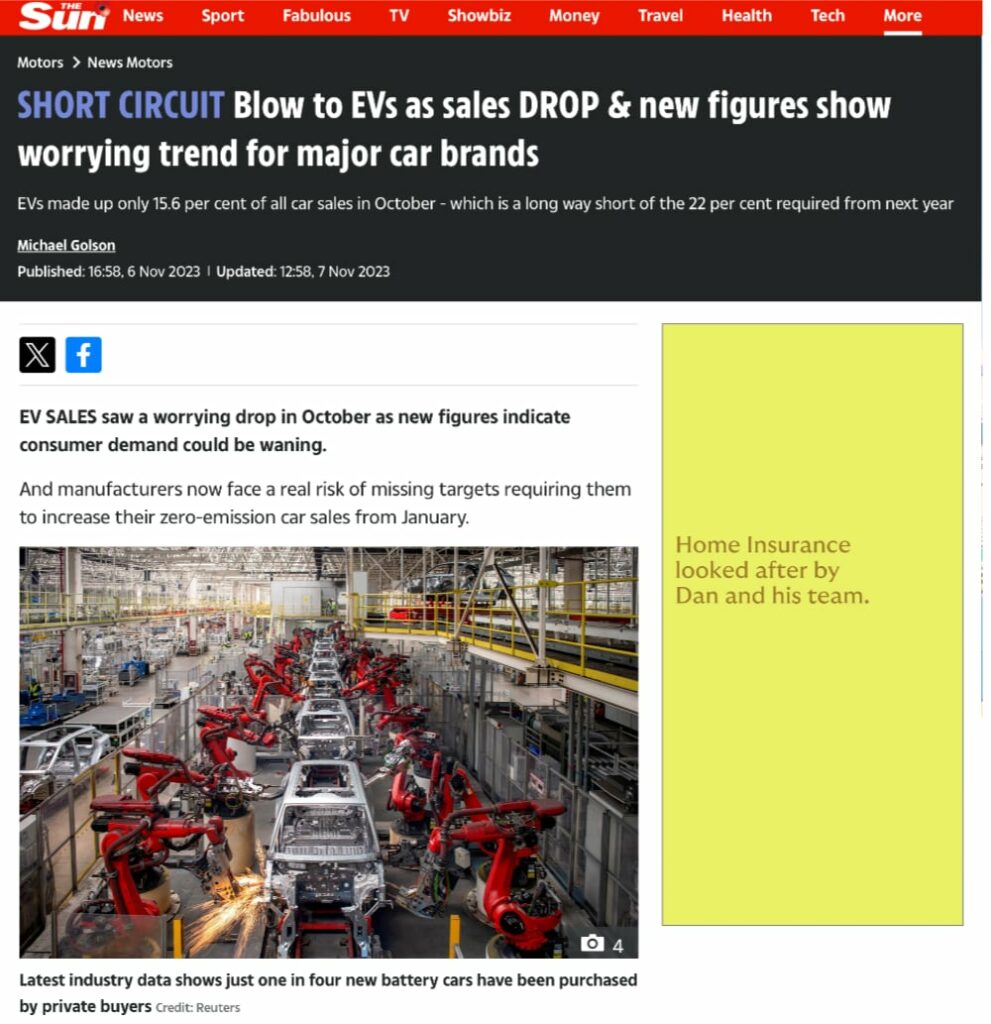 Auto Dealers Double Down On Opposition To Ev Sales Targets
Apr 29, 2025
Auto Dealers Double Down On Opposition To Ev Sales Targets
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Dealerships Intensify Fight Against Ev Mandate Requirements
Apr 29, 2025
Dealerships Intensify Fight Against Ev Mandate Requirements
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Slowing Rent Increases Persistent High Housing Costs In Metro Vancouver
Apr 29, 2025
Slowing Rent Increases Persistent High Housing Costs In Metro Vancouver
Apr 29, 2025
